Over the past three months, Japan has been the number one talking point with my clients throughout the US, Europe and Asia. The Nikkei225 was up 28% in 2023, with corporate governance reform a key catalyst. So there’s a lot more interest in the Japanese market, yet there’s also scepticism.
Previous attempts at reforming governance in Japan have stalled or disappointed and it shows in the trading valuations of Japanese stocks and their profitability metrics:
- Some 40% of Japanese companies in major indices are trading on Price-to-Book (PBR) ratios of less than one. On the S&P500 it’s just 5% and in Europe (STOXX600) it’s 24%.[1]
- Similarly, some 40% of major Japanese stocks have a Return on Equity (ROE) of under 8%. By comparison, only 14% of the S&P500 can’t beat that mark.[2]
So, while we are sure reform is taking hold (some of our recent Japanese stock picks reflect its influence), we wanted to retest the thesis. To take just one angle, we wanted to assess whether the various institutions involved in corporate governance reform were aligned in their aims and ambitions. An integrated approach is much more likely to drive change that’s broad, deep and sustainable.
Talking to the people who set the rules
On a recent research trip to Japan, our Japan strategy co-Portfolio Managers Jamie Halse and Leon Rapp, plus co-CIO Andrew Clifford, met with the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry and Japan’s Financial Services Agency.
More recently, Leon and I, plus Tim Maher (UK Managing Director) met with Mr Yamaji, the President of the Tokyo Stock Exchange (TSE). These were fascinating meetings.
Mr Yamaji was keen to stress the continuity of the Japanese approach (see the chart below). “People see the reforms as a set of individual initiatives”, he said, “but they’re not. They’re part of corporate governance process rolled out for 20 years.”
In our meeting, Mr Yamaji stressed just how seriously Japanese authorities take reform. He sees the health of Japanese companies as vital for the overall economy and the country’s prosperity.
Mr Yamaji’s expectations go beyond share buybacks and cutting excess capital accumulation. He wants Japanese companies to “understand how they can improve across a whole range of factors. How they can invest in R&D, improve working practices, invest in business growth.”
He also spoke about the importance of broadening the talent pool. “We want to see diversity of boards, a mix of males and females, more diversity of backgrounds, local and overseas directors. We now have good case studies showing the benefits of these changes. Ten years ago we had nothing.”
Top policy-makers and regulators in Japan believe many of the building blocks are now in place. They argue it’s now the job of investors – and others - to bring the weight of money to bear on Japanese corporates to drive these reforms even further.
I’m inclined to agree.
Pressure the corporates
We asked Mr Yamaji what he expects from global investors like Platinum.
He is looking for global investors to engage with companies about improved governance and capital management and to demand changes that drive sustainable growth. Our Japan strategies are putting money to work on this theme, with significant holdings in Toyo Seikan (packaging), Nittetsu Mining and confectionary-maker Ezaki Glico. All three have overcapitalised balance sheets – but improving corporate governance.
The story so far
As the graphic below shows there has been a decade of corporate governance reform in Japan, culminating in the latest efforts by the TSE.
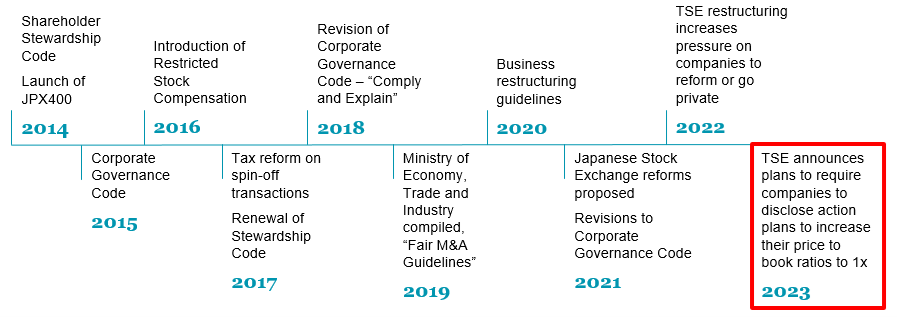
Source: Platinum
The efforts in the early years were focused on getting corporates to be more shareholder friendly. More recently the TSE has sought to change behaviour by forcing public demonstrations of a company’s reform efforts. The TSE now expect companies to publish a plan for improvement. The response has been encouraging. By July 2023, only a few months after the TSE initiatives were announced, nearly 40% of Prime Index companies had published those plans.[3]
The overall sweep of reforms have been a mix of encouragement and regulation. The final push now asks Japanese companies to make a public display of their effectiveness. A 'name and shame' approach can be an effective motivator in a country like Japan.
Evidence of change
The chart below highlights how Japanese firms have been increasing cash returns to shareholders since 2007.
