You could be forgiven for thinking lately that the only thing that drives the share market is interest rates.
Anyone who has taken even the most introductory of finance course will know the present value of an asset is the discounted value of its future cash flows. With those cash flows discounted back to today using long term interest rates.
And so, on first blush it may seem logical that higher long-term interest rates means lower share prices and valuations today.
But it’s actually much more complicated. Higher rates don’t always cut equity value. This matters because the last couple of years could have lulled investors into thinking it’s almost all that matters for share market direction.
Will interest rates continue to have an outsized influence on shares and in which direction is that most likely to be? Read on to find out.
Rate rises don’t always cut equity value
Aswath Damodaran, colloquially known as the ‘Dean of Valuation’ at NYU’s Stern School of Business asks his students up front: “If interest rates go up, what happens to equity value?”
He offers the students four options:
- Equity value will increase?
- Equity value will decrease?
- Equity value will remain unchanged?
- Or, any of the above, depending on why interest rates increased in the first place?
Now, like that friend who spoiled the end of TV series Game of Thrones and told you Jon Snow kills Daenerys before you’d even watched it, the answer to the above is D.
As you can see below in the red box in Damodaran’s diagram, the value of a business (and its shares) is the expected stream of cash flows the business generates over its lifetime[1] discounted back to today’s value, using an appropriate discount rate.
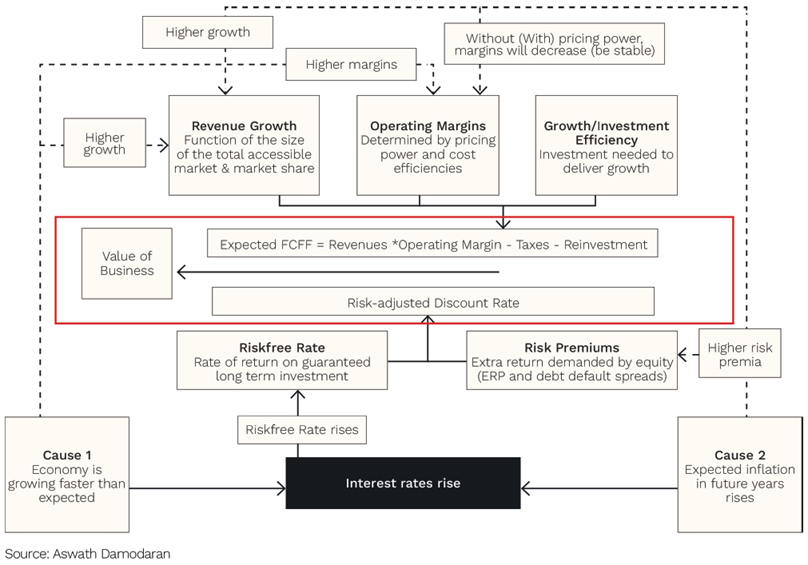
Source: Aswath Damodaran
One of the key inputs to the discount rate is the so called ‘risk-free rate’. For U.S. shares this is most often the 10-year U.S. government bond rate. It’s thought of as ‘risk-free’ because the U.S. government is taken to be the most credit worthy borrower.
If we hold ‘risk premiums’ in the diagram above constant for a moment (we’ll leave that discussion for another day), when the risk-free rate goes up – like it has for most of August through October – then the present value of those future cash flows from businesses goes down. And the share price will go down, just like we’ve seen recently.
You might ask: but how come the answer to Damodaran’s question is ‘D’ … when you basically just told me it’s ‘B’?
The reason why rates rise is important to what happens with equity value
It really all comes down to the reason interest rates rose in the first place. For simplicity there are two main reasons why long-term interest rates can rise:
- Higher real growth in the economy (Cause 1 in the diagram above)
- Higher expected inflation (Cause 2 in the diagram above)
The table below provides a good summary of the impact of each on the drivers of the value of a business:
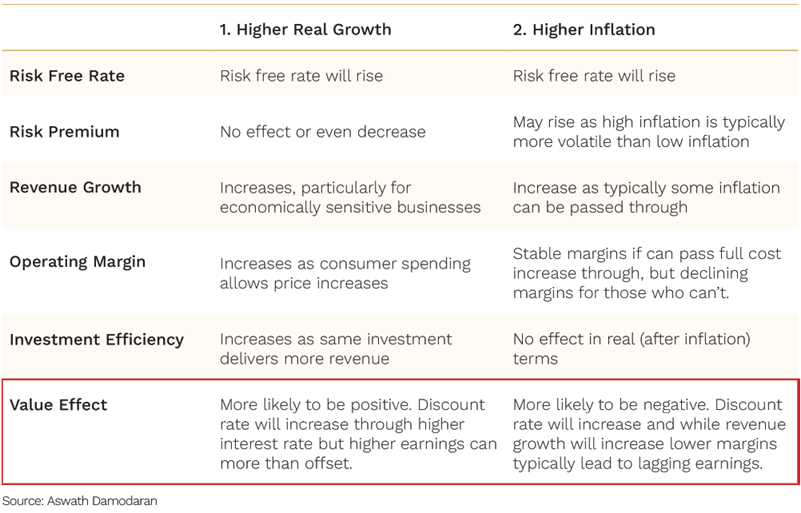
Source: Aswath Damodaran
The natural question is: why has the US 10-year government bond rate been rising recently? Is it higher real growth or higher expected inflation?
