In hindsight, it is easy to see that with seven key factors all having a positive impact on house prices in the last 20 years, strong price growth was inevitable. However, as the table below shows, it is not realistic to expect that this can continue, with the next five years looking like a mixed picture. The reasons for each view are detailed below.
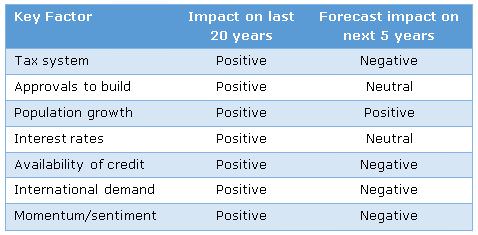
Tax system – Negative
In the next five years it is likely that Australia will implement wholesale tax reform. Twelve months ago most people thought I was crazy when I brought this up, but the national debate has advanced a long way. The Tax White Paper is due shortly, the recent Reform Summit spent most of its time focussing on tax inequity and we’ve got a new Prime Minister and Treasurer who have given signals that change is coming and the economy is the priority. With the politics involved it is not a done deal, but with a Prime Minister, two State Premiers, business groups and welfare groups making the case for change, the politics might be easier than many currently think.
Decreasing income taxes, removing negative gearing allowances, reducing or removing capital gains tax discounts and land taxes are all in the mix. The removal of stamp duty is being proposed by some, but that is highly likely to be linked to the introduction of land taxes. The vertical fiscal imbalance dictates that state taxes such as GST and land tax must increase whilst federal income taxes must decrease. The momentum behind simpler and fair taxes including removing loopholes leaves the many current tax benefits for property exposed.
Approvals to build – Neutral
There has been a jump in the amount of building approvals in recent years and record numbers of cranes for residential construction now dot our capital cities. However, there is still solid opposition at both state and local government levels to further easing of the approval process. Governments in Victoria and Queensland that focussed on easing restrictions in order to promote housing affordability have both been replaced this year with governments that are more concerned about amenity and community consultation. In other states where high density construction hasn’t seen the same boom there’s been a mild lift in approvals that should continue if demand warrants.
Population growth – Positive
Natural population growth is slowing as the Australian population ages, as well as some couples deferring having children and others having fewer. The level of migration is also trending down. However, the overall rate remains around the 20 year average and is still well above almost all other developed economies. Whilst the Australian economy is not as strong as it has been, it is still one of the more prosperous and offers among the best prospects for those with skills and the will to work hard. Even if a substantial global economic downturn occurs, Australian population growth should remain high, with a better lifestyle continuing to attract migrants from Europe, India and China particularly.
Interest rates – Neutral
The current outlook for Australian interest rates is balanced, with little change predicted by interest rate swaps over the coming five years. There has been a small increase in rates for home loans with the possibility of more margin increase for loans that have higher risk characteristics such as high LVRs or interest only periods. The higher capital levels required as part of Basel III reforms are likely to see banks increase their net interest margins to protect their return on equity ratios. Home loans are an obvious target for further rate increases, in addition to the recent ‘out-of-cycle’ rises which included the main owner-occupied variable rates.
Availability of credit – Negative
The recent crackdown by APRA and ASIC on bank lending standards has tightened the availability of credit for the most marginal borrowers. These potential purchasers will need to save more or borrow less. After six years of recovery since the last financial crisis, the next five years is likely to bring another global economic downturn and this would further tighten the availability of credit. Australian banks remain heavy users of overseas capital, which means that in any crisis there is a much greater demand for locally sourced deposits and a need to reduce the amount of lending.
International demand – Negative
The recent report that Sydney’s largest apartment developer, Meriton, has reduced prices and increased commissions in order to meet sales targets is arguably the clearest possible sign that overseas buyers are tougher to find. China has seen a minor run on its currency, which is completely rational as its citizens fear currency devaluation, confiscation of their wealth and are looking for better risk/return opportunities elsewhere. As a result, the Chinese government has been closing down avenues for capital to exit China, with reports that some buyers are struggling to have sufficient capital available by their settlement dates.
Momentum/sentiment – Negative
The massive buzz in Sydney and Melbourne property markets just a few months ago appears to have started to die down. Auction clearance rates have fallen and agents are starting to remark that vendors need to reduce their expectations. The decline in equity markets, slowing migration and the increase in interest rates are put forward as reasons for the reduced sentiment. Beyond the two largest cities price growth has been much more subdued with the pullback of mining investment impacting Perth and Darwin.
Conclusion
The solid growth in Australian house prices in the last twenty years has made Australia’s housing some of the most expensive in the world. Pushing along this price growth has been a combination of seven key factors. However, only one of these factors is likely to persist as a positive influence on prices in the next five years with two factors expected to be neutral and four factors likely to be a negative influence on prices.
Jonathan Rochford is Portfolio Manager at Narrow Road Capital. This article was prepared for educational purposes and is not a substitute for professional and tailored financial advice. Narrow Road Capital advises on and invests in a wide range of securities.