The longevity of its citizens is one indicator of the prosperity of a society. Australia is well up there – the most recent published Australian life tables (released in December 2014) show that a 65 year old man today is expected (on average) to live to 84.2 years and a female to 87.0 years. This means we will have more retirees living for longer. But in terms of their financial health, the key question is: Will their savings run out before they do?
Life expectancy continues to increase
There’s no doubt that Australian retirees will need to combine lower spending strategies and the right investment options to improve the chance that their income will last for an increasingly likely period of 25 years or more in retirement. Mortality rates for the over 65s have been improving steadily since the early 1970s and retirees are now expected to live 3 to 3.5 years longer. Using these improved life tables, there is more than a 70% chance that at least one of a retired couple will be alive at the age of 90.
Using Towers Watson’s Retirement Planner, we modelled a number of scenarios for a couple, both aged 65, retiring today with superannuation assets of $500,000. A couple was chosen based on 2007 Census data that showed more than 70% of Australians enter retirement as part of a couple. When considering how you invest for financial success in retirement, there are several factors that come into play, including how much superannuation a saver has available at the start of retirement, their spending plans, the amount of any other savings they have, as well as their risk tolerance and preferences. An individual’s spending strategy however, is one of the biggest factors that will determine whether or not they will achieve financial success.
The Retirement Planner showed the impact of different investment strategies for the couple who want to make their savings last 25 years to age 90, varying their exposure to growth assets from 0% (cash) to 30% (conservative) to 50% (moderate) to 70% (balanced) to 85% (growth) to 100% (high growth).
Investing in a balanced portfolio, the couple is expected to be able to spend $57,705 a year (including Age Pension amounts available after applying means tests) up to age 90. After that, they would be expected to rely solely on the Age Pension. It is important to recognise that this is only the expected outcome. There is only a 48% chance that their superannuation will last until age 90. But if we looked at this from the spending perspective, we can see a different impact.
If the couple adopts a lower spending strategy (say, $50,000 or $52,000 a year), there is a much higher likelihood of success (more than 80%) for both the conservative and balanced options. Alternatively, if the couple spends at higher levels (such as $54,000 to $58,000 a year) then the investment option chosen has a more significant impact on the outcome. For example, under a balanced investment option, spending $54,000 a year has a 67% likelihood of success, compared to 56% under a conservative investment option.
Impact of spending strategy and investment option on likelihood of super lasting to age 90
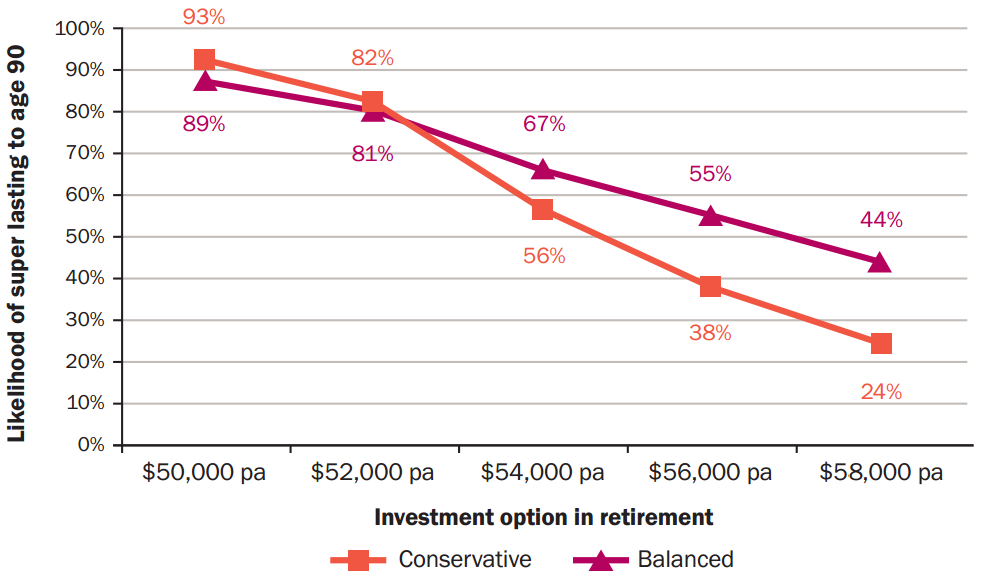
Source: Towers Watson analysis 2014
When combined with a lower spending strategy, there is little difference in the likelihood of savings lasting to age 90 for a conservative versus a balanced investment portfolio. But the residual balance left over at age 90 is likely to be much higher for a balanced investment portfolio. For the sample couple, staying invested in growth assets produces a better outcome than de-risking, either gradually via a lifecycle or target date fund or more suddenly.
