Over the past 10 years, the S&P/ASX Price Index has delivered meek returns, though the picture improves when dividends are included in the Total Return Index.
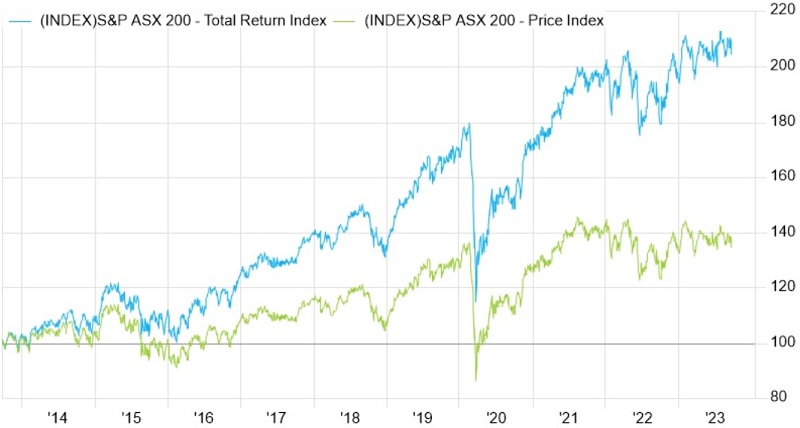
The 10-year returns are:
- The Price Index return is about 38% or 3.2% annual compound, and
- The Accumulation (Total Return) Index is about 110% or 8% annual compound (but before franking).
Following the market correction since mid-August 2023, the capital gain of the market index from when Covid hit in March 2020 is now about zero for the last 4.5 years. The return including dividends that are fully reinvested is a healthier 30% (pre franking) over the entire period. However, this 4.5-year return of about 6.6% per annum is below both our targeted and expected long-term return of 8% per annum.
In reality, the Accumulation Index return is an appropriate measure of the equity market return for an SMSF in 'accumulation mode'. However, it is not a measure of the (longer-term) return for an investor who takes the cash dividend from the market to fund a pension.
The post-Covid investment cycle
This background leads us to consider the dramatic change in income returns across asset classes that have flowed as the world economy transitioned from post GFC, through Covid and now into a post-Covid cycle.
Projected and actual asset returns drive investment allocation that is also adjusted by the risk profile of the investor (SMSF). Returns from capital gain and income, from all asset classes, will be driven by the investment climate as measured by cash rates, bond yields and the interplay of 'risk free returns' with equity prices measured by Price/Earnings Ratios (PER) and property capitalisation rates.
The world has moved from the post-GFC cycle where the introduction of quantitative easing (QE) to fund burgeoning government debt, plus highly supportive fiscal settings, dominated. Covid checked the anticipated slowdown and the reversal of QE towards quantitative tightening (QT). Indeed, it actually reaccelerated QE, noting it was aggressively introduced in both Australia and around the world. A feature of the Covid era was that most bond yields across the world hovered well below 1% and they were deeply negative in Europe and Japan.
The post COVID era, began during 2022 when lockdowns ceased, ushered in a new investing environment. The era of near zero interest rates is over, and decades of deflation driven by globalisation and demographic changes are being replaced by an extended period of cost-based inflation.
Across asset classes, the most material change has been seen in bond markets. For instance, over the last two years, the yield on an Australian two-year bond has moved from near zero to above 4%. It has been a painful period for passive bond investors with the price of all bonds materially declining. The good news today is that the annual income that can be generated from holding a 'near risk free asset' has become more attractive in nominal terms. But are bonds attractive enough?
Preferring equities over bonds
While bonds can deliver the benefits of diversification in a balanced portfolio, the argument for their role as a key driver of portfolio returns must be framed relative to inflation. Inflation has probably peaked in Australia, yet the most recent CPI release for the June quarter was 6%, still well above the two-year bond yield. Given that government bonds are a fixed income returning assets, their ability to outperform inflation is not currently on offer.
Therefore, a pension portfolio should maintain an appropriate and meaningful allocation to the Australian equity market with the purpose to deliver a growing income stream that is enhanced by franking.
Importantly when comparing Australian equity returns to global market returns, companies here have higher dividend yields. And it is a historical fact that the Australian equity market has delivered total returns, including dividends, that are above most of the developed world. The following chart from the RBA chart book demonstrates this.
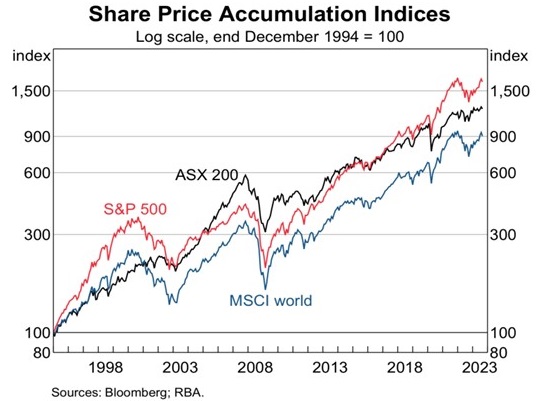
Investing in the Australian equity market, like all equity markets, is not without risk. However, with elevated inflation likely to persist well into 2024, equities will continue to play a key role in delivering on pension focussed long-term income objectives and defend against the impact of inflation.
The surging equity market during Covid was driven by bloated PERs due to excessively low bond yields. Post-Covid, PERs have declined but equity dividend payments have risen, while bonds have entered a third year of negative returns.
Will Riggall is CIO of Clime Group, a sponsor of Firstlinks, and oversees the Ralton Dividend Builder, available on several leading platforms and Clime Capital, the group’s listed investment vehicle, has been constructed to deliver a high and growing tax effective dividend stream. The information contained in this article is of a general nature only and is current as at the date of publishing. It does not take into account the goals, objectives, or personal circumstances of any person.
For more articles and papers from Clime, click here.