Share markets are ever changing. Companies come, and companies go.
But what happens to share market indexes, and the exchange traded funds (ETFs) that use them as performance benchmarks, when a company is removed because of a merger or acquisition?
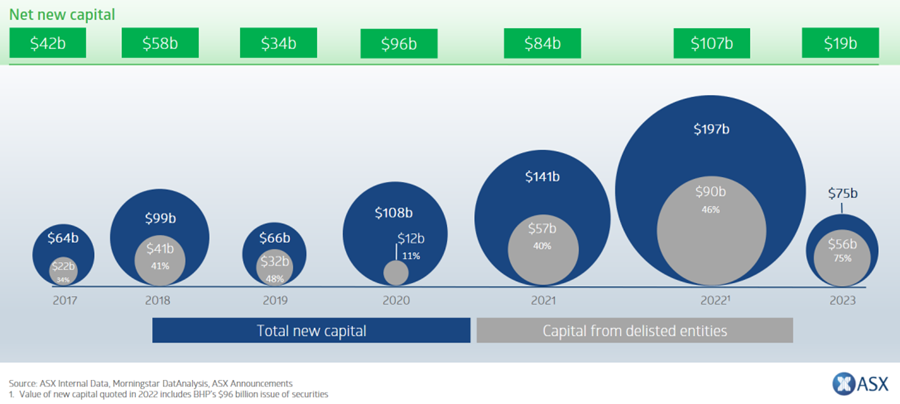
Source: ASX.com.au
One doesn’t have to look too hard to find some recent, high-profile examples of company delistings from the Australian Securities Exchange (ASX).
After more than 60 years on the ASX, the building products company CSR that started life in 1855 as the Colonial Sugar Refining Company was delisted in July following a $4.3 billion takeover by French construction group Saint-Gobain.
The construction materials company Boral (which listed in 1946 as Bitumen and Oil Refineries (Australia) Limited) also left the ASX in July after its $1.5 billion acquisition by Seven Group. Likewise, the bauxite mining and aluminium refineries investment group Alumina delisted from the ASX following its $3.4 billion takeover by U.S. giant Alcoa.
All up there have been 67 ASX delistings so far in 2024, including other high-profile removals such as concrete group Adbri (sold for $2.1 billion to Irish group CRH in July), and fruit and vegetables company Costa Group (sold for $1.5 billion to U.S. private equity group Paine Schwartz in February).
Understanding index construction
All of the companies mentioned above had been included in various ASX indexes, such as the All Ordinaries Index and S&P/ASX 300 Index, based on their market capitalisation.
Share market indexes are structured to track the broad performance of markets and specific sectors, typically by tracking the share price returns of the companies that have been included in the index.
For example, the S&P/ASX 300 Index tracks the returns of the top 300 ASX companies based on their market capitalisation. In turn, the Vanguard Australian Shares Index ETF (VAS) uses the S&P/ASX 300 Index as its performance benchmark.
So, what happens to indexes and ETFs when companies effectively vanish from a share market?
Index rebalancing
Indexes are rebalanced on a regular basis as part of scheduled reviews to ensure benchmarks stay up to date and continue to accurately reflect their purpose.
ETFs and unlisted managed funds tracking an index will adjust their own portfolio holdings in tandem with any changes made to the benchmark index.
On the ASX, scheduled rebalancing changes typically take effect after the market close on the third Friday of March, June, September, and December.
The S&P/ASX 300 is rebalanced semi-annually, effective after the market close on the third Friday of March and September.
Eligible stocks are considered for index inclusion based on their rank relative to the stated quota of securities for each index.
But company deletions also can occur between index rebalancing dates due to acquisitions, mergers and spin-offs or due to suspension and bankruptcies. The decision to remove a stock from an index rests with the index provider and will be made once there is sufficient evidence that a transaction will be completed.
Company delistings will typically trigger an intra-rebalancing process if an index level is comprised of a fixed number of companies. But not all indexes are based on a fixed count.
The S&P/ASX 300 and All Ordinaries are not fixed count indices, so intra-rebalancing additions are only made when a replacement added to the S&P/ASX 200 (or a higher index) is not a constituent of the S&P/ASX 300 and All Ordinaries.
Index additions are made according to various criteria as laid out in their respective methodologies. For the S&P/ASX300, market capitalisation, free float and liquidity are some of the criteria considered, whereas for the All Ordinaries Index, there is no liquidity screen or minimum float requirement.
The reference date used to determine an ad-hoc index replacement is determined on a case-by-case basis and taken closer to the time of the event that triggered the vacancy.
More information on how indexes are rebalanced on the ASX can be found in S&P/ASX Australian Indices Methodology.
Tony Kaye is a Senior Personal Finance writer at Vanguard Australia, a sponsor of Firstlinks. This article is for general information purposes only and does not consider the circumstances of any individual.
For more articles and papers from Vanguard Investments Australia, please click here.