A recently released paper called The Wealth of Working Nations found that, after controlling for working-age population (i.e. those age 15-64), historical GDP growth is quite similar across most developed countries. But, this got me thinking, “How much do demographics impact the stock market?”
With the Baby Boomers continuing to retire in the U.S. and population growth slowing throughout most of the developed world, will this spell disaster for future stock returns? This isn’t a simple question to answer.
For years, researchers have debated the impact of population trends on economic growth and market performance. Some have argued that demographics are the hidden force behind long-term market trends. However, others believe that other factors such as productivity growth play a far larger role.
In this post, I will explore this relationship in more detail to see whether population really holds the key to economic growth and future stock returns. Let’s dig in.
Does population predict GDP growth?
When it comes to population growth and GDP growth, there is some evidence that they are positively correlated, at least within developing countries. The Federal Reserve released a note in September 2016 which concluded that, “demographic changes account for a significant portion of growth slowdown in several of these [OECD] economies in recent years.”
Looking at GDP growth and population changes over time makes this more apparent. For example, from The Wealth of Working Nations paper, you can see how GDP has changed in a handful of advanced economies since 1991:
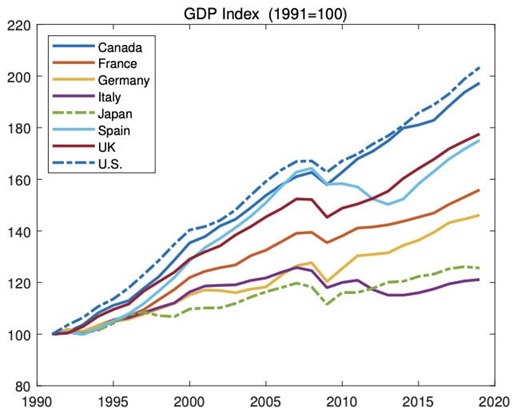
What you may notice is that countries like Italy and Japan have had worse GDP growth than countries like the U.S. and Canada. This has occurred for a multitude of reasons, but one of them is related to changes in working-age population.
When we look at the changes in their working populations, there are many parallels:
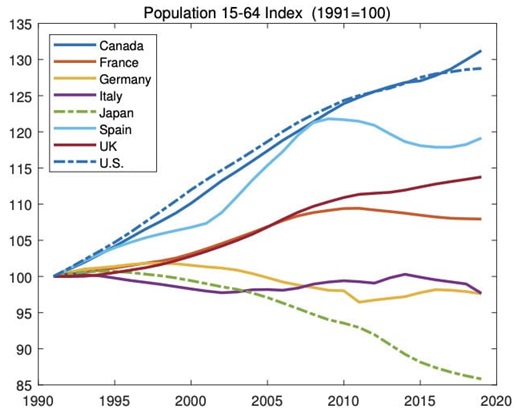
As you can see, countries with the largest working-age population declines have also seen some of the worst GDP growth since 1991.
Putting it altogether, the authors divided GDP by the change in working-age population and found some remarkable convergence across countries:
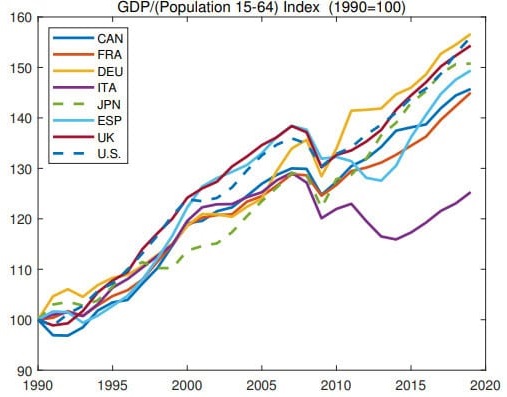
After controlling for working-age population, basically every country besides Italy has had remarkably similar changes in their overall GDP. This isn’t GDP per capita because it doesn’t use total population, but working-age population. In other words, GDP per worker has grown roughly the same across these developed economies.
But if this relationship seems to be true for the economy, what about the stock market?
Does population predict stock returns?
When it comes to population changes and the stock market, one of the most comprehensive papers on this topic was released by Rob Arnott and Denis Chaves back in 2012. Their research examined 60 years of data to see how demographic changes impacted stock returns and found a somewhat positive relationship.
For example, after regressing the size of different population cohorts on future stock returns, they found that a roughly 1% increase in those aged 50-54 was associated with a 1% higher annual return for a country’s stock market. You can see this in the figure below:
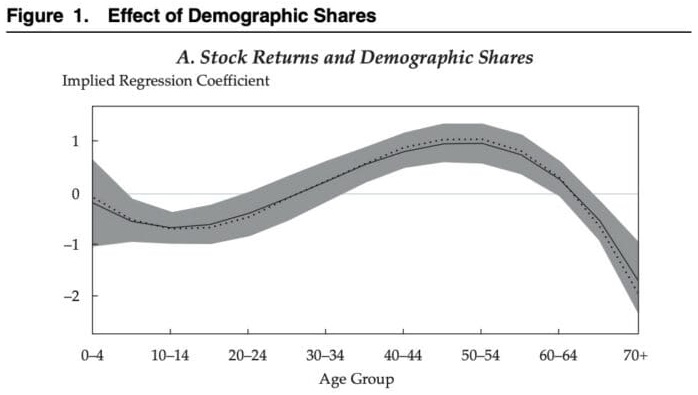
Now compare this with the 70+ age cohort where every 1% increase in their share of population suggests 1.5% annual decline in future stock returns. In other words, countries with a higher share of workers have improved stock returns. Arnott and Chaves concluded as much in their paper:
“Large populations of retirees (65+) seem to erode the performance of financial markets as well as economic growth. This finding makes perfect sense; retirees are disinvesting in order to buy goods and services that they no longer produce, and they are no longer contributing goods and services into the macroeconomy.”
