The Labor Party needs to articulate how it will treat shareholders in Listed Investment Companies (LICs) fairly under their proposal to deny refunds for excess franking credits.
The current system of taxation of dividends ensures that Australian resident shareholders are taxed at their applicable rate of income tax on dividends received from companies, rather than a minimum of the company tax rate. Denying refunds for excess franking credits will require complex changes to legislation to maintain the existing policy of allowing shareholders in LICs to effectively receive the CGT discount on capital gains earned by the LIC.
When a LIC earns a capital gain it pays income tax on the capital gain at the corporate tax rate, typically 30%. When it pays the capital gain to the shareholder as a LIC dividend, the shareholder is taxed on the dividend and franking credit in the usual way, but also receives a tax deduction that represents the CGT discount the shareholder would receive if they derived the gain directly or received it from a trust.
Below is the analysis showing the calculations for an investor (super fund or High Net Wealth Individual) investing in a LIC or either directly in shares or via a trust.
Calculation of tax payable on a $10,000 capital gain by:
- Super fund in accumulation phase invested in an LIC (Super-LIC)
- Super fund in accumulation phase invested in a trust or direct shares (Super-Trust)
- High net worth individual (HNWI-Trust)
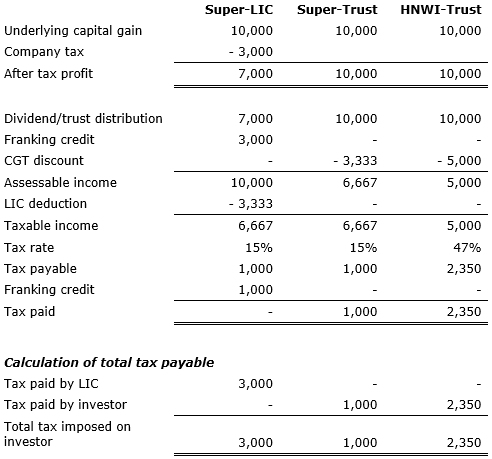
Currently, they receive a refund of the excess tax paid by the LIC above their tax rate after the tax deduction for the CGT discount. Denying the refund of excess franking credits results in the shareholder paying 30% tax on the dividend. This is a 27% higher rate of tax on a capital gain than is paid by someone on the top marginal rate of tax. This means a super fund will pay at least three times that rate of tax on a capital gain distributed by a LIC when compared to a capital gain it earns itself or via a trust and 27% more tax than an individual on the highest rate of tax.
(That is, a HNWI pays $2,350 on a $10,000 capital gain. A super fund in accumulation phase pays $3,000 on a capital gain earned by a LIC. The difference is $650 divided by the tax paid by the HNWI of $2,350 gives 27% more tax payable by the super fund).
Given that a large percentage of investors in LICs are super funds and that many investors in LICs are not wealthy, this is an inequitable result that will need to be addressed.
Howard Badger is a Partner in Tax Consulting at Pitcher Partners. This article is general information that does not consider the circumstances of any individual.