Every day the prices of individual company shares rise and fall and so does the overall market index. Sometimes the broad market index falls because of a sell-off in a particularly large stock, as happened recently when Apple fell 4% on the 22 July 2015 after its profit report. As Apple is the largest listed stock in the world, the 4% Apple sell-off dragged down the market index due its large weighting in the index. But most market-wide sell-offs are caused by factors affecting general market confidence, like the Greek debt crises, which are unrelated to particular companies.
Long term investors look forward to market-wide falls because good companies are sold off along with the rest. It gives us a chance to buy into companies we have been wanting to buy but have been too expensive. Every market including Australia has a few fine companies but most of them are simply too expensive most of the time, so we need to wait until the share price drops in general sell-offs.
Fortunately for long term investors, sell-offs of 10% or more occur quite often, about once every couple of years. We have had 38 market dips of 10% or more in Australia in the past 70 years since shares came off war-time price controls at the end of 1946 (Editor's note: make that 39 after this week took the fall since April 2015 over 10%).
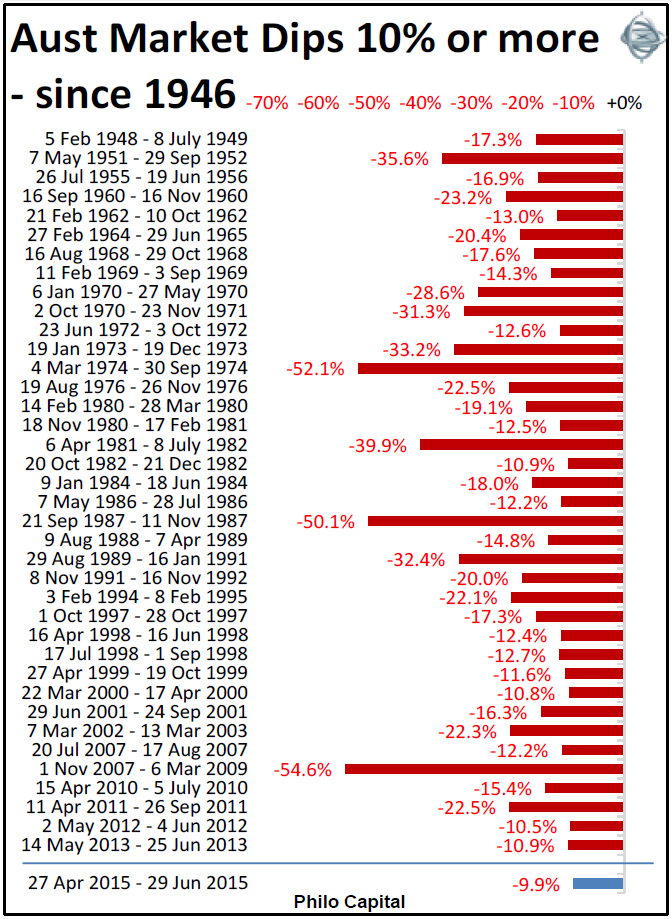
In recent years the overall market has fallen -55% in 2008-9 (sub-prime), then -22.5% in 2011 (Greece 1), -10.5% in 2012 (Greece 2), and then -10.9% in 2013 (US QE taper scare), but markets have been ultra-calm since then.
We had a nice 9% dip from 27 April to 29 June 2015 but it didn’t quite hit -10% because the market rebounded. Investing requires patience and it seems we will have to wait a little longer for the next buying opportunity.
A brief look at the markets:
Australia
The local economy is still limping along as RBA governor Glenn Stevens warns the market to expect slower long term growth rates ahead. The corporate earnings season has kicked off and with some exceptions, the outlook is for very modest growth. The aggregate will be dragged down by mining company earnings which are expected to fall by around 20-30% due to the collapses in commodities prices and excess production. Iron ore prices fell heavily early in the month and ended down another 7% in July, down 23% year to date. Households and business were also warned of dramatic prices rises ahead for gas because cheap gas is being exported so foreigners reap the benefits of our LNG ‘boom’. It is the opposite of the US, where government policy is for Americans to benefit from the energy revolution, and the debate is whether foreigners should be allowed to benefit at all.
Europe
July was a drama-filled month in the long-running Greek debt saga. As expected the government failed to repay the ‘bundled’ debts due at the end of June, then on 13 July the Greek government finally gave in and accepted an austerity and reform package to release another €86 billion in bailout funds. Even if tax rates are raised and pensions and other government spending items are cut, it is still unlikely that enough additional net revenue will be raised to repay the debt on schedule. The reason is that the austerity measures will most likely slow economic activity and tax revenues even further. As the debts pile up they are increasingly appearing impossible to repay, but Germany and the IMF look like resisting another bailout. Global stock markets fell in the lead-up to the Greek deal and rebounded strongly when the deal was done. The next critical milestone is 20 August, which is only a week away.
United States
The US economy is ticking along steadily, driven by relatively strong consumer spending and confidence, boosted in turn by falling fuel prices, rising house prices and share prices, and now rising wages. The Fed appears to be on track to start raising interest rates later this year but it is going out of its way to assure investors that the rises will be slow and well signalled to the market.
In the race for the Republican nomination for the presidential election next year, unlikely candidate Donald Trump had taken the lead. His strategy is simple but thus far effective – blaming Mexicans for just about everything wrong with America and the world. This is gaining traction particularly amongst working class whites. The African American share of the US population has remained relatively constant in recent decades at around 14% but the steadily rising Hispanic share will soon make whites ‘a minority in their own country’, and Trump’s rhetoric is designed to tap into that base racial fear.
Asia
In China the main story continues to be the unwinding of the latest stock market bubble. Last year a range of government policy initiatives encouraged investors to switch to shares to give them something to gamble on while property prices were falling. As a result, share prices shot up astronomically and even the broad market indexes more than doubled in an almighty policy-induced, margin lending fuelled bubble. We wrote about this and its inevitable collapse in our April report this year. Speculators had little understanding of the companies whose shares they were buying. Miraculously the economic growth numbers for China came in at exactly 7%, spot on the government’s stated goal, although few have any faith in the official government numbers.
Ashley Owen is Joint CEO of Philo Capital Advisers and a director and adviser to the Third Link Growth Fund. This article is educational only. It is not personal financial advice and does not consider the circumstances of any individual.