Yields on long-term bonds issued by many developed nations, including Australia, have declined significantly since about 2008. In Australia, 10-year Government bond yields have fallen from 5.8% in 2008 to the current rate of about 2.7%. In October 2016, the Government issued a 30-year bond at a yield of about 3.3%. These low yields are also evident in the overnight cash rates, currently at an historically low 1.50%. Compared with long-term historical averages, these yields reflect a number of factors including quantitative easing and the intervention of central banks, reduced public sector investment, strong investor demand for low-risk quality assets such as government bonds, and lower long-term growth and inflation expectations.
Historical Yields of 10-year Government bonds and ASX All Ordinaries Index performance
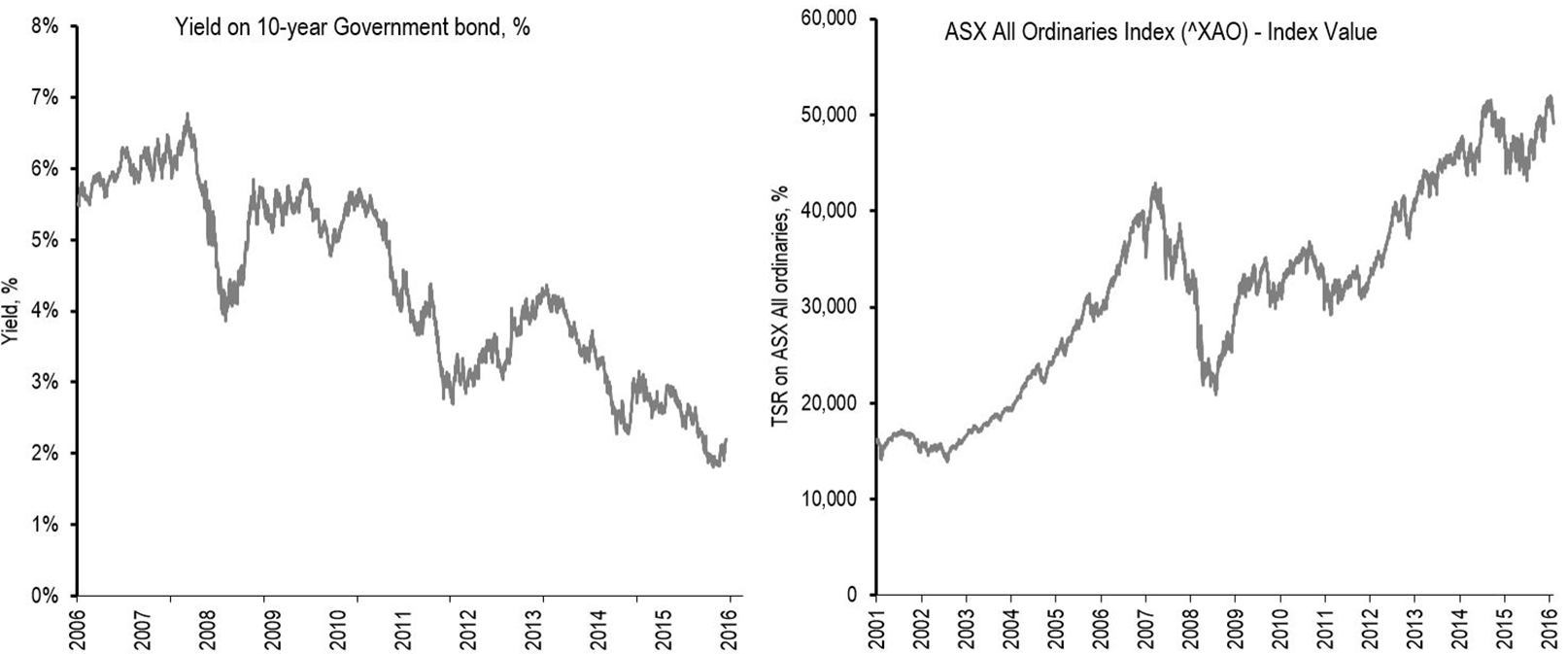
Click to enlarge. Source: RBA, Capital IQ
Impact of low bond rates
In valuing assets, the income approach is often applied, using the discounted cash flow methodology. This effectively requires forecasting future cash flows from the asset, which are then discounted to present value at a rate that reflects the time value of money and riskiness of the cash flows. The discount rate applied in this method is usually a blend of the cost of debt and the cost of equity in the relevant sector, based on the market-average level of gearing.
One of the key inputs to the discount rate is the cost of equity. This is commonly derived by adding a premium to the ‘risk-free’ rate to reflect the excess return required on equity investments and the proportion of that premium applicable to the asset. The link between government bond yields and valuation is due to the common practice of basing ‘risk-free’ rates on long-term government bond yields, the best observable proxy for a riskless asset. All else being equal, lower yields on ‘risk-free’ assets would result in a lower discount rate, and therefore an uplift in value. However, while expected returns on risk-free investments have fallen over the past few years, the market is not pricing in a direct corresponding increase in the value of equities.
