Australians are experiencing a major societal transformation as the baby boomers, around 5.5 million people born between 1946 and 1964, are reaching retirement. While they are living longer than ever, it presents a conundrum – many of this cohort simply don’t have sufficient superannuation to fund a comfortable retirement for their projected lifespan.
Australians are living longer
The life expectancy of Australians in retirement has almost doubled in the last 150 years due to better lifestyles and medical breakthroughs. Since the introduction of compulsory superannuation in 1992, Australians at retirement have gained an extra decade of longevity.
Figure 1 shows the range of expected increases in longevity after retirement for Australian men and women based on current assumptions. It is estimated that retirees aged 65 now will live on average until 84 for men and 87 for women.
Figure 1: Historic and future life expectancy for Australian men and women aged 65
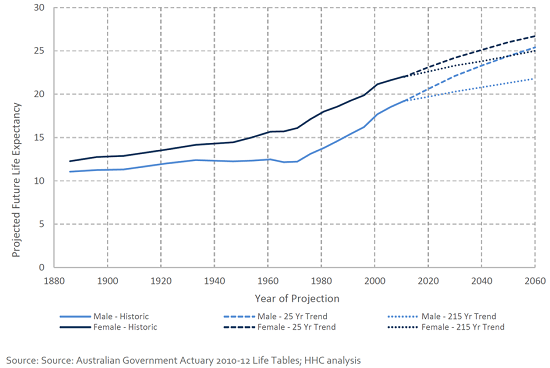
The blessing of longevity is a new and extended phase of life which will endure well past 90 years-of-age for many people. The downside is that individuals should plan for 25-30 years of retirement.
Retirees are not always prepared
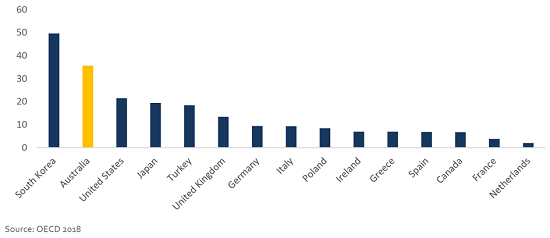
According to the Credit Suisse Research Institute Global Wealth Report 2018, Australians have the highest median wealth per adult. Despite this, retired Australians experience high levels of relative poverty, as shown in Figure 2. When compulsory superannuation was introduced in 1992, many baby boomers were more than halfway through their working life, and they missed out on the benefits of compounding returns over time. As a result, the median household superannuation balance for retiring Australians currently sits around $200,000, estimated to support a ‘comfortable’ retirement income for just 10-15 years.
Figure 2: Percentage of those aged 65+ living in poverty
Most baby boomers were busy paying off their mortgages, with approximately 80% of retirees owning their own home. For most home-owning Australians, the majority of their wealth is tied up in their home equity. In total, there is over $900 billion in untapped home equity owned by Australian retirees, according to the Productivity Commission.
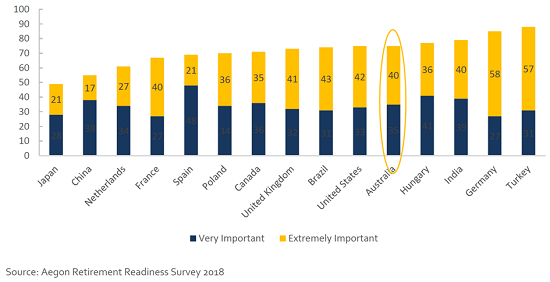
Long, healthy lives enable Australians to spend a greater part of their retirement living independently. Most retirees prefer to stay in their own home as they age, as illustrated by Figure 3, and this untapped savings pool is a valuable resource that could be utilised to provide improved retirement funding.
Figure 3: Importance of remaining at home in retirement
How can investors access home equity?
There are four main approaches used by retirees to access home equity, as shown in Figure 4. Each of these approaches has downsides in terms of cost of access, security of tenure in the home or the ability to fund a long-term retirement income.
