Amid the growing popularity of ASX-listed real estate investment trusts (A-REITs) as a way for investors to obtain exposure to real estate, there is a debate over whether investors should use an actively managed A-REIT securities fund, a passively managed index unlisted fund or an exchange traded fund (ETF).
What is active versus passive management?
Active management focuses on identifying securities that the market may have mispriced through analytical research and judgement to minimise exposure to riskier or overvalued securities. A passive index manager owns all the securities in the S&P/ASX 300 A-REIT Index even those A-REITs which may have poor management, lower quality assets or high gearing, or are overvalued on a relative basis.
The A-REIT sector
In the last five years, the A-REIT sector has recorded strong performance relative to the broader equities market (Figure 1), due largely to the low interest rate environment which has diverted capital from cash and bonds to higher yielding assets such as real estate. Not surprisingly, with the S&P/ASX 300 A-REIT Index generating such a strong return, the spotlight has turned back to active managers of A-REIT securities funds to justify their relevance.
Figure 1: Performance of A-REITs vs Australian Equities: 31 October 2014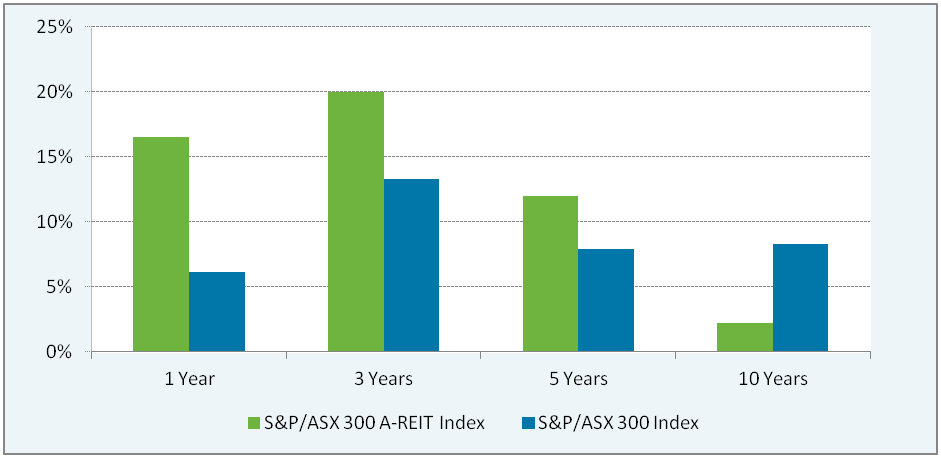
How can active managers add value?
An active A-REIT securities manager has a number of opportunities to add value to a portfolio, including:
- tactical allocation to real estate subsectors
- analysis and research on individual A-REITs
- building a more diversified portfolio based on value, and
- participating in securitisation opportunities.
1. Tactical allocation to real estate subsectors
Real estate is not a homogenous asset class in which real estate subsectors (office, retail, industrial, residential, social infrastructure) or individual securities generally move together. Each real estate subsector has its own supply and demand drivers, which can alter the duration and direction of its cycle, often resulting in significantly different returns (see Figure 2).
A specialist A-REIT manager who understands the relationships between economic drivers and the real estate cycle may acquire A-REITs in subsectors they believe are more attractively priced in the current market and conversely avoid or underweight subsectors that they believe are expensive or are likely to underperform. A passive manager must own A-REITs in every subsectors within the index.
