Retirees looking to develop a sustainable financial plan face a challenging technical problem, so it makes sense to simplify some of the inputs. Those of us who focus on the production of investment returns for retirees’ financial assets often choose to make simple assumptions about consumption patterns in retirement. A more detailed understanding of priorities for spending in retirement, however, can inform the design of appropriate investment strategies and improve confidence around attainment of goals.
Retirement risks, including longevity and health
The following schematic shows the risks a financial plan for retirement ought to address and some of the management choices.
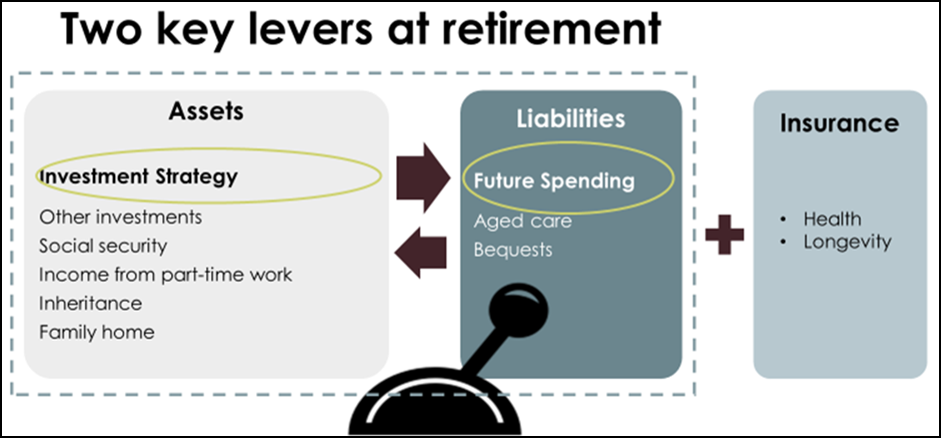
Longevity risk means there is uncertainty around the duration of the planning horizon. Should a retiree look to insure, partially insure or self-insure against that risk? Poor health is another risk where timing of onset and financial impact is also subject to uncertainty and arguably best addressed through insurance.
Then there are the risks to the household balance sheet at retirement. A key ingredient for retirement planning is the spending strategy – which is represented as future liabilities on the balance sheet – as well as the investment strategy. By contrast, the focus is solely on investment strategy during most of the accumulation phase. It makes sense to manage the asset strategy and the spending strategy on an integrated basis, much like a defined benefit scheme or an insurance company managing its balance sheet.
There’s also a considerable behavioural challenge to maintaining a retirement strategy in the face of market volatility, especially for retirees who are drawing down on their capital. The more confidence retirees have that their spending strategy is sustainable, the more likely they will stick to their investment plan and maintain focus on their personal goals.
Decide on the highest priority goals in retirement
A good place to start is to understand spending goals in retirement. While it is possible to simplify the analysis by assuming annual spending in retirement is constant in real terms over the planning horizon, this misses valuable information for many retirees. It doesn’t allow for the capacity for a retiree to adjust their spending to create a more sustainable journey. Widespread capacity to adapt spending was demonstrated immediately after the GFC when a reduction in minimum payments from allocated pensions was allowed temporarily.
Not all spending goals are of equal priority and behavioural finance suggests creating separate accounts to fund different goals can assist in making the journey more sustainable. The priority of a goal informs the design of the investment strategy, including the interest rate and inflation sensitivities and the use of hedging and protection strategies. For high priority goals, there must be a low probability of failure and therefore limited capacity to take risk relative to the goal’s cash flow profile.
The highest priority spending goals in retirement include covering the necessities of life such as food, health services and housing. The cash flows associated with essential goals can depend materially on personal circumstance. For example, a homeowner is likely to require less cash flow than a renter. An investment plan ought to reflect these differences in size and duration of cash flows, suggesting a suite of products is required to implement retirement plans.
If high priority goals are needs, then intermediate priority goals are wants. Goals associated with discretionary spending are important but not essential as failure to completely fund them, while disappointing, is not devastating. For such goals, there is more scope to be flexible through adjusting or deferring consumption.
Some people have sufficient assets in retirement to fund an aspirational goal to build a legacy for their family or a charity. This type of goal is not focussed on personal consumption over an immediate time horizon, which suggests there is considerable capacity for thoughtful long horizon risk-taking.
Surfacing and sizing goals
There are a variety of approaches to estimate retirement spending. Some old rules-of-thumb express spending as a percentage of final salary. ASFA has adopted a more granular approach and publishes a baseline standard for an average retiree that incorporates both essential and some discretionary spending.
It is widely observed that many retirees only take the regulated minimum payment from their allocated pension even though research suggests this is not their best spending strategy. A possible explanation is that this reflects self-insurance against longevity risk. Therefore, observed spending patterns may not reflect actual preferences.
There is great value in helping people identify and express their spending preferences. Technological developments can assist with this. Visualisation tools will soon enable people to better picture potential future lifestyles, helping them prioritise goals in retirement and perhaps triggering a change in behaviour around savings. Meanwhile increased access to large data sets should support a more accurate personalised estimate of desired cash flow given individual preferences and priorities.
Improving confidence in a retirement plan
If you are planning a journey and you know the destinations that are of most importance, then it is easier to create a suitable travel plan and stick to it. A deep understanding of goals in retirement and their relative priority enables the design of investment strategies that fit those goals and support a more sustainable journey.
Jeff Rogers is Chief Investment Officer at ipac Securities, AMP Capital. This article is general information and does not consider the circumstances of any individual.