We never know what each new day will bring and unfortunately for some the new day could be the last. Sudden and unexpected illness, death or disability hits us all at some stage, either ourselves or someone we know. This article explains the different superannuation entitlements if you are faced with a terminal illness, death or disability.
If an SMSF member is diagnosed with a terminal illness, they need to consider how they would like their superannuation entitlements to be paid. Options include taking entitlements as a terminal illness benefit, a permanent disability benefit or a death benefit to their family after they are deceased. The choice of superannuation benefit could make a difference to how much is retained in the family instead of the Taxation Office.
Terminal illness benefit
For a benefit to be released under terminal illness grounds, the SMSF member will need to satisfy the following conditions:
- two registered medical practitioners have certified, jointly or separately, that the person suffers from an illness, or has incurred an injury, that is likely to result in their death within 12 months
- at least one of the registered medical practitioners is a specialist practising in an area related to the illness or injury and
- the benefit is taken within 12 months of the certification.
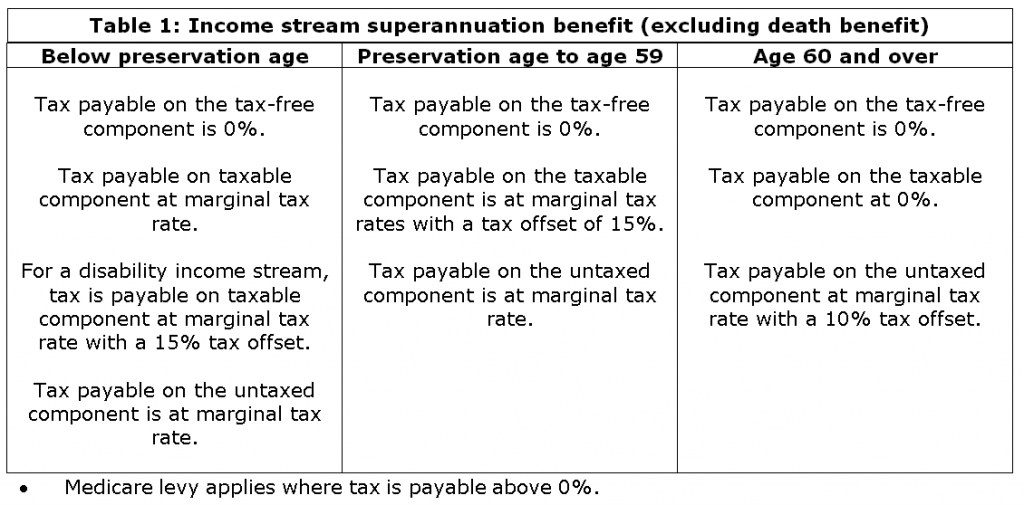
The member can elect to receive the payment either as a lump sum benefit or an income stream (eg. a pension).
If the member elects a lump sum benefit, the benefit will be paid to the member tax-free, regardless of the member’s age, provided the above conditions are met. You may also be able to claim a refund of tax withheld from super payments received while you had the illness up to 90 days prior to advising the fund of your condition.
If the member elects to receive a pension benefit, the benefit is taxed as a normal superannuation income stream. If the SMSF’s trust deed only allows for a lump sum, then the member would be unable to take their benefit as an income stream.
Care is needed when considering transferring a terminal illness benefit to another superannuation fund for payment as an income stream. Under the Income Tax Assessment Act 1997, the transfer would not be treated as a rollover and therefore would count towards the member’s non-concessional contribution cap. This could result in the member incurring an excess contributions tax liability.
On the other hand, if the member elected to have their superannuation savings transferred to another superannuation fund prior to applying to have their benefit released on terminal illness grounds, then it would be treated as a roll-over and it would not count as a contribution to the new superannuation fund.
Permanent disability (PD) benefit
To claim a PD benefit, the trustee of an SMSF must be reasonably satisfied that the member is unlikely to engage in gainful employment in a capacity for which the member is reasonably qualified by education, training or experience. A medical certificate is not a requirement as it is up to the trustee to decide what standard of proof will reasonably satisfied them. A PD benefit can be paid in the form of a lump sum or an income stream.
