There is a well understood principle in investment known as the law of large numbers. Essentially, it says that the larger a company is, the harder it is to increase revenue growth rate, since most people already have the product or service. It’s why revenue growth for big banks and retailers like Coles is almost always below 10%. Of course, this is after having got large in the first place, which is another story (about economies of scale, about which we all know).
But back to the main point. In the past few years, something very unusual has been happening to some of the biggest companies in the world, like Google (Alphabet), Amazon, Microsoft, Tencent and Alibaba. The revenue growth for these companies isn’t tapering off, it is actually accelerating. Meaning that growth this year is higher than growth last year.
It’s known as ‘runaway returns to scale’. The formal definition of this is based around the concept that when output increases by more than the proportional change in inputs, there are increasing returns to scale.
Is this happening, and if so, how?
One thing that has definitely emerged in the past 20 years is the network effect. This states that arithmetical growth in users leads to geometric growth in value of the network, since each incremental user increases the number of transactions by more than just the one incremental user.
It’s true that one telephone and one person cannot transact with anyone. Even two people can only do one transaction (assuming for a moment, one transaction per connection). But ten people can do 45 transactions.
There is a formula for this: n(n - 1) ÷ 2. In this case, if n is the number of users, then:
10 x (10-1) ÷ 2 = 45 connections
This is the network effect in simple terms.
So it is that growth rates for some of the largest companies in the world, as measured by revenue, are increasing, in part because of the network effect, as shown below:
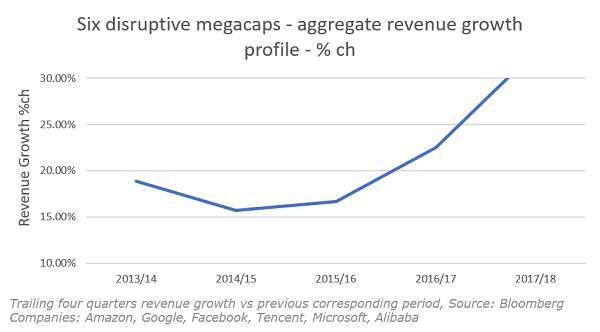
The chart above shows revenue growth in aggregate for six of the world’s largest companies: Amazon, Google, Facebook, Tencent, Microsoft, Alibaba. It shows revenue growth accelerating in the past few years, not slowing down as could be expected from the law of large numbers. So perhaps these are examples of runaway returns to scale? (There is some further explanation needed for Microsoft and Apple, which will we get to.)
The connection between these companies is their use of software to connect users arithmetically, in the process increasing transactions, and the value of their networks, geometrically. Alibaba and Tencent connect more people in China than any other network, so have the largest dollar value of transactions. Same with Amazon in the US. For clarity, we have broken out the revenue growth of the individual companies in question.
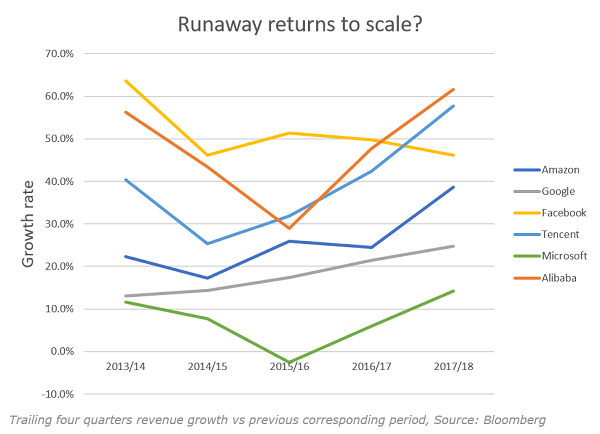
Microsoft works slightly differently, but is still showing big returns to scale. The company’s major products, enterprise software and Windows, are the largest corporate operating system in the world. The company is shifting from the provision of these products within individual companies to providing them as a service in its datacentres, effectively moving every on-premise data centre to Microsoft’s own datacentres, and providing the product (IT) as a service. We are not certain whether this is part of a network effect or simply a one-time business migration. The acquisition of LinkedIn a few years ago suggests that Microsoft is trying to turn itself into a network company. But in any case, it is showing runaway returns to scale as it moves whole industries to the datacentre.
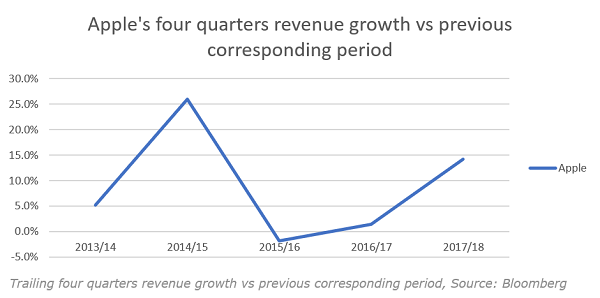
As a separate case, we should consider Apple. It hasn’t primarily been a network company. It sells phones, which are hardware, and are interoperable with all other brands of phones, and most all other networks, so while it is a beneficiary of the network effect, it is not driven by it. Its product set is expanding, in turn attempting to lock users to its ecosystem to ensure seamless operability, which is driving sales, though previous quarters’ growth don’t point to runaway returns. And its expansion into networked services like the app store, music, entertainment etc. can be classed as a network, (though it has been the company’s choice to pursue this more slowly because of privacy issues) but it is much smaller though faster-growing than the hardware business.
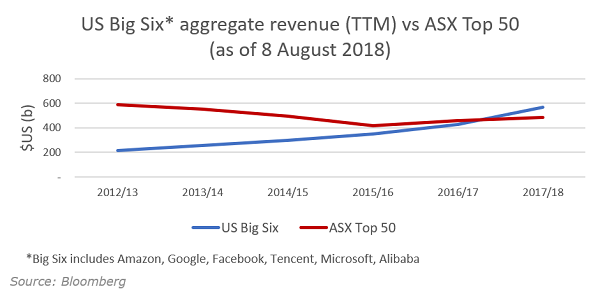
Just how big are the big six? They are now bigger in revenue than the ASX top 50, once the currency conversion is considered. And growing faster.
Does size bring problems?
What happens when companies become so large that they create problems for lesser competitors? Eventually, they get broken up, like AT&T or Standard Oil, into a group of smaller businesses. And of course, as Thomas Piketty noted in his excellent book Capital in the Twenty-First Century, every so often a major global calamity comes along, like say a World War or even two), at which point everything is blown up, quite literally, and everyone starts again from a more or less zero base.
The first is preferable to the second. And it should be noted, in the case of the Standard Oil break-up, the sum of the parts wound up being much greater than the whole.
Alex Pollak is Chief Executive, CIO and Founder of, and Anshu Sharma is Portfolio Manager at, Loftus Peak. This article is general information and does not consider the circumstances of any individual.