Chart 1: Topix – Aggregate Dividend and Buybacks Trend
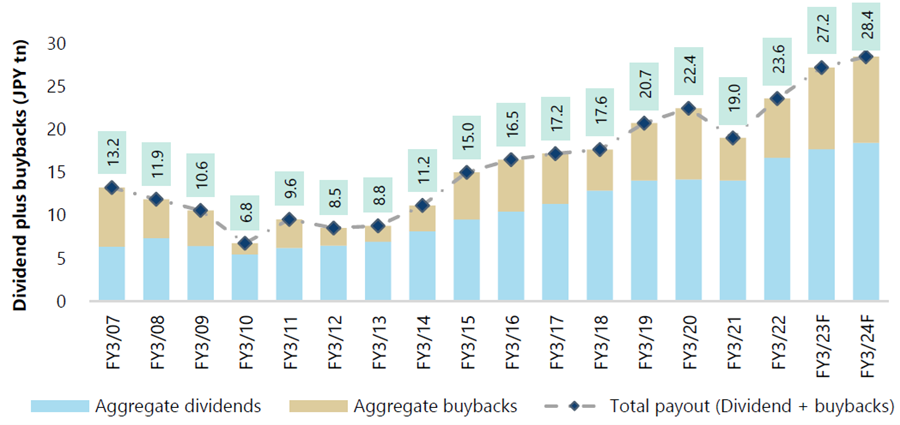
Source: FactSet Research Systems, Bloomberg, Jefferies
For too long, the Keiretsu style cross-shareholdings in Japanese companies protected management and boards from demands for shareholder-friendly change. Now, as the charts below show, the effective free float of shares is widening. That means big new (and global) investors can take a position in a company and demand a change or angle for a takeover. That builds the pressure for strategic, operational and financial innovation that moribund boards have resisted in the past.
Charts 2&3: Fewer aligned shareholders
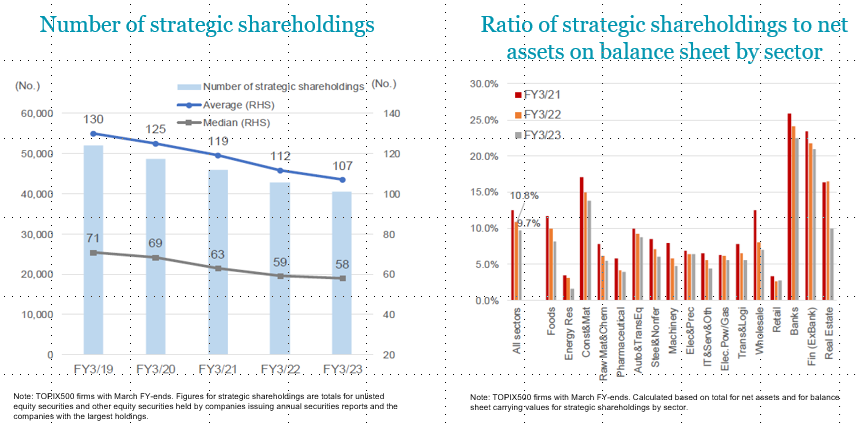
Source: Mitsubishi UFJ Morgan Stanley Equity Research Report, 28 July 2023
The leaders are moving
While the economy-wide numbers are positive, in the Japanese market it’s always good to see what the giants are doing. Our Japan strategy Co-Portfolio Manager, Jamie Halse, says Toyota is an example of what’s changing: “Their web of cross shareholdings between “group” companies is legendary for its scale, complexity and circularity”.
Toyota has already sold US$1.8bn of KDDI shares and now the Group is selling US$4.7bn worth of major parts supplier Denso. Group company Aisin has announced it will sell off US$700m of cross-shareholdings, with plans to reduce the remainder of its holdings to zero over time.[4]
“With a leader like Toyota now pushing these changes we expect to see more of the Japanese market undertake similar measures,“ says Jamie. “That could be positive for returns on equity and stock prices.”
Where from here?
Understandably, many investors have been sceptical about the reality of Japan’s corporate reform efforts. However, after talking to the regulators and to the corporates we believe the forces of change – political, regulatory and commercial - are now aligned. In a consensus society like Japan that momentum can be hard to stop. That’s good news for investors.
[1] Source TSE
[2] Source: TSE
[3] Source: TSE
[4] Source: Toyota website
Charles Brooks is Investment Specialist at Platinum Asset Management, a sponsor of Firstlinks. For more articles and papers by Platinum click here.
View Disclaimer: This article has been prepared by Platinum Investment Management Limited ABN 25 063 565 006 AFSL 221935 trading as Platinum Asset Management (“Platinum”). While the information in this article has been prepared in good faith and with reasonable care, no representation or warranty, express or implied, is made as to the accuracy, adequacy or reliability of any statements, estimates, opinions or other information contained in the article, and to the extent permitted by law, no liability is accepted by any company of the Platinum Group or their directors, officers or employees for any loss or damage as a result of any reliance on this information. Commentary reflects Platinum’s views and beliefs at the time of preparation, which are subject to change without notice. Commentary may also contain forward-looking statements. These forward-looking statements have been made based upon Platinum’s expectations and beliefs. No assurance is given that future developments will be in accordance with Platinum’s expectations. Actual outcomes could differ materially from those expected by Platinum. The information presented in this article is general information only and not intended to be financial product advice. It has not been prepared taking into account any particular investor’s or class of investors’ investment objectives, financial situation or needs, and should not be used as the basis for making investment, financial or other decisions. You should obtain professional advice prior to making any investment decision.