Arnott and Chaves aren’t the only researchers do to an analysis on demographics and stock returns. The blogger EconomPic had a post on the same topic back in 2017. He also found a positive relationship between population growth and real equity returns across countries from 1900-2013:
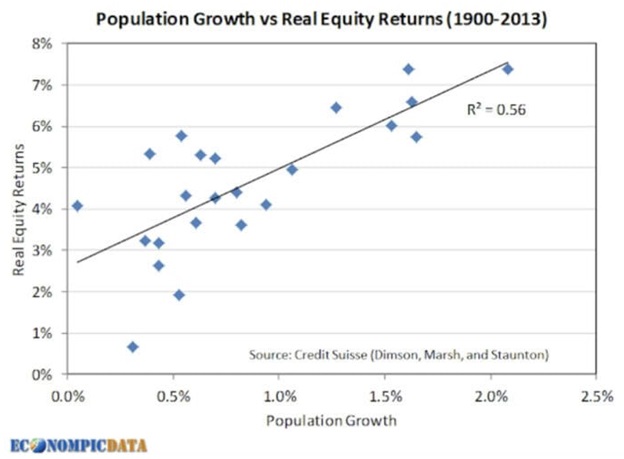
So, is this a closed case? If population growth is so important, why do we even bother making predictions about anything else related to stocks?
Because population growth isn’t the whole story. If we go back to Arnott and Chaves’ paper, they actually made some predictions on future stock returns by country based on their demographics. Here’s a map of their annualized stock market forecast by country for 2011-2020:
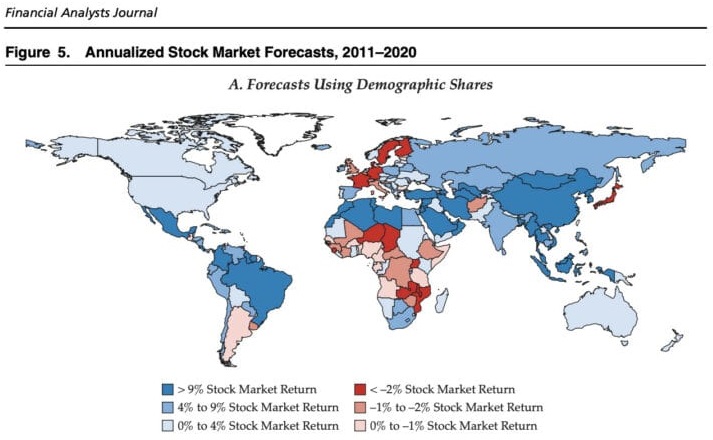
According to this, the U.S. should have had a 0%-4% annualized stock market return, Japan should’ve had less than a -2% return, and China should have had a greater than 9% return over this period. But what actually happened? None of those things.
From 2011 to the end of 2019 (pre-COVID), the U.S. had the highest return with China and Japan performing roughly similar:
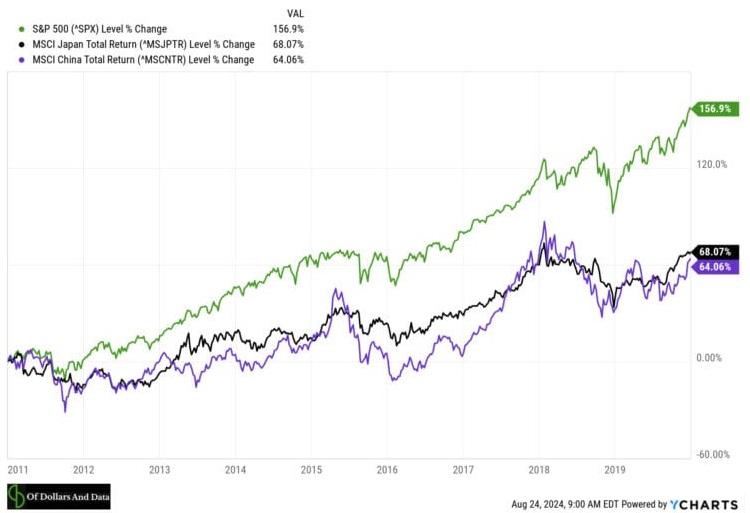
While this is only three countries from the many listed above, it illustrates the difficulty of predicting future stock returns based on demographics alone. Yes, population matters, but other factors such as technological change, productivity growth, and investor preferences can matter even more.
The bottom line
Demographics play a significant role in shaping economies and their underlying stock markets. The research I’ve highlighted shows a clear relationship between population trends, GDP growth, and stock returns. In general, countries with growing working-age populations tend to experience stronger economic growth, which often translates to better stock market performance.
However, demographics are not always destiny in the stock market. Technological advancements, productivity growth, policy decisions, and shifting investor preferences can all significantly impact stock returns, sometimes overshadowing demographic effects. Additionally, a country’s market performance isn’t solely determined by its own demographic profile, but can also be influenced by other global trends and capital flows.
While the retirement of Baby Boomers will present future challenges to stock returns, this doesn’t necessarily spell doom for your portfolio. A changing demographic profile could spark innovations in productivity or reorient the global economy in a way that mitigates these negative demographic pressures.
Yes, work will need to get done for civilization to keep moving forward. But with the continued development of AI, there’s nothing that says that these future workers must all be people.
Either way, what matters for you isn’t the demographics of any one country, but owning a diverse set of income-producing assets. That’s how you counteract a changing population and build wealth for the long run.
Nick Maggiulli is the creator of personal finance blog Of Dollars And Data and the Chief Operating Officer at Ritholtz Wealth Management. For disclosure information please see here. If you liked this post, consider signing up for Nick’s newsletter.