Who is the greatest market analyst of all time? Some will nominate Benjamin Graham. Some may opt for his student Warren Buffett. I liked Ron Brierley in his day, although his lustre has faded.
But towering above them all is Mark Twain. Mark Twain, you may ask? Wasn’t he a writer and a Mississippi riverboat poker-shark? What does he know about markets? Well, everything apparently.
"The Celebrated Jumping Frog of Calaveras County" is an 1865 short story by Twain, his first success as a writer, bringing him to national attention. In it the narrator tells a story about a gambler betting on a jumping frog.
In this story, Twain pens an immortal line for stockmarket scholars about his favorite theory: “no occurrence is sole and solitary, but is merely a repetition of a thing which has happened before, and perhaps often ...”
Like Twain, we have asked ourselves, “Haven’t I seen this all before?” At an individual level this is usually called déjà vu and can strike with incidents in life, memories triggered by visits to different places, smells or sounds.
On a bigger canvas, this is called historic recurrence and is the repetition of similar events in history often separated by long periods of time. The concept of historic recurrence has been applied particularly to the rise and fall of empires and the continual and relentless wars that erupt between tribes and nation states. Nowhere is this better observed than in the history of Afghanistan. Since the time of Alexander the Great, this beautiful but blighted region has been subjected to continual periodic invasions where the invader always and inevitably loses and goes home with its tail between its legs. If G.W. Bush had been a student of historic recurrence, much American blood and treasure (and a not inconsiderable amount of Australian) could have been saved. Alas, he doesn’t appear to have been much of a student of anything!
While people often say, “History repeats itself" in cycles, this is never exactly true. This was also appreciated by Twain, obviously a student of the long cycle, when he wrote, "History does not repeat itself, but it does rhyme."
Recurrences take place due to sometimes subtle and not readily identifiable circumstances. Some of these factors may not be understood at the time the event is occurring and may only become apparent years later. The reason for the recurrence will often be hotly debated. Nowhere is this better evidenced than in the stockmarket.
As the chart below shows the stockmarket may not be repeating history but it’s rhyming, with all the exuberance of a Wordsworth poem.
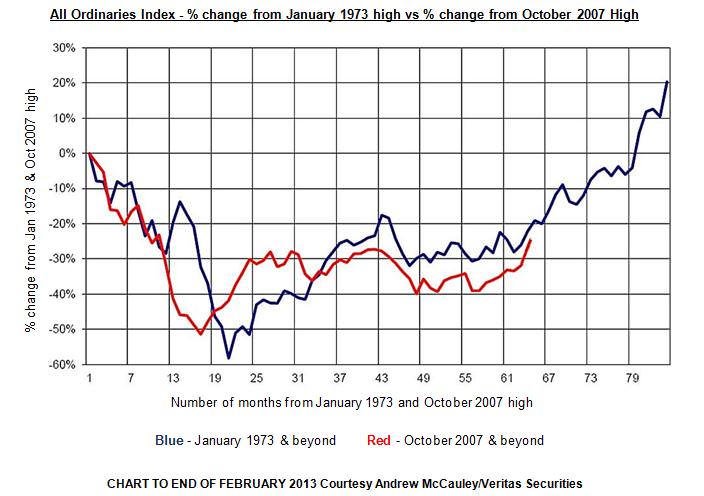
The Australian equity market is presently repeating a performance pattern similar to the mid 1970’s recovery. It’s not performing exactly the same way, but it’s close. It is now 65 months with a 25% decline since the Australian equity market peaked in late 2007. Over the same time frame (65 months) from the pre-decline peak in January 1973 to March 1978, the All Ordinaries Index had fallen by approximately the same amount as shown in the chart. Both periods experienced peak to trough reversals of more than 50%.
The chart shows the returns from the All Ordinaries Index post the 1973 and 2007 peaks. As is readily observable, the moves in the two periods tend to mirror each other. Let’s say it is not repeating itself but it sure is rhyming.
“So what?”, you may ask. The model, if it is a true example of historical recurrence, may predict the course of the sharemarket over the next couple of years. Or it may not.
Why would this rhyming model work? Simple. The stockmarket is a barometer of human emotion and particularly human frailty. It registers them all … fear, greed, lust, paranoia, confusion, panic, herd-mentality, envy and disappointment. It’s a big human stew but the ingredients never change so the taste is the same, although it comes to the boil at different times. “Gee haven’t I tasted this somewhere before?” The ingredients never change because people never change. Not really. Not even over long periods of time.
The herd always charges off together in one direction then just wait, what’s that sound you hear? It’s the herd charging back again in the opposite direction. They head off over the hill. What is the only thing you know for sure? That given time you will see them all come thundering over that same hill heading in the direction they first came from. Humans, like jumping frogs and migrating wildebeest, never change. The graphs from 1973 and 2007 demonstrate this.
Writing novels and playing poker on riverboats, while consuming large quantities of whisky, does not a great market analyst make! Or does it? I think I’ll try it.
Kieran Kelly is Managing Director of Sirius Fund Management and has over 30 years’ experience in fund management and sharebroking.