One of the classic signs that the strong credit cycle is nearing its end is that borrowers that should not be getting financed are not only raising money, but doing so on terms that seem crazy. I have recently written about the silly things happening in global high yield debt, Chinese debt and the global attitude to sovereign debt. Continuing this theme are recent examples of emerging market sovereign debt in Greece, Argentina and Iraq. Each of these should not have been funded, but the desperation for yield saw all three achieve crazy funding levels. Here are the details to show how investors have gone mad.
Argentina
In June, Argentina sold $2.75 billion of US dollar denominated 100-year bonds at a yield of 7.92%. This was a mere 5.18% yield pick-up over 30-year US Treasuries. Argentina has a long history of defaulting on its government debt, including four defaults in the last 35 years. The 2001 default took 15 years of negotiation and litigation to resolve, with most bondholders losing their shirts and a few who bought late and fought hard achieving extraordinary returns.
The current outlook shows that not much has changed for Argentina. Inflation is running at over 20% and the government is aiming to cut the deficit this year to 4.2% of GDP, hoping to stimulate the economy out of recession. Investors are banking on the recent change in government to increase foreign investment and see sound economic management implemented. The need to reduce politically popular subsidies will be a major hurdle to that plan. S&P’s rating of “B” and Moody’s at “B3” reflect the country’s weak credit profile. Taking all of this into account, Argentina is unlikely to get through a decade without defaulting, let alone 100 years.
Greece
In July, Greece sold €3 billion of five-year bonds at 4.63%, a 4.78% yield pick-up relative to five-year German government bonds. Investors have particularly short memories on Greece’s sovereign debt, with the 2012 default seeing bondholders take losses of around 75%. The 2014 issue of five-year bonds traded as low as 56% of face value, a horrible ride for those who bought into it. The constant negotiations for further bailouts always come with the threat that Greece will not make further concessions and this time the Europeans and the IMF might have had enough.
Greece’s position remains precarious as debt to GDP currently stands at 179%. The economy has been stagnant for years as its government continues to resist the structural reforms proposed by the IMF and Europeans. Some are optimistic as Greece recorded a primary surplus (before interest expenses) in 2016. Unlike the buyers of the recent bond issue, S&P (B-) and Moody’s (Caa2), do not see a good prospect of Greece paying back its creditors.
Iraq
In early August, Iraq sold $1 billion of five-year bonds at 6.75%, a 4.93% premium to US Treasuries. Iraq faces three major medium-term issues: the ongoing war, export revenues reliant on oil prices and dependence upon military and financial support from the US government. Each of these is out of its control. The 2016 deficit at 14% of GDP shows Iraq clearly cannot service its debts without a substantial financial turnaround. By buying the bonds, investors have effectively banked the equity case of the war ending and oil prices improving. The credit ratings from S&P (B-) and Moody’s (Caa1) are a better reflection of Iraq’s economic prospects.
Conclusion
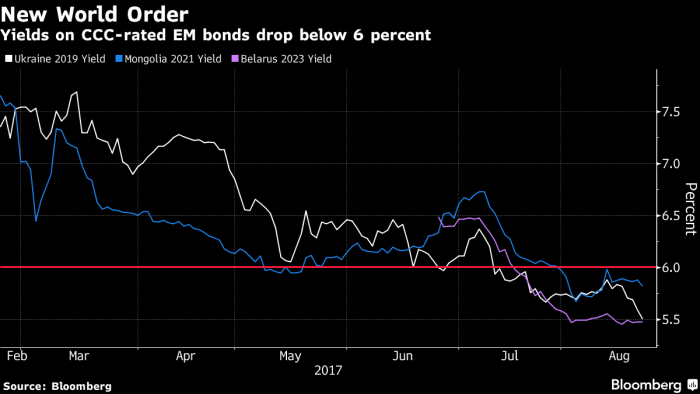
In considering emerging market sovereign debt, investors must consider each country on its own merits. In the examples of Argentina, Greece and Iraq, bond buyers have suspended sceptical analysis. They have banked the equity case, hoping for a substantial change from historical precedents, even though they will not get a share of the upside if the rosy scenario occurs. The examples are not unusual, as shown in the graph below from Bloomberg. Belarus, Mongolia and Ukraine are all CCC-rated but have bonds yielding less than 6%.
Yields on CCC-rated emerging market bonds
sovereign debt
These examples point to the greater fool theory playing out in many credit markets. We have now reached the point in the credit cycle where further gains seem dependent upon more dumb money arriving and pushing spreads even tighter. Calling the top of any cycle is nearly impossible, but calling out the current higher risk/lower return environment is simply common sense.
Jonathan Rochford is a Portfolio Manager at Narrow Road Capital. This article has been prepared for educational purposes and is not a substitute for tailored financial advice. Narrow Road Capital advises on and invests in a wide range of securities.