“Do the right thing. It will gratify some people and astonish the rest.” Mark Twain
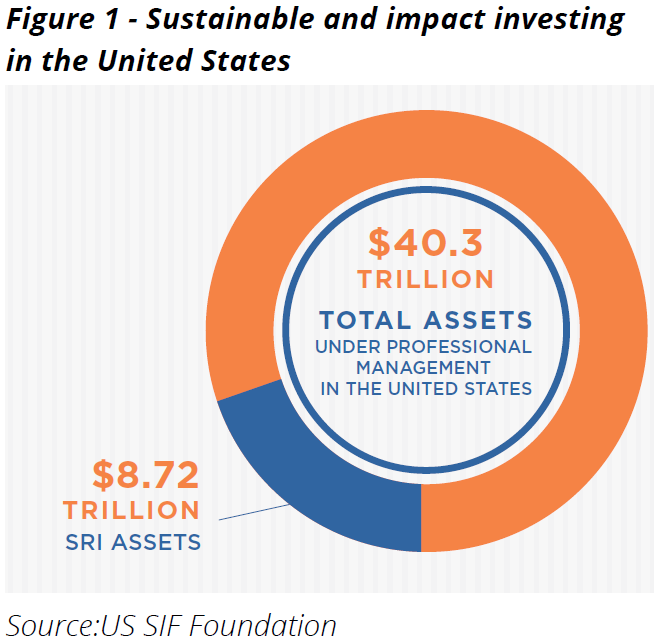
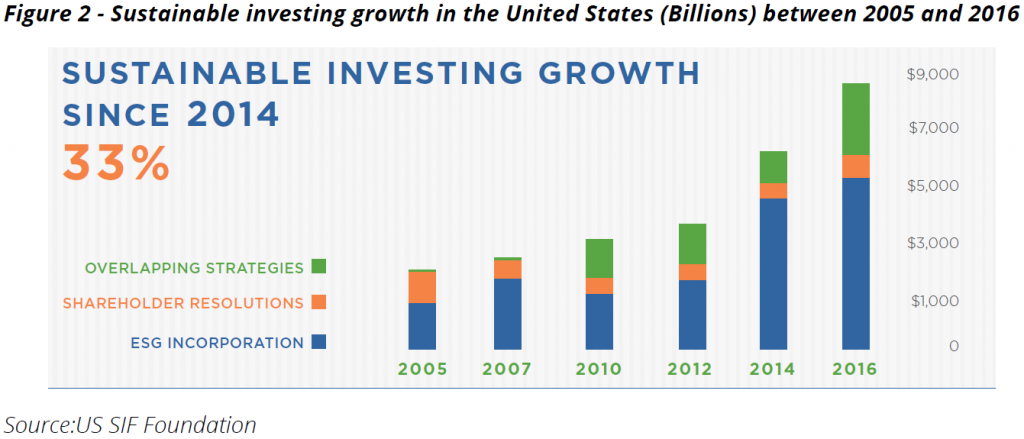
In the past few years, there has been a significant increase in the interest in environmental, social and governance (ESG) investing. According to a paper released recently, more than $8 trillion of the $40 trillion of money managed in the USA is now under some form of Sustainable and Responsible Investing (SRI) or ESG, up 33% since 2014 and up fivefold from $1.4 trillion in 2012 for money run by fund managers.
Australian fund managers caught unready for this change
If we look at the Mercer survey data for January 2017, the Global Equities strategy section contains 127 global funds sold in Australia. Of this, only five are classed as SRI funds. It is somewhat better for Australian equities with 157 funds in the survey, of which 13 are SRI. If we were to use the ratio of assets in the USA, the number of SRI funds should be 27 and 34 respectively.
One reason could be the view among many people, particularly fund managers, that ‘you can’t have your cake and eat it, too’, that SRI means lower returns for investors.
This misconception of accepting lower returns for being ethical goes against another tenet of conventional investing wisdom: buy good businesses. In his letters to Berkshire Hathaway shareholders, Warren Buffett often discusses the importance of ethics and the quality of the character of the people running the businesses he owns.
Implicitly he is saying that businesses which have an ethos and focus on ‘doing the right thing’ by staff and customers should generate higher returns. Admittedly, he is discussing the character of the people rather than the nature of the business, and some people would find owning Coca-Cola shares unethical. It’s this differentiation between good people and bad unethical businesses that opens an interesting next line of inquiry.
What do the statistics say?
UBS recently published an excellent summary of academic literature which concluded that SRI did not negatively affect investor returns.
Verheyden, Eccles & Feiner (2016) wanted to look at whether a portfolio manager would be at a disadvantage in terms of performance, risk, and diversification if he/she were to start from a screen based on ESG criteria. The empirical evidence shows that all ESG-screened portfolios have performed similarly to their respective underlying benchmarks, if not slightly outperforming them. Put differently, the findings of the paper show that, at the very least, there is no performance penalty from screening out low ESG-scoring firms in each industry.
This is consistent with our own experience as portfolio managers at Hunter Hall, where we outperformed against an all-inclusive benchmark, despite having a restricted ownership list.
Nagy, Kassam & Lee (2016) wanted to see not only if highly-rated ESG companies outperform, but if businesses are rewarded for improving, going from okay to good? The answer was unequivocally yes. Both outperformed, but the improvers outperformed at double the rate.
The most interesting article by Statman and Glushkov (2016) created what they called 'Top Minus Bottom' (TMB) where stocks were ranked on their ESG criteria and then modelled how being long the ‘better-ranked’ versus the ‘worse-ranked’ performed. This concept is similar to the studies above and could be called the ‘good screen’.
The innovation was to look at ‘Accepted Minus Shunned’ (AMS) separately. Here the authors looked at the returns from stocks commonly accepted in SRI funds versus those that are typically avoided. Shunned companies are those with operations in the tobacco, alcohol, gambling, military, firearms and nuclear industries. Call this the “negative screen”.
Like the earlier studies, it was found TMB outperformed the broader market but interestingly the AMS (the bad screen) stocks didn’t outperform, that is, the excluded stocks did better than the broader market. But AMS under-performed by less than the TMB screen outperformed. That is, it was a net positive for investors. I think it is this AMS effect that fund managers have focused on in their view that SRI/ESG does not work.
What does this mean for fund managers?
Investors globally are demanding more focus from their fund managers on ESG issues. The implications of these studies are that ESG does not detract from returns and investors are therefore not irrational to ask for more focus on ESG and SRI issues by their money managers.
But it also says running a positive screen in combination with running a negative screen is a better way to generate returns for investors while also satisfying investor’s ethical investment needs.
Chad Slater, CFA, is Joint CIO of Morphic Asset Management. This article is general information that does not consider the circumstances of any individual.