Below, we show the answer from interest rates that are implied by the market.
The increase in the U.S. 10-year government bond rate (orange line) has been driven by an increase in real interest rates (grey line), which signals an expectation of higher real economic growth, with virtually no contribution from higher expected inflation (yellow line).
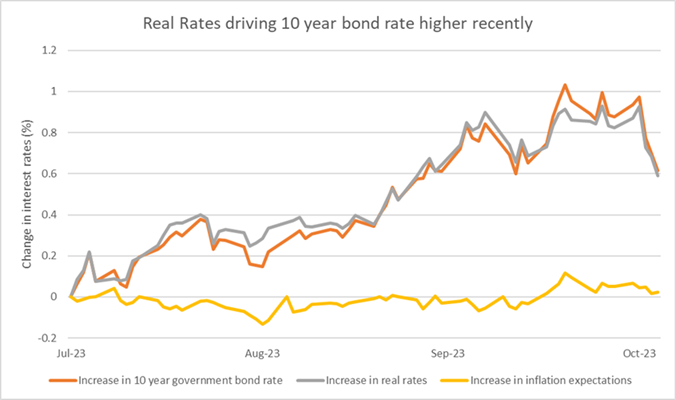
Source: Factset. Data from 31 July to 3 November 2023
This lines up with economic data in the U.S. over much of the last three months showing a resilient economy that is so far withstanding increases in short-term interest rates by the Fed (Exhibit A being U.S. Q3 GDP at a very strong 4.9% annualised).
But reasons other than rates are driving rates higher now
But why, if economic growth has been more resilient and long-term interest rates have headed higher as a result, which more often than not is positive for equities, have shares sold off over August through October? (We did tell you the relationship is complicated!)
It’s not clear that stronger economic growth is the only reason long-term rates have headed higher. Other reasons have likely played a role, including worries about the size of the U.S. fiscal deficit, the Fed continuing to sell its U.S. government bonds as part of its quantitative tightening program and expectations for the timing of Fed rate cuts being pushed out.
These other reasons, if holding sway, could mean that higher long-term rates will create a headwind for the economy down the track, and that is what shares are reacting to over the last few months.
Rising rates are also hurting young companies more
Another important point is that the pain from higher long-term interest rates has not been dished out evenly across the share market. In fact, it’s been the small caps and more growth-orientated businesses (as shown by the ASX Small Ords, Russell and Non-Profitable Tech indices) that have fallen the most.
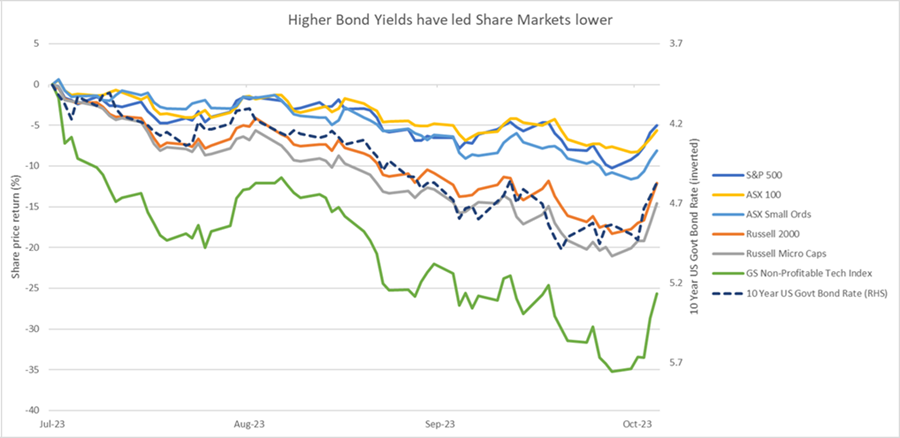
Source: Factset, Ophir. Data from 31 July to 3 November 2023.
There is some intuition behind this. When interest rates rise, the value of growth in cash flows projected further out in the future decrease more than those closer to today.
In short, the valuations of younger, high-growth businesses are impacted more. This has been THE key influence on the relative performance of different share market segments since long-term interest rates started increasing in 2021.
The correlation between rising rates and falling equity prices is relatively weak
History suggests that generally higher rates tend to be associated with lower share market valuations, but it’s not a particularly strong relationship. The answer really is, as alluded to above “it depends”.
