The 2018 Federal Budget announcements regarding default insurance in superannuation have turned many heads in the direction of insurance. Understanding the different types of disability insurance and how they can be held inside and outside of super can assist in managing the cost of insurances and taking advantage of tax concessions.
Definitions of disability in superannuation
Since 1 July 2014, superannuation law requires that insurance issued by a super fund must have disability definitions that are consistent with the superannuation conditions of release. This is to ensure that in the event of a successful claim, the insurance payout can be accessed immediately. Prior to the change, it was possible for the trustee of a fund to receive the insurance proceeds from a successful claim, but not be able to make a payment to the member as they had not met a superannuation condition of release.
Super conditions of release include death, terminal medical conditions, permanent incapacity, and temporary incapacity. Members who were insured under inconsistent definitions before 1 July 2014 are able to retain their policies under grandfathering arrangements.
The most significant impact of the change meant that super funds cannot insure new members for own occupation permanent incapacity or for trauma insurance.
Two different insurance definitions
There are two different insurance definitions for ‘any occupation’ and ‘own occupation’:
1. Any occupation
The superannuation condition of release for permanent incapacity definition is important. It requires that the trustee of the fund is reasonably satisfied that the member’s ill health makes it unlikely that the member will engage in gainful employment for which the member is reasonably qualified by education, training, or experience. This is commonly referred to as the ‘any occupation’ definition.
2. Own occupation
The commonly used ‘own occupation’ insurance definition requires that the member’s ill health makes it unlikely that the member will engage in gainful employment in their usual occupation.
The own occupation insurance cover is more likely to result in a successful claim and many individuals will be keen to ensure that they are covered by the more flexible definition. However, the insurance will need to be held outside of super.
Policy linking in and out of super
Many super funds and insurers offer ‘policy linking’ whereby the any occupation insurance is held inside of super where the insurance premiums may be paid from the super balance and are tax deductible to the fund. The own occupation insurance is held outside of super where the premiums are not tax deductible.
Any claim is firstly assessed using the any occupation definition. If the any occupation definition is met, the permanent incapacity benefit is paid to the super fund and can then be released to the member. If the any occupation definition is not met, the claim will be assessed against the own occupation definition and if successful the insurance held outside of super will be paid to the individual.
The policy linking can avoid a duplication of insurance and generally offers a cheaper premium than would be available by holding only an own occupation insurance outside of super.
Taxation of permanent disability benefits
Tax concessions may apply where a super fund member meets the definition of a disability superannuation benefit and the benefit is paid as a lump sum or rolled over.
An additional tax-free amount is payable if the benefit is paid to a member due to their ill-health (whether physical or mental). Two legally-qualified medical practitioners must certify that because of ill health, it is unlikely that the member can be gainfully employed in a capacity for which they are reasonably qualified by education, training or experience.
Although this is similar to the condition of release definition, it has the requirement of the certification, without which the benefit may be paid from the fund but not with the tax concession.
Where a permanent disability benefit includes life insurance proceeds, the insurance proceeds will form part of the taxable component.
Lump sum tax-free uplift
Permanent disability benefits are eligible for an additional tax-free amount. The tax-free component is the sum of:
- the ordinary tax-free component
- the tax-free uplift amount calculated as:
Benefit amount X days to retirement / (service days + days to retirement)
Where the:
- benefit amount is the total amount of benefit to be paid
- days to retirement is the number of days from the day the member stopped being capable of being gainfully employed to their normal retirement date (generally age 65)
- service days is the number of days in the benefit service period (usually from date joined fund to date of benefit payment)
The lump sum tax treatment is shown in the table below:
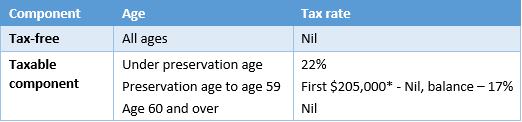
* As at 1 July 2018 and indexed annually
Case study
Jake ceased work on his 50th birthday as a result of permanent incapacity. His accumulated super balance was $200,000 (all taxable component) and he received $500,000 of insurance. He joined his fund on his 30th birthday.
If Jake withdraws all of his benefit, he receives a tax-free uplift of $300,000 ($700,000 x 15 years / (20 years + 15 years) = $300,000).
Pension payments
A disability pension paid from super does not receive an additional tax-free amount. The tax-free and taxable percentages of a pension are determined at commencement and are based on the proportion of the tax-free and taxable components of the accumulation benefit used to commence the pension. Any insurance proceeds forms part of the taxable component.
For members under age 60 the taxable component of the pension payment received is included in their assessable income and taxed at marginal tax rates. However, a 15% tax offset applies to the taxable component of each pension payment. For members age 60 and over the pension payments are tax-free.
Julie Steed is Senior Technical Services Manager at Australian Executor Trustees. This article is in the nature of general information and does not consider the circumstances of any individual.