Good share market returns require identifying companies likely to produce healthy earnings and dividends over time. Investors traditionally have had the choice of active managers attempting to pick winners, or passive managers taking a rules-based approach, such as investing in companies that meet criteria relating to price momentum, valuations or financial metrics, or the overall index.
The problem with many of these approaches is that the choice can be governed by short-run – or cyclical – dynamics. Deciding which part of the cycle we’re in, and which companies will do well in that part of the cycle, is no easy task.
Thematic investing offers an alternative approach, embracing the cost and diversification benefits of passive investing but with a rules-based strategy to identify companies with the potential to benefit from predictable, longer-run structural changes.
What is thematic investing?
The goal of thematic investing is to identify megatrends and enduring structural forces that will affect the economy over time, and then position one’s portfolio to benefit from those forces, irrespective of the ups and downs of current or future economic cycles.
The table below summarises the differences between thematic investing and approaches relying on identifying and positioning for short-run economic cycles.
Thematic or secular investingCyclical investing
Investment FocusMegatrends: disruptive technologies, demographic changesGeographic regions, sectors of the economy, factors such as momentum, value, quality, volatility
Type of change focused onStructuralCyclical
Investment horizonLong termShort-mid term
Timing considerationsEntry and exit timing less importantEntry and exit timing important
Illustrative size of portfolioSmaller universe of securitiesLarger universe of securities
Advantages of thematic investing
A primary benefit of longer-term investment approaches like thematic investing is that the timing of entry and exit points is typically less crucial than with more cyclically-sensitive investment strategies.
As seen in the table below, the rate of adoption of major technology changes over the past century – such as the telephone, electricity, cars and radio – has been measured in decades. The pace of technological innovation is unrelenting, with more recent changes such as the internet, smart phones and social media just as disruptive, and take-up more rapid.
Adoption of technology in the US (1990 to the present)
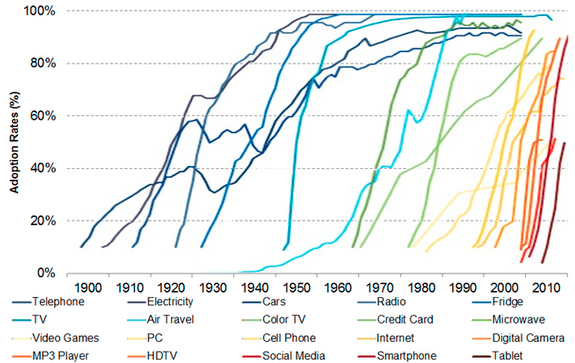
Source: Asymco, BlackRock
Other megatrends likely to be sustained over coming decades include:
- climate change and the demand for clean energy
- Asia’s rising middle class
- adoption of robotics, and
- the increasing threat of cybercrime.
Thematic investing can improve portfolio diversification, as returns are likely to have low correlation to swings in major regional or sector investment benchmarks.
Thematic investing readily lends itself to a globally diversified passive approach – using rules to identify companies with revenue exposure to a secular trend, and then investing in a broad selection of the leading players anywhere in the world.
Of course, active managers are also able to take a thematic approach to investing. However, they are likely to face just as many challenges ‘picking winners’ from secular change as they currently do in picking winners from cyclical change.
One of the benefits of a passive market capitalisation indexing approach is that it tends to increase portfolio weightings to emerging ‘winners’ with rising market cap over time, while cutting exposure to ‘losers’ with declining market cap. In dynamic forward-looking markets of the type that lend themselves to thematic investing, the market, on average, has demonstrated a tendency to get it right over time with prices (or market capitalisation) leading fundamentals such as actual revenues and earnings.
Thematic investing is an approach that resonates with investors, as it taps into economic changes they can see and hear taking place around them every day. What’s more, many of these megatrends – such as environmental, social, or technology-focused themes – tap into an increasing interest in socially responsible investing.
Megatrend opportunities on the ASX
Thanks to the advent of exchange traded funds (ETFs), it has never been easier for investors to gain diversified, transparent and cost-effective exposure to these major investment themes shaping our world.
Don Hoang is an Assistant Portfolio Manager and Ilan Israelstam is Head of Strategy at BetaShares, a sponsor of Cuffelinks. BetaShares offers a wide range of thematic ETFs. This article is for general information purposes only and does not address the needs of any individual.
For more articles and papers from BetaShares, please click here.