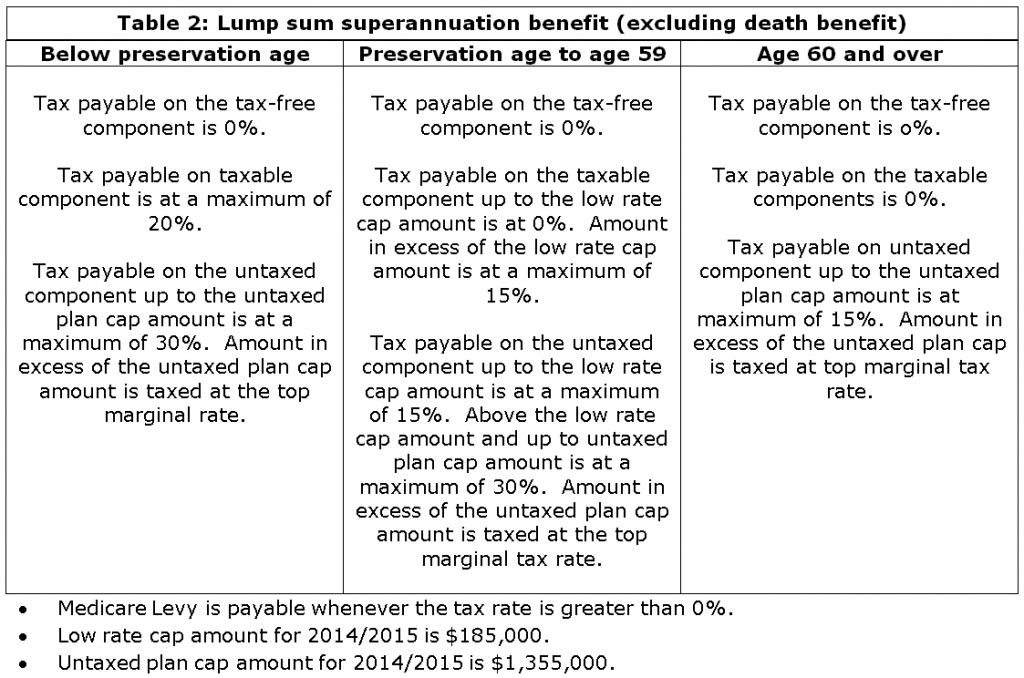
If a person chooses to take the benefit as a lump sum, the entire lump sum is tax-free if paid to a person aged 60 or over. For a person under 60, tax is payable on the lump sum depending on its tax-free and taxable components.
A lump sum PD benefit qualifies for an increased tax-free component, where two legally qualified medical practitioners have certified that, because of ill-health, it is unlikely that the person can ever be gainfully employed in a capacity for which they are reasonably qualified. The increased tax-free lump sum amount is calculated using the following formula:

Days to retirement is the number of days from the day the person stopped being capable of working to their last day of work (which for most people will be their 65th birthday).
Service days is the number of days in the service period for the lump sum (usually the period from when the person began contributing to super).
Example: Bev had an accident that stopped her from being able to work on 3 September 2007. She received a PD lump sum benefit of $160,000 from her SMSF. The total value of Bev’s superannuation account consisted of 25% tax free component and 75% taxable component made up solely of an element taxed in the SMSF. Her days till retirement (the day she turns 65) total 6512. Her number of days in service was 8099.
Bev’s PD lump sum benefit of $160,000 will therefore consist of an initial tax-free component of 25% and a 75% taxable component mirroring the components of the entire super account, that is, $40,000 tax-free and $120,000 taxable. The above formula is then applied to work out the increased tax-free component.
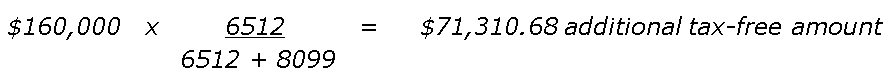
Bev’s PD lump sum benefit paid from her SMSF will now have a $111,310.66 ($71,310.68 + $40,000) tax-free component and a $48,689.34 taxable component. The tax treatment of the recalculated lump sum will be as per normal lump sum benefits paid from a complying superannuation fund.
If a person chooses to take the PD benefit as an income stream, they are not entitled to the calculation of a larger tax-free portion. The income stream is taxed at the person’s marginal tax rate with a 15% tax offset available if the person is under the age of 60. If the person is aged 60 or over, then the disability income stream is tax-free.
Again, trustees of SMSFs must follow the rules in their SMSF’s trust deed as to whether benefits can be paid out under permanent disability grounds as well as the form of the benefit.
