When we write our pieces, we have a reasonable idea of how popular they will be. The list of the most popular articles on Morningstar.com.au is predictably filled with pieces on shares. Given our audience, this makes a lot of sense.
We have self-directed investors that are largely invested in equities – and are hobbyists. We are an equity research house, and our readers enjoy the ‘art’ of investing. We enjoy providing in-depth analysis on companies. They enjoy picking the winners and investing towards their financial goals.
Most of these investors are looking to make well-informed and thoughtful decisions about investments that will impact whether their achieve their financial goals -whether that be a comfortable retirement, paying for education, purchasing a home, or travel. Investment selection is important.
I’m not here to try and change the perspectives of that camp. I’m here to provide the perspective that successful investing does not mean constantly searching for new investment opportunities.
The foundation of that widely held belief is that at any particular moment there are investments that are good and will outperform in the immediate future, and ones that are bad that will underperform. This view is reinforced and encouraged by professional investors who are selling investments and their ability to navigate markets to find opportunities.
I’ve come to an approach that flips this conventional wisdom around.
Selecting individual investments for my portfolio is not my primary concern and is the final step in my process. Other concerns, like having a well-defined budget and clear investing goals, come first and lay the foundations for everything else. Hence why they are shown at the bottom of this diagram showing my approach:
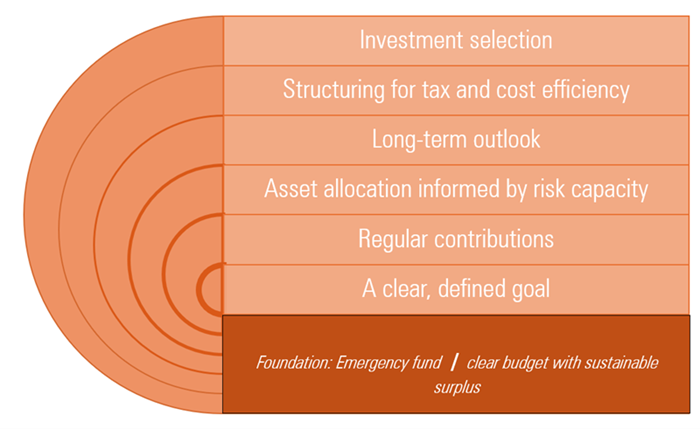
I arrived at this approach for technical and circumstantial reasons.
Let’s start with the technical. In 1986, Brinson, Hood, and Beebower’s seminal paper ‘Determinants of Portfolio Performance’ attributed 93.6% of investment performance to asset allocation. The paper focused not on the return level, but on the variation of returns. A 1991 update to the paper concludes that active decisions on investment selection by pension plans (which were used as a basis for the study) made little improvement to performance over a 10-year period. The paper championed a focus on strategic asset allocation over the long-term to increase the chances of reaching successful outcomes.
There were several adaptations of this research by other academics, including Ibbotson and Kaplan’s report in 2000 – ‘Does Asset Allocation Explain 40, 90 or 100 Percent of Performance?’. Ibbotson and Kaplan focused on the key question for investors – what percentage of the actual return comes from the asset allocation decisions that they make? Ibbotson explains the results in a CFA Institute paper from 2010:
“Asset allocation policy gives us the passive return (beta return), and the remainder of the return is the active return (alpha or excess return). The alpha sums to zero across all portfolios (before costs) because on average, managers do not beat the market. In aggregate, the gross active return is zero. Therefore, on average, the passive asset allocation policy determines 100 percent of the return before costs and somewhat more than 100 percent of the return after costs. The 100 percent answer pertains to the all-inclusive market portfolio and is a mathematical identity—at the aggregate level.”
Ibbotson’s point is that because most investors can’t put together a portfolio of individual investments that beat the index, the only driver of returns is the asset allocation of their overall portfolios.
The second guiding principle to my investing strategy is a focus on factors in my control as I try to build wealth and achieve my goals. That is my savings. It is minimising taxes and fees and limiting the impact of poor decisions on my investment approach.
I have rigid savings goals that are governed by my Investment Policy Statement (IPS). I try to consider these as non-negotiable fixed costs.
I have not read any academic papers on the importance of saving. I don’t think any academic is going to get accolades for pointing out the revolutionary idea that capital is important to build wealth. The math isn’t difficult. If I contribute $1,000 a month and am able to contribute $100 extra, it is the equivalent of a 10% monthly return. Of course, there is an opportunity cost attached to extra contributions – you don’t get to spend the extra money. You don’t have this same cost with investment returns. I’ll touch on my experiences with savings and how it has formed such an integral part of my perception of successful investing further down.
Academic arguments are interesting but they often ignore the realities of life. Nassim Taleb writes about this in his book ‘Skin in the Game’. He speaks about ‘skin in the game’ being contact with the real world that informs your decision making. Taleb explains ‘The knowledge we get by tinkering, via trial and error, experience and the workings of time…is vastly superior to that obtained through reasoning.’
He refers to Pathemata mathemata - a Greek concept that describes how the abrasions on your skin guide your learning. Investing has not drawn blood (yet), but I strongly believe that your circumstances, temperament and experiences guide the type of investor you are and the investing strategy that will maximise your outcomes.
Different investment priorities in practice
There are two types of investors that prioritise security selection. There are investors, and there are speculators. New investors tend to go straight into selecting investments because strong returns from an asset class (maybe even one asset in particular) was their reason for entering the market. We saw this with the influx of new investors in 2020 and 2021.
