Over the next several weeks, investors will experience horrendous macroeconomic data. For instance, based on initial jobless claims data, more jobs were lost in the US in four weeks recently than were created during the entirety of the now-ended 11-year business cycle. So yes, economic data will get worse, but it may not matter to capital markets because this is a market known.
Markets factor in expectations
Markets are a discounting mechanism of ‘known knowns’ and the weighted probabilities of many ‘known unknowns.’ And an upcoming earnings recession won’t surprise markets any more than terrible labour data will.
Two known unknowns are the pace of the economic recovery and the path of post-recession earnings. Since the March 2020 lows, US equities have retraced over half of their losses. Stated another way, in the face of the worst recession of our lifetimes, equity valuations are down only to June 2019 levels. Over the past few weeks, investors have increasingly assigned a higher probability to a shorter-than-anticipated recession and a stronger acceleration in profits.
We’re not epidemiologists, so we won’t opine on the infection curve or the risks of a second wave, though we certainly hope for the best. But as they say, hope isn’t an investment thesis.
Regardless of when the virus peaks or the economy reopens, life will be different. Politicians, the media and investment strategists and economists (but not us!) have equated the world’s efforts to contain COVID-19 with fighting a war. While it may feel that way with everyone pulling together (thank you to the brave health workers and first responders!), pandemics alter long-term behaviour differently than wars.
The catalysts that generally drive V-shaped postwar recoveries are very different from pandemic-driven ones. In short, precautionary savings by both consumers and businesses create different economic and inflation environments than those previously observed in postwar economies.
The scramble into new capital raisings
A market known unknown, if you will, that we want to explore further is the likely earnings dilution resulting from future equity capital having to be raised.
During periods of economic strength, many corporations take advantage of all available levers to maximise their appeal to equity investors. Part of the reason for this is that the wrong incentive structure is in place for many corporate leaders. Over the past decade, working capital has been the priority for most CEOs, and lower balance sheet quality has been the lever. That dynamic has been on display more in the recent past than in any other period of recorded history. Exhibit 1 details the steady increase of billions of dollars’ worth of shares repurchased in the S&P 500 Index.
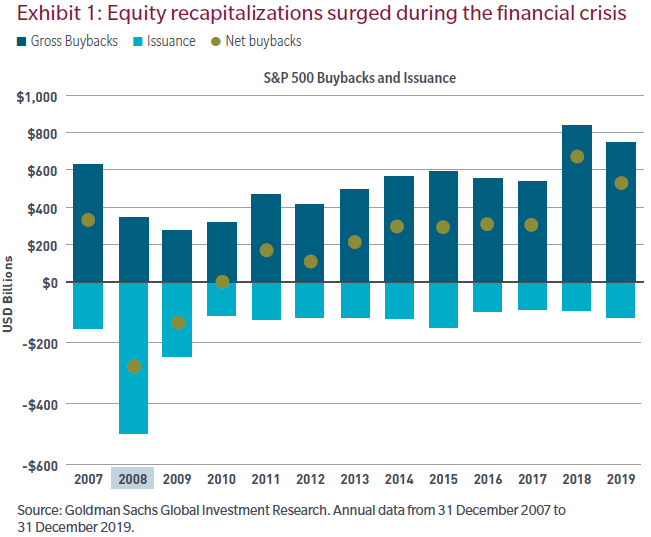
This isn’t new information, so we highlight 2008. As the fat tail risk of the GFC faded, emphasis turned from maintaining liquidity towards recapitalisation. That recapitalisation came via the equity market and at the expense of shareholders who suffered substantial dilution on a per-share basis.
Today, CEOs and CFOs — particularly those of companies that might not be able to carry on — are scrambling to secure liquidity. Profit maximisation is no longer the priority. Survival is the goal, as meeting next month’s debt maturity is all that matters. Balance sheets are now the focus, unlike in the past dozen years.
However, the nature of this recession is different from that of 2008, and not only because the recession is driven by a pandemic. The 2008 meltdown was driven by an overleveraged financial sector. However, this time around, banks and real estate investment trusts (REITs) weren’t the entities that extended balance sheet leverage to unsustainable levels in order to repurchase stock.
Instead it was every corporate sector but financials. And a fresh wave of recapitalisations is likely just getting started. There’s already been equity issuance by leisure and professional services companies in the US and Europe.
Too many unknowns for recovery conviction
None of us can guess what the duration of this recession will be, nor can we tell how strong the recovery will be. Yet many seem to believe they have sufficient visibility into any such recovery’s many known unknowns to make the high-conviction call that the recovery will be strong. We wish we had such conviction, but we don’t, and we don’t think you should either.
Instead of trying to make those calls, we’ve chosen to invest carefully, owning assets of enterprises for which the growth of working capital isn’t dependent on externalities such as financing, recognising that you can’t plan perfectly for black swan events such as the one we’re experiencing.
Robert M. Almeida Jr. is a Portfolio Manager and Global Investment Strategist, and Erik Weisman, Ph.D. is a Portfolio Manager and Chief Economist at MFS Investment Management. The comments, opinions and analysis are for general information purposes only and are not investment advice or a complete analysis of every material fact regarding any investment. Comments, opinions and analysis are rendered as of the date given and may change without notice due to market conditions and other factors. This article is issued in Australia by MFS International Australia Pty Ltd (ABN 68 607 579 537, AFSL 485343), a sponsor of Firstlinks.
For more articles and papers from MFS, please click here.