We view the Australian stockmarket as highly efficient. There are a large number of domestic research analysts, brokers, fund managers and investment professionals poring over the listed securities. In such an environment it is difficult, if not impossible, to regularly be smarter than the other informed market participants.
How does an individual stock picker outperform over long periods of time? Why would such a market present outstanding individual risk-adjusted opportunities for investors? It is a good question to ask if you are invested with an active manager. It has been a key question for researchers for a long time. Professor Eugene Fama’s Efficient Market Hypothesis (EMH) proposed that it is impossible to beat the performance of a liquid stockmarket over time because prices constantly incorporate and reflect all relevant information.
Opportunities come from cognitive biases
If we find a stock that we think is compellingly cheap, one of the first questions we ask is why we are getting the opportunity. What circumstances have led to the mispricing? What are people reacting to in order for the stock price to have deviated so far from our perception of fair value? The absence of a logical answer might infer a problem with the analysis, rather than an opportunity for an attractive purchase. The collective market is almost always more informed than the individual investor, assuming the investor is an outsider to the company under consideration.
We think we find opportunities for one predominant reason. Market participants have cognitive biases that lead to emotional rather than rational responses to new or changing circumstances. We are no different. We feel the same emotional responses. Our role is to invest as rationally as possible. We focus attention on the facts and try to remove the influence of the emotional response from our thinking.
Good investments typically come in one of three forms. The first is at the stock level. A company has a temporary setback or earnings revision and the market extrapolates the problem across the entire business. We focus on the medium-term outlook and ask whether we can make sensible, modest forecasts about earnings over the following few years. If earnings are delivered as expected, would this make buying at the current stock price attractive? A favourable answer means there’s a time horizon arbitrage in a company we would like to own for a long time.
Secondly, sometimes a whole sector might screen as attractively priced because the market is focused on a threat that appears overblown. An example is shown in the chart below.
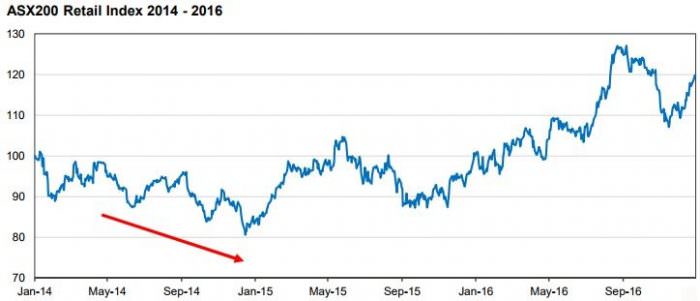
In May 2014, the Federal Government proposed a restrictive and somewhat unpopular budget to assist in repairing the budget deficit. Over the following six months, the market sold retail stocks that many assumed would be significantly impacted by any cut to disposable income. The likely numerical impact of any budget measures on consumer discretionary spend was, on our analysis, likely to be small and transitory in nature. It gave an attractive entry point into a number of high quality retailers that we had been watching for some time.
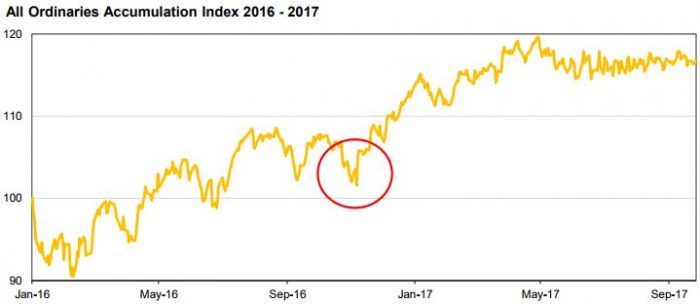
Thirdly, there may be a market-wide reaction to a particular event, such as the surprise election of Donald Trump or UK’s Brexit vote. Participants in the domestic market reacted to Brexit by selling financial stocks in the weeks that followed. We believed the risks to corporate earnings were relatively low. Similarly, it was unclear why the election of President Trump would negatively impact the earnings of Australian companies, yet at one point in the afternoon of the election the domestic stockmarket was down nearly 4% (as highlighted below). Many individual stocks were down considerably, having already fallen on the uncertainty heading into the election.
Need to be patient for these opportunities
Outstanding opportunities do not come along frequently, and certainly not predictably. In the intervening periods, investors should be as patient as possible, remaining focused on their existing portfolio and ready to respond rationally. There may be an opportunity to invest sensibly in familiar companies with quality attributes.
We agree with the notion that the market is most often efficient, but that the difference between ‘often’ and ‘always’ is like night and day. Opportunities for the value investor occur when the majority of market participants are distracted from the immediate opportunity by an issue where the impact is either exaggerated or transitory. This is when we become most interested and plan to take full advantage for the long-term.
Tim Carleton is Principal and Portfolio Manager at Auscap Asset Management, a boutique Australian equities long/short investment manager. This article is general information and does not consider the circumstances of any individual. A person should obtain the Product Disclosure Statement before deciding whether to acquire, or to continue to hold, units in any Auscap fund.