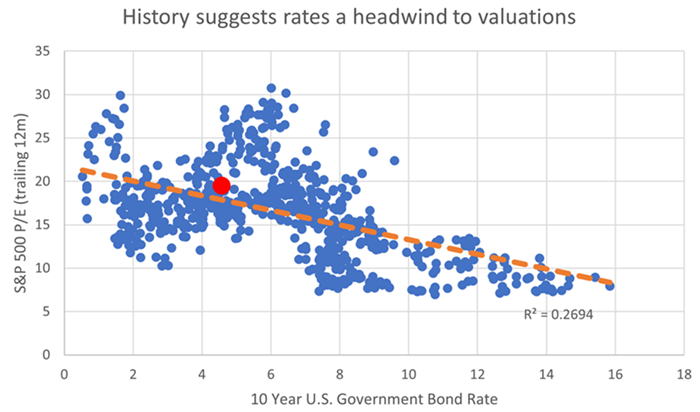
Source: Factset. Data from March 1962 to October 2023.
Today’s U.S. long-term interest rates and share market valuation is represented by the red dot in the chart above. It’s above the orange trend line, meaning the current setting of rates is likely a headwind for U.S. share market valuations, though they are not pre-ordained to fall.
In fact, historically when rates have been between 4-6% they have spent about 50% of their time with a price-to-earnings (P/E) ratio above 20, which is fractionally higher than it is today.
But as we show below, the rates sensitivity of the U.S. share market has increased a lot more recently. The chart shows correlations of one-month returns for the S&P 500 and its sectors – as well as the Growth and Value factors – to one-month changes in U.S. 10-year bond rates.
The correlations are negative, so higher bond yields typically lead to lower share prices. And the highest sensitivity tends to be in the more growth-orientated sector such as Communication Services, IT and Consumer Discretionary where more of their lifetime cash flows are projected further out in the future.
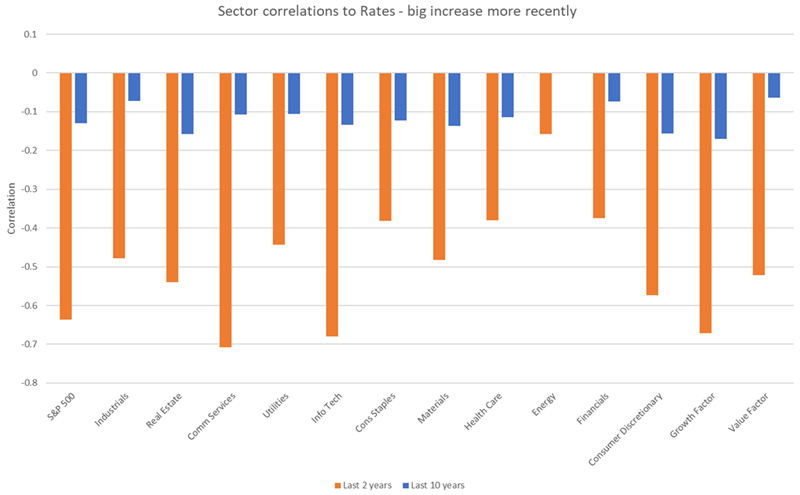
Source: Factset. Data from October 2013 to October 2023.
Data shows correlation of one-month share market returns to one-month changes in 10-year US government bond rate.
For the investor worried about higher for longer interest rates the message above has been that Energy, Financials and Value style companies have provided the best hiding place.
Influence of rates to wane, fundamentals to return to the fore
In sum, the best we can say is typically higher interest rates are associated with lower share market valuations, but not always and over the long term the relationship hasn’t been that strong.
Valuations and share market returns seem to have been particularly sensitive to higher interest rates in the last 2-3 years, probably because the rate moves weren’t initially expected, and they have been so swift from such low levels.
The valuations of younger, faster growing companies have been particularly susceptible to increasing rates of late.
Providing inflation is controlled, most of the move higher in long-term interest rates is likely behind us in the U.S. But until inflation is truly dead, any large, short-term moves in rates is likely to have outsized outcomes for both the overall share market, and its winners and losers.
Ultimately though, over the next year or two investors should expect movements in long term interest rates to reduce and therefore their influence on share market valuations to move more to the background.
Fundamentals such as revenue, margins and profits will likely come more to prominence again as key drivers of share prices, much as they always have over the long term. This would be a welcome development for us and our fellow investors as the assessment of a business’s fundamentals and their resulting investment merit is where we believe we have an edge.
[1] Also known in finance nerd speak as the Expected Free Cash Flow to the Firm (FCFF)
Andrew Mitchell and Steven Ng are co-founders and Senior Portfolio Managers at Ophir Asset Management, a sponsor of Firstlinks. This article is general information and does not consider the circumstances of any investor.
Read more articles and papers from Ophir here.