Figure 2: A-REIT Subsector Performance to 31 October 2014 (Source: UBS)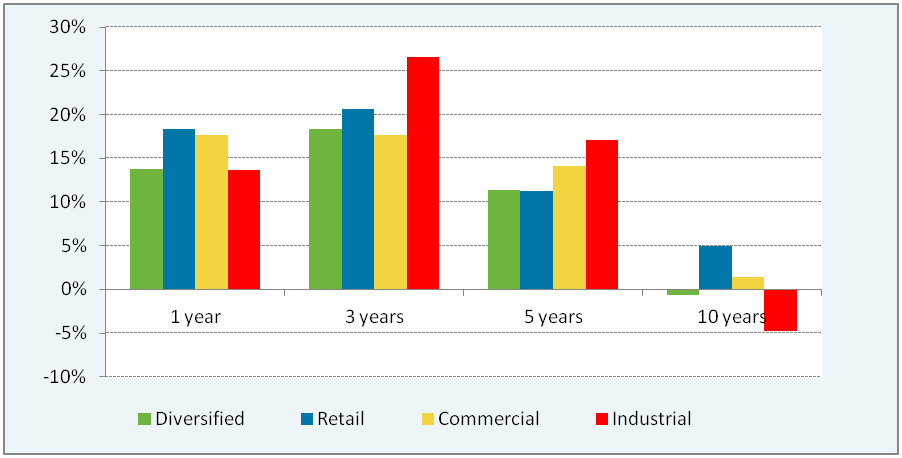
2. In-depth analysis and research of individual A-REITs
A specialist active management team has the ability to uncover relative value between A-REIT securities. Smaller cap A-REIT securities have the greatest potential to be mispriced by the market due to lower liquidity and less broker research coverage than the large cap A-REITs.
Within the A-REIT sector, there has also been a wide variation in the performance of individual securities, up to 196% in one month (Figure 3). The variation can be driven by the quality of management, specific issues relating to the underlying assets, the ability of management to grow earnings through accretive acquisitions or development and capital management strategies such as gearing levels, debt profiles and security buy-backs.
The growing presence of general equity and hedge funds in the A-REIT sector also creates short-term mispricing opportunities at the individual security level. For many of these investors, their rationale for investing in a security maybe very different to that of a A-REIT securities manager, often driven by their short-term investment horizon or an arbitrage trade around corporate activity. The recent Australand takeover by Frasers Centrepoint saw large inflows from hedge funds seeking to capture the spread between the price at the time of the announcement and the eventual price paid by the acquirer.
Figure 3: Highest and Lowest Monthly Total Returns from A-REITs – 2009 to 2014 (Source: UBS)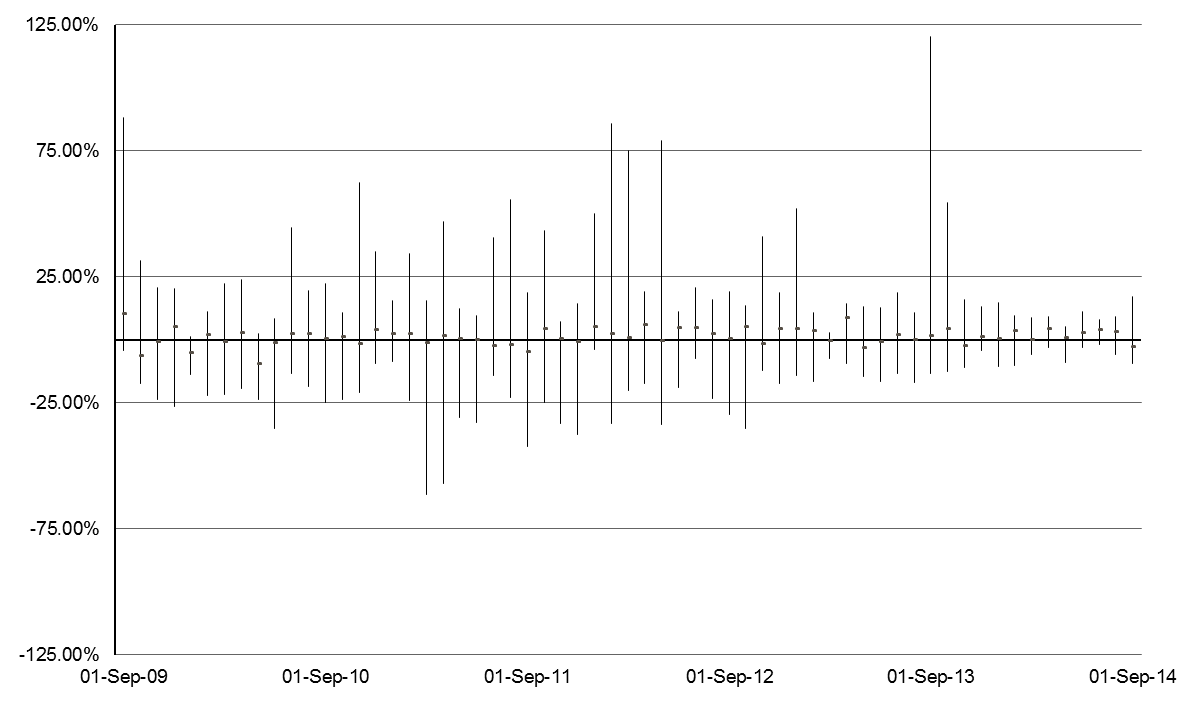
3. Building a more diversified portfolio based on value
Most indices, including the S&P/ASX 300 A-REIT Index, are weighted based on market capitalisation resulting in a high concentration of larger companies within the Index. The top eight A-REIT securities account for approximately 82% of the index and the retail sector focused A-REITs account for nearly 50% of the Index.
