American venture capitalists (VCs) often talk about home runs. VC portfolios are structured to maximise the chance of at least one successful investment that will return the fund multiple times the original investment. Statistically, we know that around 90% of returns for VC investors will come from just 10% of early-stage investments. These are the home runs. The other 90% of businesses will either deliver a modest return or worse-case scenario, no return at all. Home runs are essential to provide the returns that set VCs apart and that investors are expecting.
In the more popular language of cricket for Australia, VC investors need to maximise their chances of hitting a six when constructing their portfolio. And those of us who have dedicated many a summer (or winter in the recent Cricket World Cup) to watching cricket will know that if a batsman protects their wicket too intensely, they can’t take the backswing necessary to hit the six. Instead, they will be forced to settle for singles and dot balls.
Losing wickets is inevitable in early-stage investing
VCs also know that losing a few wickets is an inevitable and necessary part of the game. VCs are generally comfortable with this but for some investors the idea that loss is inevitable can be uncomfortable and off putting. These investors are hindered by loss aversion and the belief that losses fundamentally loom larger than gains.
VC is different and requires a different mindset. Every investment is made with the conviction that it could be the outlier and an acceptance that many will not. It is okay to lose if there’s a big winner in the portfolio.
To labour the cricket metaphor, we can look at the statistics of cricket legend and former Indian captain, Sachin Tendulkar. During his test career, Tendulkar did not score a single run from 57% of the 29,000 balls he faced. He either blocked or let them go through to the keeper. But of the total runs he scored during his test career, over half (55%) were from fours or sixes although these made up just 7.2% of the total balls he faced. Like Tendulkar and the 29,000 balls he faced, investment in early stage businesses requires VCs and their investors to face a lot of companies and know which are worth a big swing. This is a strategic and disciplined approach to risk taking that VCs gain after years of facing start-ups.
Management of the risk
Portfolio construction in VC is geared to address and mitigate against risk factors as much as possible. Good VCs will ensure that there are enough companies in the portfolio and that there is enough diversity in terms of the different sectors and the underlying technology. Experienced VCs are also adept at spotting patterns and identifying strong founder characteristics, technical expertise and market opportunities that maximises the chances of success.
Hitting a six is not always the end game for VCs and their investors. For larger investors, this is often the beginning of a long partnership, particularly those looking to move the needle on a multi-billion dollar fund. Having identified those start-ups that are rapidly gaining traction and showing accelerated growth, larger institutional investors such as superannuation funds are able to write bigger cheques with lower risk at later stages of the business’ lifecycle. Table 1 shows the company funding life cycle with private market investors at the earlier stages and public market investors being involved at the later stages.
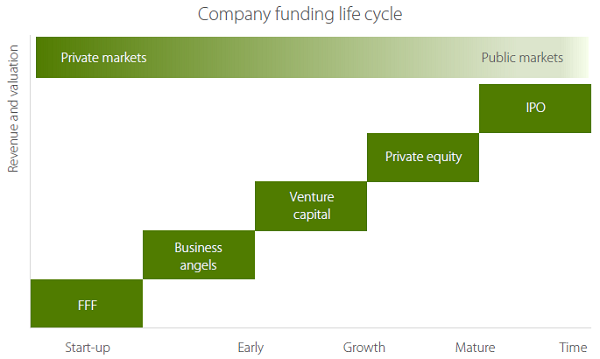
Source: Right Click Capital
The big wins afford VCs and their investors the opportunity to double down on later funding rounds (A, B or C rounds) and participate in growth across other stages such as co-investment opportunities, whether directly or through a mandate structure, and public listings. As high-performing investments progress through the business lifecycle, over time they provide strong returns for a superannuation fund’s venture capital, private equity and listed equities teams.
Table 2 shows an estimate of the number of Australian-based companies raising money in 2018 by stage of investment and reveals a far greater number of opportunities to invest in seed rounds than series A, B and C rounds.
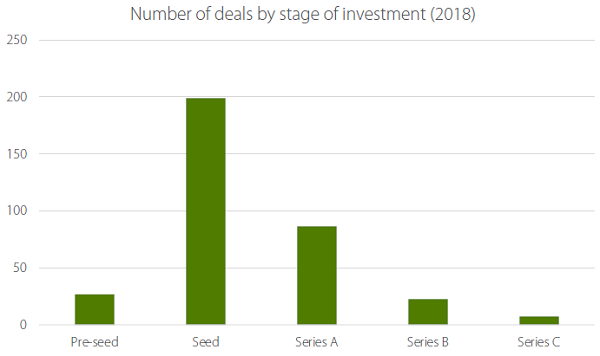
Source: Crunchbase
Table 3 shows the median and average amounts invested in the same deals in 2018 and demonstrates the ability of VCs to invest larger amounts at the later stages of funding as they identify the investments where they have hit a six. VCs who put money to work in businesses at earlier stages need to continue investing in a business’s subsequent rounds in order to maximise their upside when they’re on a winner.

Source: Crunchbase
It’s more about the long term than quick wins
VC often marks the start of a long-term partnership between an investor and a start-up. Ram Nath Kovind, the first Indian President to visit Australia recently commented, “The most successful Australian batsmen in India have been those who have shown patience, read the conditions carefully, settled down for a long innings, nurtured their partnerships and not fallen for spin”.
The same is certainly true for VC investors.
Benjamin Chong is a partner at venture capital firm Right Click Capital, investors in high-growth technology businesses. This article is general information and does not consider the circumstances of any investor.