Death benefit
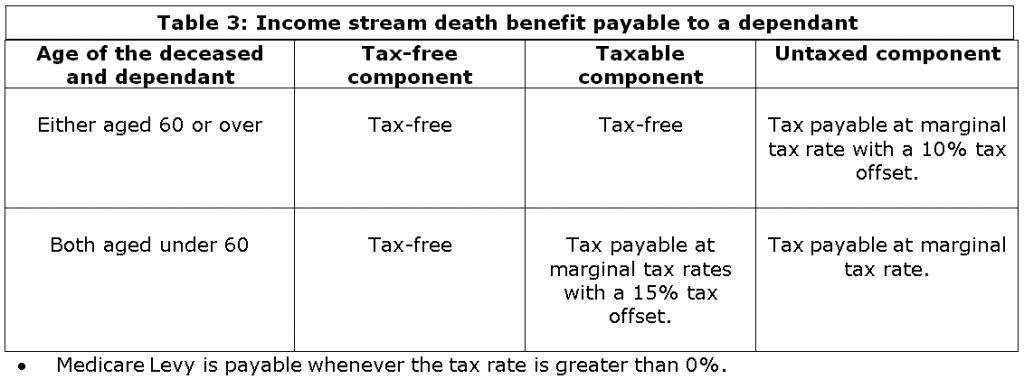
Death benefits are mainly paid as a lump sum, but can be paid as an income stream to a spouse, a child under 18 years of age, a financially dependent child aged 18 – 24 years, or a child with a disability. This means a child who is considered a dependant of a deceased member can receive a death benefit pension until the age of 24 or longer if the child suffers a disability.
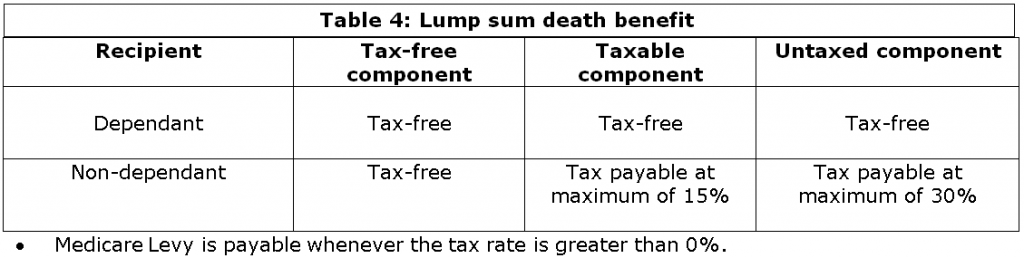
The tax treatment of a lump sum death benefit depends on whether the recipient is a dependant of the deceased member. A dependant is defined as:
- a spouse or former spouse of the deceased (including a spouse of the same sex)
- a child of the deceased under the age of 18
- a person financially dependent on the deceased at the time of death
- a person who had an interdependent relationship with the deceased just before death.
A lump sum death benefit paid to a dependant is tax-free. If it is paid to a non-dependant, then tax is payable at 0% on the tax-free component, a maximum of 15% on the taxable component already taxed within the fund, and a maximum of 30% on the untaxed component. The Medicare levy is payable whenever the tax rate is greater than 0%. Also if a death benefit is paid to dependants they may be able to take advantage of the anti-detriment provisions and receive a larger death benefit.
An anti-detriment payment is essentially a refund of the 15% contributions tax paid by an SMSF. It is an additional amount that may be paid to provide a death benefit of an amount that would have been payable if contributions tax was not deducted from the deceased member’s account.
The tax payable on a death benefit income stream depends on the age of the deceased, the age of the dependant and the component of the income stream. If either the deceased or the dependant is aged 60 or over, then no tax is payable on the tax-free component and the taxable component. The untaxed component is taxed at the dependant’s marginal tax rate with a 10% tax offset. If the deceased and the dependant are both under the age of 60, then the tax-free component remains tax free, the taxable component is taxed at marginal tax rate with a 15% tax offset and the untaxed component is taxed at the marginal tax rate. The Medicare levy is payable whenever the tax rate is greater than 0%.
Other considerations
There are other considerations which should be examined. For example:
- an anti-detriment payment is not payable if a benefit is accessed under a terminal medical condition or a PD condition, as it is only payable on death benefits
- it is important to consider whether your SMSF holds any life insurance for you prior to rolling money into another superannuation fund
- if you receive a lump sum terminal illness benefit, it may affect your entitlement to a disability support pension.
Superannuation savings are important whether you enjoy them in retirement or pass them on to your dependants when you die. Carefully considering how your savings will be passed on could be one of your greatest legacies.
Monica Rule worked for the Australian Taxation Office for 28 years, is a SMSF Specialist Advisor, and is the author of The Self Managed Super Handbook, recently released in its fourth edition. Monica is running SMSF Seminars in various states. For more details visit www.monicarule.com.au. This article is general in nature and readers should seek their own professional advice before making any financial decisions.