Looking at the performance of the ASX All Ordinaries Index since 2008 (as shown in the chart above), there has been significant volatility. Yet the share prices of ASX All Ordinaries companies have generally risen over the same period. Some of the factors driving share prices up, despite the low-growth environment, include:
- As overnight cash rates have fallen, companies having taken advantage of lower borrowing costs
- Debt levels have generally fallen across the market, arguably strengthening balance sheets
- The low growth environment has highlighted the need for strong management focus on long-term cost savings and efficiencies, as well as innovation and technology developments
- Investor demand for defensive or lower risk assets
- Falling yield expectations from investors
- Achieving real growth through acquisitions, offering the potential for growth and scale/cost savings.
However, on average, share price rises have been less than the direct impact of the lower risk-free rate on discount rates. In fact, total shareholder returns, calculated as share price growth plus dividends, have fallen in recent years, with average returns of 5.9% over the three years to October 2016, lower than the average returns for the past 10 years (10.3%) and 15 years (8.4%).
ASX All Ordinaries Total Shareholder Return (TSR) performance
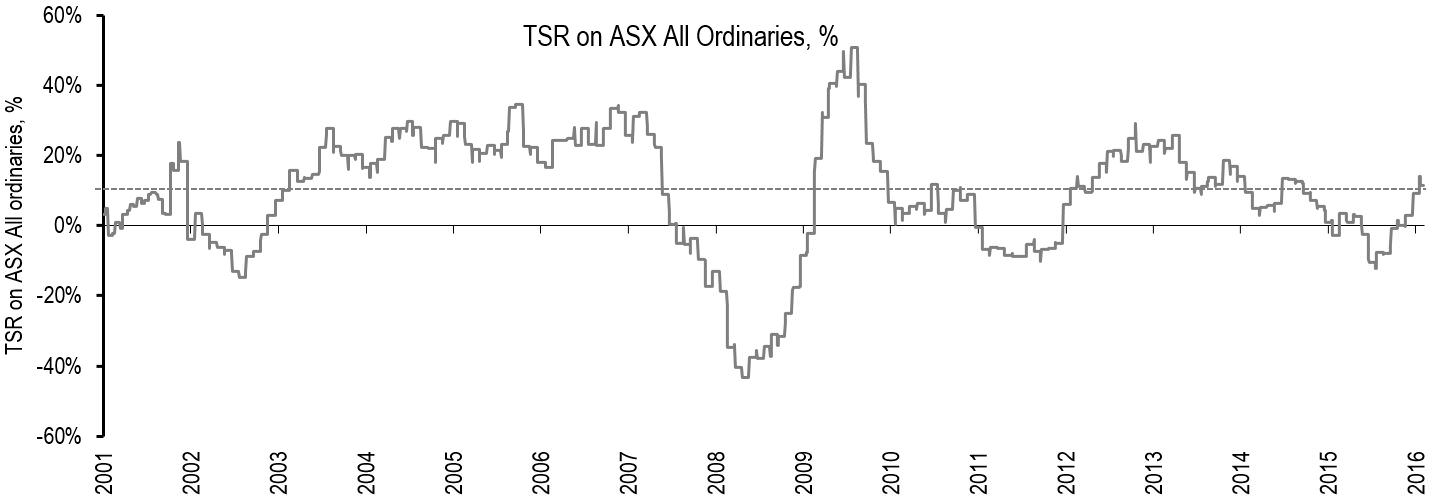
Click to enlarge. Source: Capital IQ
Other factors than low bond rates reflected in share prices
So, while on average share prices have risen in recent years, the market is arguably not fully reflecting the fall in government bond rates in equity prices. Other factors must be in play.
Many valuation professionals consider the impact on valuations of the current lower yields by:
- Critically examining the expected future cash flows to ensure they reflect lower long-term growth and inflation expectations
- Considering the impact of volatility and expected returns in assessing equity market risk
- Using a blend of current actual rates, historical averages and views on longer-term investment yields.
Valuers may also form a view on a ‘normalised’ long-term yield for a ‘risk-free’ asset allowing for the long-term history of Australian Government bond yields, fundamental real return expectations, inflation forecasts and implied equity market returns. This has generally resulted in an additional risk premium being applied, over and above the current bond rates, in assessing an appropriate cost of equity and overall discount rates.
While there is no consensus on the correct approach, most equity analysts apply some form of adjustment in assessing their discount rates. These will likely unwind as and when government bond rates increase. Ultimately, the reasonableness check on values for investors is the earnings multiples implied by companies trading on the stock exchange and prices paid in recent transactions.
Julie Wolstenholme is a Partner in EY Australia Transaction Advisory Services. The views expressed in this article are the views of the author, not Ernst & Young. The article provides general information, does not constitute advice and should not be relied on as such. Professional advice should be sought prior to any action being taken in reliance on any of the information. Liability limited by a scheme approved under Professional Standards Legislation.