If our working years can be regarded as the time when we aim to build up our superannuation savings, our retirement years can equally be regarded as the time when we aim to spend them.
At least that’s the objective for most Australians. Which generally leads to the question: how do I start accessing my super funds when I do stop working, or maybe even before I stop working?
This article focuses on the basics, including the general eligibility rules around accessing your super and how to switch your super accumulation account to an account-based pension.
What age can I access my super?
To legally access your super, you generally need to have met a condition of release after turning 60-years-old.
You can do so by either stopping work completely (retiring) or by keeping working and starting a transition to retirement income stream (TRIS). Doing so can enable you to reduce your current working hours and use your TRIS pension payments to top up your part-time income.
In either case, you have the options of turning on a pension income stream, making a lump sum cash withdrawal, or doing a combination of both.
How do I start a pension account?
Importantly, to start accessing your super, you will need to roll some or all of it over from your accumulation account into a newly created pension account.
Those starting a TRIS continue to receive compulsory super guarantee payments from their employer (which are taxed at the normal rate of 15%) into their super accumulation account. The funds held in a pension account can be accessed, however keeping in mind that investment earnings in the pre-retirement phase are also still taxed at 15%.
Most super funds offer pension account products and different investment options, similar to their accumulation account products. Those with a self-managed super fund should contact their SMSF accountant and/or financial adviser to facilitate the super rollover and pension account conversion processes.
You may need to contact your super fund to find out their process, which is typically as simple as lodging a request with your fund by filling out a form and providing information such as how much of you super you want to roll over, and where to.
Once your funds are in a pension account you could then take some out as a lump sum. The Australian Tax Office (ATO) has mandated minimum annual withdrawal amounts, which depend on your age.
There is a limit on the maximum amount that can be transferred as a tax-free retirement income stream from super to a pension account, known as the transfer balance cap. This is currently set at $1.9 million. The ATO keeps track of how much you transfer, and if you go over the cap it will levy an excess transfer balance tax.
If you have more than $1.9 million in super you have the option of keeping the excess in your super account and paying up to 15% tax on your earnings, or you can withdraw the excess super as a lump sum.
What are the tax considerations in pension mode?
If you’re aged 60 or over and fully retired, any income earned on your pension assets is tax free and so are the pension payments you withdraw.
Also, a major advantage is that the profits from any investments sold within a pension account are completely capital gains tax free.
What are the minimum pension withdrawal amounts?
Once you’ve rolled over some or all of your super to an account-based pension you are required by law to withdraw a minimum pension amount each financial year, which is a percentage of your account balance based on your age.
For new pensions, the minimum withdrawal amount is calculated on a pro-rata basis from when a pension commences to the end of the financial year.
There are restrictions on how much can be withdrawn tax free through a TRIS in a financial year if you’re under 65, until you’ve met a condition of release. The minimum withdrawal amounts is 4% of your super balance and the maximum is 10%.
The table below shows the required minimum withdrawal rates if you're in pension phase and are fully retired.
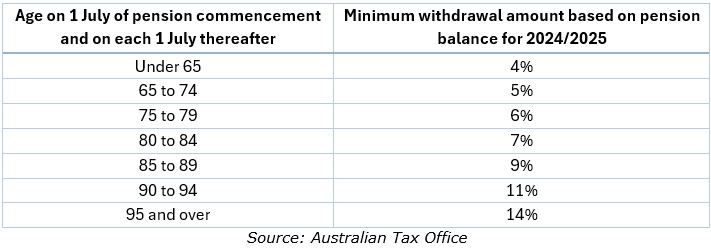
Any amounts leftover in your pension account when you die will go to your nominated beneficiaries. Depending on the type of beneficiary (reversionary, spouse, dependant or non-dependant) the amounts can be paid as an ongoing pension stream until the account runs out or as a lump sum.
Consider getting professional advice
If you’re wanting total financial flexibility in retirement, you could consider leaving part of your money in super, rolling over some of it into an account-based pension, and also withdrawing lump sums whenever you need to.
There are a range of benefits from adopting a combination of your options, although there may also be potential tax consequences for both you and your beneficiaries.
Managing the combination of a super accumulation account, an account-based pension, an Age Pension entitlement (if eligible), potential investment earnings outside of super, and irregular lump sum payments, can be highly complex.
Using the services of a licensed financial adviser is a worthwhile consideration as you weigh up all of your retirement options.
Tony Kaye is a Senior Personal Finance writer at Vanguard Australia, a sponsor of Firstlinks. This article is for general information purposes only and does not consider the investment objectives, financial situation or needs of any individual.
For more articles and papers from Vanguard Investments Australia, please click here.