$50,000 pa spending strategy – residual balance and likelihood of super lasting to age 90
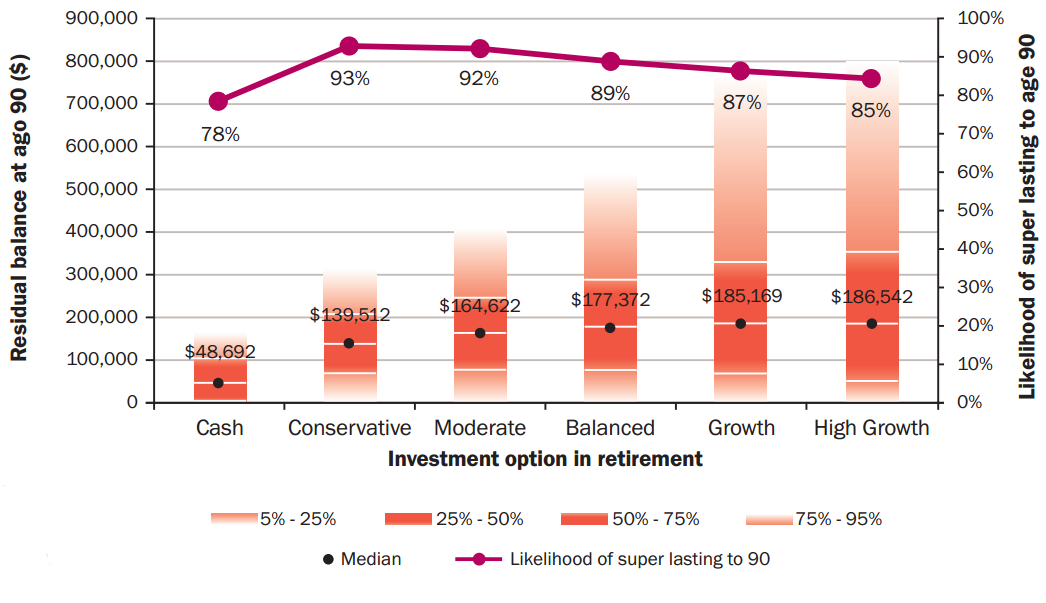
Source: Towers Watson analysis 2014
Retirees likely to have variable spending patterns
A number of academic research papers suggest that a retiree’s spending is likely to start reducing by around age 80. This is supported by recent ASFA research which produced a revised Retirement Standard for a 90 year old (the original ASFA Retirement Standard is based on a 70 year old), which shows that the ‘comfortable’ level of expenditures for a 90 year old is about 10% lower than for retirees aged 65-80.
This provides a good opportunity for a retiree in their 70s to purchase some form of guaranteed annuity or other longevity risk pooling vehicle. An adaptive spending strategy, where people adjust their spending based on recent performance, is also likely to further improve the likelihood of financial success in retirement.
When designing default retirement income solutions, superannuation funds first need to understand the demographics and expectations of the members they are targeting. The funds also need to help their members to understand more about their own expected retirement outcomes and the risks they face, by providing tools such as written retirement income estimates and online calculators. Only then will funds be able to guide their members more effectively into retirement income solutions that better suit their needs.
Andrew Boal is Managing Director for Towers Watson in Australia. This article is general information and readers should seek their own professional advice. A full copy of the paper: The path to retirement success: How important are your investment and spending strategies? can be found here.