The past year was one for the record books as the pandemic inflicted synchronised economic impacts across the globe. The economic downturn generated significant challenges in determining the path forward. However, as the year progressed, it was evident this economic recession was different from the GFC, distinguished by the magnitude of the initial downturn but also the speed of the recovery.
The Australian recovery experience
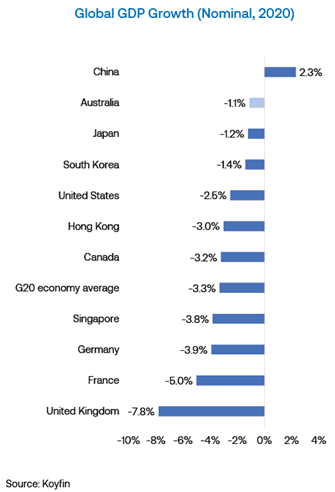
The Australian economy has benefited from strong government fiscal support and the exemplary containment of the virus, resulting in a materially stronger than anticipated economic recovery. In April 2020, consensus GDP forecasts for 2020 ranged between -3.4% and -10.0%. These forecasts strengthened over time, with 2020 growth results finishing the year at a manageable -1.1%.
Perhaps even more remarkable was the recovery across the labour market, with forecasts that the unemployment rate would exceed 10% over the year. It peaked at 7.5% before progressively reducing to the most recent reading of 5.8% in March 2021). This is approximately 0.5% above the pre-pandemic trend of 5.25%, a level most economists didn’t expect until 2022. Although many advanced economies shared similar recoveries, Australia’s comparative containment of the virus and effective policy support fuelled a shorter downturn and subsequently, a stronger economic recovery.
The economic recovery and bond yields
Given the speed of the economic recovery, the stimulatory government policy support and the further relaxation of government restrictions, forward projections for growth in Australia have been upgraded. These factors and the rebound in commodity prices have increased expectations for inflation, wages and longer-term economic growth. As such, bond yields have now lifted from historically-low levels.
The Reserve Bank has separately suggested that both wage growth and the consumer price index (CPI) could initially show some ‘catch up’ after slowing sharply during the depths of the pandemic. However, annual inflation is not expected to move within its target range of 2-3% for several years. In response to this relatively good news, over the calendar year 2021, the 10-year bond yield increased from around 1.0% to a high of 1.9% before more recently trading down to approximately 1.7% (at the time of printing).
Bond yields and real estate
The gap between property yields and bond yields is known as the ‘risk premium’, or the excess yield that can be achieved from investment in commercial property versus the ‘risk-free rate’ of an investment in a government bond.
So even though bond yields are increasing (this is known as the ‘steepening’ of the yield curve), the spread – or the difference between commercial real estate yields and bond yields, remains high – even when compared to historical levels (as illustrated in the office and industrial yield charts below). Based on these measures, this signals limited downside risks to commercial real estate valuations.
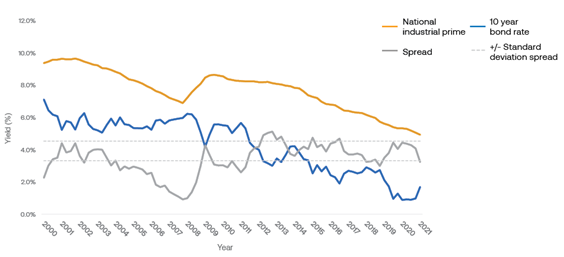
Prime industrial yield versus 10-year government bond rates
Industrial spreads have narrowed and approached the lower bound of historical movements. However, given the structural tailwinds, implied risk premiums are being adjusted lower.
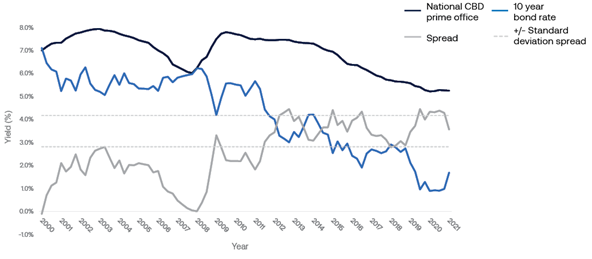
Prime office yield versus 10-year government bond rates
Office risk premiums remain within typical historical ranges.
Source: JLL Research, Charter Hall Research
Sector and industry outlook
Assets with long Weighted Average Lease Expiries (WALE) and quality income streams from strong tenants are well placed to absorb any sustained rise in bond yields. Further strength can be found in assets that benefit from leases with fixed annual rental escalations, as this hedges against any significant and sustained increases in inflation.
Average ‘risk premiums’ should reflect the associated risk and future growth of an investment.
As an example, the discretionary retail and industrial real estate sectors have been experiencing very different structural changes from the rapid growth in online retailing. These trends are being reflected with the two sectors undergoing different ‘re-ratings’: industrial risk premiums are narrowing, while regional and sub-regional retail risk premiums are expanding. The discretionary retail sector can be further compared to non-discretionary retail (think Bunnings, Coles or Woolworths), which have performed strongly over the last year. The average risk premiums for neighbourhood shopping centres that have a majority of non-discretionary retailers as tenants have also been narrowing.
There are several reasons to be positive about the near-term outlook for the Australian economy and the real estate sector. Global and US growth has strengthened significantly, the Australian housing market is in a cyclical upswing, and the drag on the economy generated by Australia’s adjustment to lower commodity prices have now passed. In fact, commodity prices have now increased to decade highs, providing a real income boost for the wider economy. These factors are expected to support the momentum already underway across the Australian commercial real estate sectors, in particular for the industrial, non-discretionary retail and social infrastructure sectors.
Adrian Harrington is Head of Capital and Product Development at Charter Hall, a sponsor of Firstlinks. This article is for general information and does not consider the circumstances of any investor.
For more articles and papers from Charter Hall, please click here.