Figure 4: Approaches to access home equity
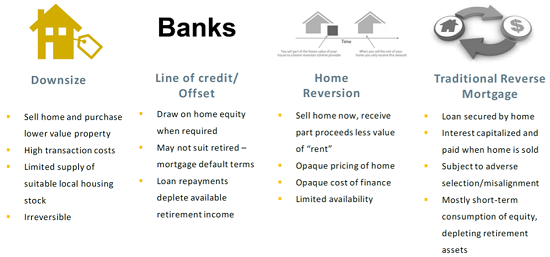
Source: Household Capital
The reverse mortgage experience
A. Overseas
Canada and the United Kingdom have a similar demographic composition to Australia with an ageing workforce and a large baby boomer cohort entering retirement. Residential property values have skyrocketed in these markets and many individuals approaching retirement are asset rich, cash poor, with home equity significantly outweighing the value of retirement savings.
There has been significant growth in reverse mortgages used to fund long-term retirement income streams in these markets, with both Canada and UK experiencing 30% growth, year on year since 2013.
B. Australia
Traditional bank reverse mortgages were generally unaligned with the long-term housing and funding needs of Australian retirees, and therefore failed to provide genuine retirement funding adequacy and certainty. These products failed to meet the widespread needs of Australian retirees, including:
- Adverse selection – seen as a form of ‘last resort’ financing for many older Australians, historical access of home equity was often for inappropriate purposes for potentially distressed borrowers. These circumstances provide a recipe for dissatisfaction for the product and the provider.
- Misaligned distribution – while financial advice was often recommended, access to home equity in Australia was never directly linked to long-term retirement planning or financial advice. It left many borrowers cash poor and asset depleted throughout the remainder of their lives.
- Short-term consumption of equity – according to a recent ASIC review of reverse mortgage lending, the application process historically focused primarily on the borrower’s short-term objectives, with limited attention paid to future needs.
- Lack of intergenerational transfers – traditional reverse mortgages failed to provide a structured mechanism to satisfy the long-term retirement income needs of a borrower and enable the responsible transfer of home equity to subsequent generations at a time they incur major lifetime expenses.
By the end of 2018, CBA, Westpac and Macquarie, the three big-bank providers of traditional reverse mortgages, had all withdrawn from the Australian market. Reasons for the withdrawal include: the Royal Commission, proposed APRA capital risk weighting changes, an inability to scale the traditional reverse mortgage product, and perceived reputational risks. Since the withdrawal of the major banks, Australian retirees have been left without widespread access to their home equity as a means to fund retirement.
The future of home equity
The next generation of home equity lending must identify a range of responsible retirement funding needs, and overcome the shortcomings of traditional reverse mortgages. Two guiding principles should govern this approach.
First, long-term retirement funding needs are responsibly met by the transfer of illiquid home equity into appreciating, diversified assets in a more liquid form. The improved accessibility can meet those funding needs over time.
Second, funding availability is constrained to prevent spending for short-term consumption or deployment into depreciating assets.
By restructuring responsible access to home equity, retirees can receive multiple benefits:
- Access to savings – where the majority of lifetime savings are in the home.
- More reliable retirement income – for some retirees, income is volatile relative to the performance of superannuation and home equity can smooth income and capital supply.
- Asset diversification – as superannuation is depleted, retirees’ assets become increasingly concentrated in a single residential property, and a transfer to superannuation can diversify assets.
- Long-term financial advice – higher super balances during retirement create benefits that come from holistic management of household savings.
- Sequencing risk management – responsible, long-term access to home equity adds a second, independent, largely uncorrelated source of income should super assets decline periodically, especially where age pensions are inadequate.
- Imputed rent annuity – non-recourse borrowing provides certainty of occupancy of the home, increasing the annuity value of long-term imputed rent and enhancing real retirement incomes.
Traditionally, Australia’s retirement income policy has been framed as having three pillars: superannuation, non-superannuation savings and the age pension. It is time to include the fourth, and largest, pillar of retirement funding: home equity. By drawing on multiple sources of income, Australian retirees can achieve funding adequacy throughout the full course of 25-plus years of retirement. To do this, however, retirees must be able to responsibly and cost-effectively access home equity savings to generate retirement income.
Joshua Funder is Chief Executive Officer of Household Capital. This article is general information and does not consider the circumstances of any investor.