There is no such thing as a perfect stock, but there are stocks that are priced to perfection. Some examples in Australia include REA Group (REA), Domino’s Pizza (DMP), Aconex (ACX), Bellamy’s (BAL), and Cochlear (COH).
All of these companies are trading on earnings valuations between 150% and 300% above the market average. And, give or take, all these companies continue to trade higher day after day.
For many investors, this can elicit emotional responses ranging from envy to despair. So as a professional investor, how do we treat already high-priced stocks that just keep on rising in value?
As with everything in investing, we cannot determine the right course of action until we understand the cause of the action. In other words, we need to understand what is driving the share price in each instance. For purposes of illustration and simplicity, I have broken these causes down into three categories: The Good, The Ok and The Ugly.
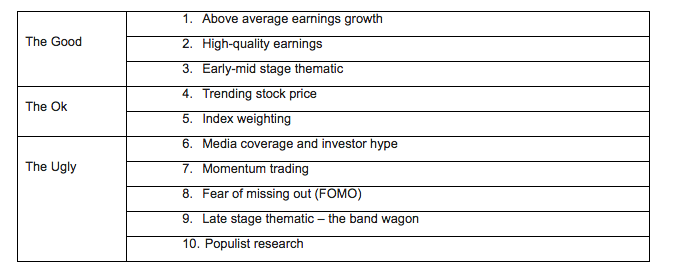
The Good
1. Above-average earnings growth
The best reason for a highly-priced stock’s continued rise is a very high level of underlying earnings growth. In this instance, a stock that is over-priced has earnings that are growing at a rate that will make the current price look ‘cheap’ at some point in the not-too-distant future.
The price to earnings growth ratio (PEG) has been steadily growing in prominence as a way of better-reflecting and analysing future growth. It is calculated by dividing the price to earnings ratio (PER) by earnings per share (EPS) growth. For example, in the case of Cochlear, the 2016 financial year consensus PER is 36.5 times – well above the market average of 15.1 times. However, the PEG ratio (36.5/EPS growth of 30.2%) equals 1.2 times, reflecting the fact that EPS is growing at a rate well above the market.
It is possible to generate above-average earnings growth in the short term without a sustainable competitive advantage. However, to generate long-term EPS growth the company must have a sustainable competitive advantage – some ‘moat’ or barrier to entry. This, of course, is the Holy Grail of investing.
2. High-quality earnings
A company may also trade on a high valuation where its earnings are considered ‘high quality’. There are many views as to what defines high quality, however, it should contain some or all of these attributes:
- Consistency and certainty of earnings (~transparency)
- A high percentage of recurring revenue
- Operate in a structurally sound sector with the right pricing power (suppliers vs clients), industry concentration and rational competitors
- Client concentration (a large number of small clients vs a small number of large clients)
- Profit drivers inside management control
- High gross and net margins.
3. Early-mid stage thematic
High-priced stocks may also rise where there is some significant macro thematic. For example, China-facing consumer brands are benefitting from the emergence of the Chinese middle class. Ultimately, the prices are moving higher because of the anticipated change in earnings (ie point 1), but often it is the sentiment around the macro theme itself that is driving the price ahead of the curve.
Identifying the theme early can be hugely advantageous, but, as we shall see below, if you are late to the party you’d better dance close to the exit.
The OK
4. Trending stock price
There is a body of evidence that shows that if a stock price is in a defined trend (up or down), it is significantly more likely to continue in that trend than to reverse. Some believe this likelihood is as high as 80%. Therefore, buying an up-trending stock is an ‘ok’ reason in itself. However, investors often lack conviction, and volatility – known in trading circles as ‘whipsaws’ – can scare investors out of a position.
5. Index weighting
A large number of fund managers anchor their portfolios around a stock’s index weighting. As a company’s share price increases, so too does its market capitalisation and hence index weighting. This may cause fund managers to purchase more stock if they are underweight. This added demand drives the price higher, further increasing its index weighting and hence driving further demand. This may be particularly noticeable when a company’s size increases to the point where it moves into a larger index (eg from the S&P ASX300 into the S&P ASX100). Index buying can be a powerful force driving high share prices even higher. But remember, this can also work in reverse.
The Ugly
6. Media coverage and investment hype
Often, share price movements are driven by the amount of airtime or publicity the company attracts. Strong media exposure, parochial management, investor and analyst hype can all drive share prices higher in the short term. However, these influences are often symptomatic of being late to the party.
The key as always is to look behind the headlines and focus on the fundamentals – ie what tangible impact is there to the underlying earnings growth?
7. Momentum trading
This is where someone buys a stock simply because they believe someone will buy it at a higher price. There is no reference, understanding, or for that matter interest in any fundamental driver. The stock quite often may not even be in a properly defined up-trend. The buyer simply believes they can sell the shares at a higher price.
This is the realm of ‘hot money’, and history has proven time and time again that those who try to make money quickly are destined to lose it.
8. Fear of missing out (FOMO)
Our desire not to miss out can drive our investment decisions, to the disregard of other considerations. Sometimes we resist FOMO all the way up, only to finally capitulate and buy at the peak.
Early in my career, I worked with an old broker who would continually ask: ‘Who is the marginal buyer; who is left to buy?.’ There is much wisdom in that question. In short, a stock price needs new buyers to drive the price higher. If everyone is already ‘set’, then there’s often nobody left to buy.
9. Late stage thematic – the band wagon
Boarding a macro theme early can be lucrative, but most investors don’t recognise a bandwagon until the band is about to stop playing. And as we highlighted above, the exit door in a dance hall is small. Being late to the party can hurt in the ensuing stampede.
10. Populist research
‘Success has a thousand fathers and failure is an orphan.’ For the majority of analysts and fund managers alike, being associated with a failing investment is professional suicide. However, being linked to the best performers is a wonderful way to disguise failures. Even if the reality is that the group was ‘late to the party’, there is the possibility of creating a different perception. This type of behaviour is hard to analyse, and when the sentiment changes it becomes self-perpetuating on the downside.
Summary
The key is to determine what is really driving the share price and your compulsion to buy. If your buying decisions are being driven by a lack of emotional quotient rather than earnings growth, the best thing you can do is turn off the screen and dust off your copy of Warren Buffet’s The Snowball.
Romano Sala Tenna is Portfolio Manager at Katana Asset Management. This article is general information and does not consider the circumstances of any individual.