The Australian equity market has performed well over the past few months, though it is once again facing valuations challenges. Irrespective of how the market deals with this challenge, one fact is indisputable: income returns from the market remain attractive relative to interest rates.
Market rebounds amid valuation concerns
The S&P/ASX 200 has staged a feisty comeback (see chart below) and is now over the 5500 barrier. However, this rise has come amid continued weakness in forward earnings. The market’s price-to-forward earnings ratio has again increased to the peak of just over 16 times we saw in early-2015 when the market last ran out of steam. In fact, market prices remain lower now than in early 2015, despite similar PE valuations, due to a decline in forward earnings expectations over this period.
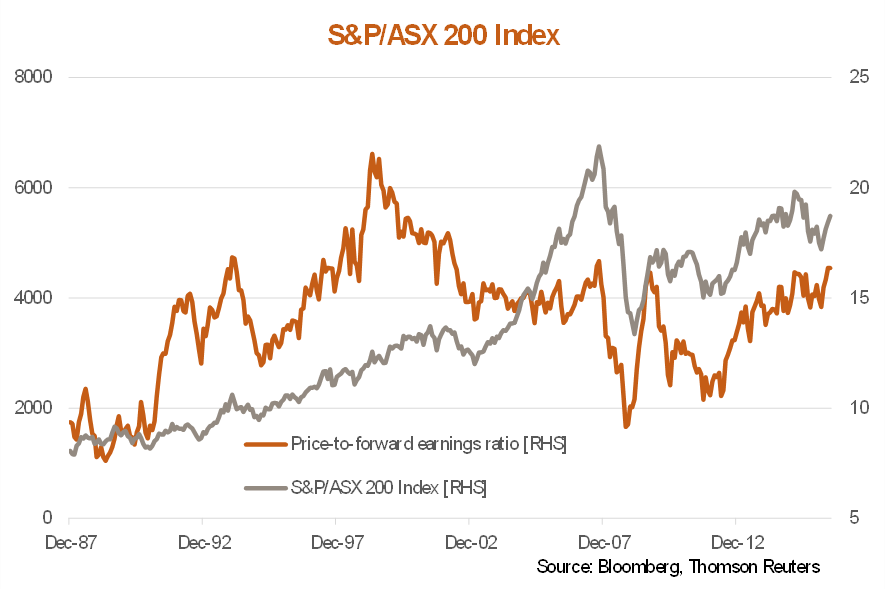
By other measures, however, the market is less overvalued, and potentially cheap. For example, the market’s gross dividend yield (GDY) as of late July 2016 was 6%, which is still significantly above the approximately 2% rate available on 10-year government bond yields and 2.4% on 1-year bank term deposits.
The margin between the GDY and these interest rates is currently around 3.75-4%, which is considerably higher than the (relatively stable) average margin of around 0.75% p.a. between 2003 and 2013. At today’s interest rate levels, retention of this previous average margin would justify a gross dividend yield of only 3.25%, or almost half the current rate.
Does this mean that the market is cheap and should simply surge to reduce the dividend yield? Not necessarily. One complication is the fact that earnings have been relatively weak in recent years, and maintaining a stable dividend yield in the face of rising equity prices has required a rising payout ratio.
Stretched payout ratios
Indeed, the implied payout ratio – or the ratio of the GDY to the forward-earnings yield (inverse of the forward PE ratio) – has risen to about 100% in recent months, compared with a long-run average of around 75-80%. Relative to earnings, the current level of dividends appears unsustainable. Earnings will rise and/or dividends will fall to restore a more normal payout ratio.
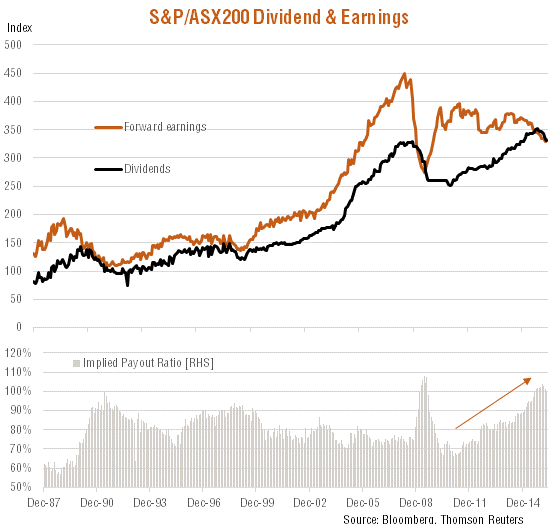
Given that dividend yields remain so high relative to interest rates, they are likely to remain attractive even if they do fall to some extent. Let’s assume two scenarios, for example, that earnings hold around current levels for some time, but dividends are eventually cut by 20%, restoring the payout ratio to 80%.
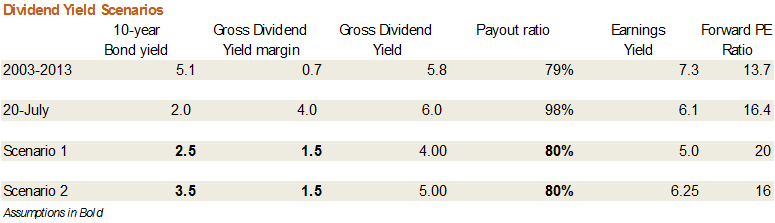
That would imply a decline in the GDY to 4.9%, which is still a substantial 2.4% p.a margin over current 10-year bond yields and 1-year term deposits, while keeping the price-to-forward earnings ratio at its present relatively elevated level of 16.3.
But if interest rates were to hold at current levels, however, there’s even some chance that equity market valuations could be ‘rerated’. This is explored in the table below.
Again, let’s assume that the sustainable margin between the GDY and interest rates referred to above declines to around 1.5% p.a. (which is still twice that averaged between 2003 and 2013), then the gross dividend yield could decline to 4% p.a. Assuming an 80% payout ratio, that in turn would imply a sustainable price-to-forward earnings ratio of 20x!
If we allow for a moderate 1.5% rise in interest rates (to 3.5% p.a.), then keeping all else constant the GDY could still fall to 5%, implying a sustainable price-to-forward earnings ratio of 16x – or not far from current levels.
Official interest rates could fall even further in coming months, suggesting the high-yield equity theme is likely to continue. There’s even a chance the equity market could be rerated higher if interest rates remain below historic average levels.
David Bassanese is Chief Economist at BetaShares, whose range of Exchange Traded Funds include high-yield Australian equity investments with ASX codes QFN (aims to track the S&P/ASX200 Financial–x-A-REIT index), HVST (aims to provide investors with a strong income stream from dividends and franking) and YMAX (aims to provide exposure to the S&P/ASX20 index while cushioning returns in weak markets). BetaShares is a sponsor of Cuffelinks. This article is general information and does not consider the circumstances of any individual.