Passive investment strategies face significant concentration risk and therefore are taking on more security specific risk. Diversification is one of the basic strategies for reducing risk. An active manager can mitigate the concentration risk by taking more meaningful positions away from the top eight securities by investing in smaller caps or A-REITs not included in the Index.
4. Participation in new issue opportunities
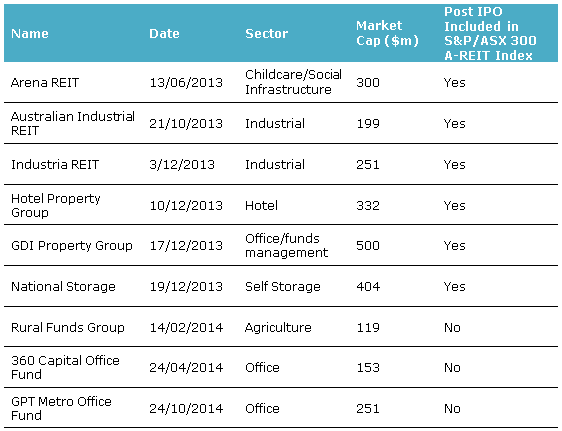
Advocates for passive management often argue that the corporate activity in the A-REIT sector results in a smaller number of securities for active managers to choose from. The number of A-REITs in the index has declined from 62 in June 2006 to 47 now. However, the recent increase in initial public offerings (IPOs) has added breadth to the A-REIT sector (Table 1). This in turn creates more opportunities for active managers.
Whilst the number of new A-REITs has been welcomed by active managers, it is the widening of the subsector offerings (other than the traditional retail, office and industrial) that provides the greatest opportunities through portfolio tilts to the various subsectors. Self-storage, health and agriculture are just three of the new sectors, albeit they are still small.
Table 1 - IPO activity 2013/2014
Active managers also have the opportunity to participate in the recapitalisation of an A-REIT through placement and rights issues. Whilst an index manager is forced to participate to maintain their relative exposure to A-REIT, an active manager has the opportunity to assess the merits of the transaction and act accordingly.
Conclusion
Active management of A-REITs securities has a role to play in either listed or unlisted funds, notwithstanding the higher fees charged by active funds. In choosing a manager, the skill and track record of an active A-REIT securities manager is paramount, and also their level of funds under management. Ultimately, their long-term success depends on how well the manager understands the dynamics of the listed real estate securities market, the interaction with the broader capital markets and real estate sector and whether the manager has a disciplined, risk-adjusted investment approach.
Adrian Harrington is Head of Funds Management at Folkestone Limited.