These investors rode the wave of Covid market returns and gained premature confidence in their investment selection capabilities. It was a momentum fuelled rally and buying shares which had done well paid off. A large cohort of these entrants I would classify as speculators making tactical allocations based on recent performance.
This was a perfect example of riding the asset class wave and mistakenly attributing it to the prowess of the individual. Since then, there has been volatility but markets continue to climb and reach new highs. A contraction, and therefore a reality check, is inevitable. We’ve historically had a bear market every 3.5 years – it is folly to think that we will continue to avoid one going forward.
This situation is avoidable when building a portfolio from the foundations up.
Anchoring your investments to a goal means that you will have an intimate understanding of the purpose of each security in your portfolio. It will be part of an allocation to an asset class that is connected to the returns required to reach that financial goal. It will prevent poor behaviour by selling at inopportune moments to try to time the market, or because holding an investment you have surface level faith in drops which makes you nervous.
What’s also worth mentioning about bear markets is that tactical allocation of funds can severely rig the game against you. Over the last 30 years, if you missed the S&P 500's 10 best days, your return would be cut in half. If you missed the best 30 days over the last 30 years, your return would be 83% lower.
This is why timing the market is an issue, but also why an overreliance of tactical asset allocation in your investment strategy can also be an issue. Not being invested in the right securities means missing most of those days. 78% of the best days occurred in a bear market. I don’t want to miss out. I am perfectly content capturing the average return of the market.
Just as bull markets drive new investors, bear markets cause people to give up. Those that don’t quit may find their way to adopting a strategy that focuses more on what they are trying to achieve, rather than the vehicles to get there.
I know this because I used to be one of these investors who focused more on investments than investing. When I first started investing, I purchased funds that had sex appeal with terms such as ‘pure alpha’, ‘long-short’ and ‘innovation’ in the name. I was extremely lucky that I invested during a very long bull run and didn’t get badly burnt.
The good times kept rolling as equity markets continued to trounce other asset classes. As my career progressed, I felt an obligation to start making direct equity investments to ‘justify’ my work. I didn’t get burnt, but I was sitting in a stockpot that was slowly coming to a rolling boil.
I started understanding myself better as an investor through these holdings. I learned two main things:
- I get incredibly nervous with direct equity holdings
- I tend to spend a lot of time over-analysing my decision and seeking information to confirm I made the right decision
How bloody exhausting. This is where I realised that a large part of investing is understanding what works for you, and deeply understanding yourself as an investor. Investing was a means to an end for me and not a journey I would actively enjoy along the way.
Fast forward to today. My portfolio outside of superannuation consists of cash and collective investment vehicles – managed funds and ETFs. The investment vehicles are concentrated mainly in equities. My cash portion is held in my emergency fund.
I no longer feel the need to continually justify my investment decisions at every turn of the market. My portfolio is connected to the foundations of the pyramid – to my goals. I have a strong understanding of why I hold each position and why it behaves the way it does through different market conditions. This understanding and the connection to my goals means that I am not tempted by each new opportunity. I have a long-time horizon for my capital to grow and compound. I’ve evolved my perception of investing from maximising wealth to building a model that works best to maximise my outcomes.
This has had a flow on effect of other benefits. I am more tax efficient. I limit selling and that lowers my transaction costs (as well as tax). I am cost conscious. I stay invested for the long-term. I think about how to structure my investments, so they are in the most tax efficient vehicle. These benefits are hugely important when considering total return outcomes. I’ve calculated the actual total return of investments in this piece. It shows the individual impact of return influencers.
I prioritise savings. This is a hard lesson to learn without experience, but I was fortunate to work early in my career at a fund manager where I could see the history of individual accounts. This drove home the importance of contributions and compounding to building wealth.
I worked in Client Services and with transaction histories and account balances all day. It was basically a view of the blueprint to building wealth – I saw how individual investors had built up their portfolios over time. Going into this job, I believed that investing was for the wealthy and had no exposure to it growing up.
Working in this role allowed me to see every type of scenario imaginable played out – including those that were contributing small amounts per week over a long time period. I have not had any lump sum wind fall and I do not expect anything in the future. I know that for me to build a comfortable life, I need to prioritise saving to build my capital base. This approach resonated with me on a graduate salary, and it kickstarted my journey with investing.
Selecting investments brings a lot of people joy. I am much more focused on investing regularly in the right asset allocation and committing over the long-term. I believe that will provide more of a difference to my outcome than choosing between two stocks.
Now, after reading this – you may ask, well, for someone that has such a hands-off approach, why on earth would you decide to make your whole career about investments?
The answer to that is – I didn’t. During that story where I had that ‘a-ha!’ moment at the fund manager, I asked myself ‘why doesn’t everyone invest?’. The answer is that some people don’t know this is the way to build wealth.
A lot of those people that could drastically improve their outcomes for themselves and future generations have not been exposed to their version of the ‘blueprint’. It is fulfilling to be able to make this information accessible to everyday Australians and all types of investors.
My investment philosophy is individual to me. It has evolved over time and I imagine it will continue to. That is the beauty of investing. It is being able to take on other perspectives – many of which I am lucky to have shared with me by readers and listeners of the podcast. It is understanding what works for you and understanding that all of this is really just a journey to create a better life for yourself and your loved ones.
Shani Jayamanne is a Senior Investment Specialist, Individual Investor at Morningstar Australia. This article is for general information only and is provided without reference to your financial objectives, situation or needs.