There is a long-running debate about SMSF exposure to global equities, driven by the misleading interpretation of the data issued by the Australian Taxation Office. The ATO only lists direct holdings on global exchanges in its international equities allocation, and this number misses the billions held by SMSFs in managed funds, Exchange Traded Funds and Listed Investment Companies. Drilling into the actual fund data, SMSF allocation to international equities is about 7%, which is one-third of the 23% allocated by large institutional funds, but much higher than the 1% suggested by the ATO data.
Drilling deeper into the listed trust allocation
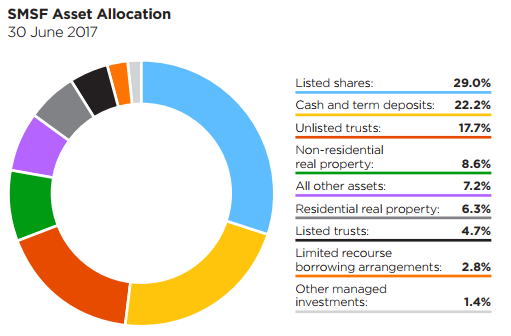
Compensating for the ATO data weakness is the Class Limited SMSF Benchmark Report. We have early access to the June 2017 numbers compiled from over 130,000 SMSFs using de-identified fund-level data. Initially, for consistency with the ATO data, Class uses the same asset allocation categories, as shown below.
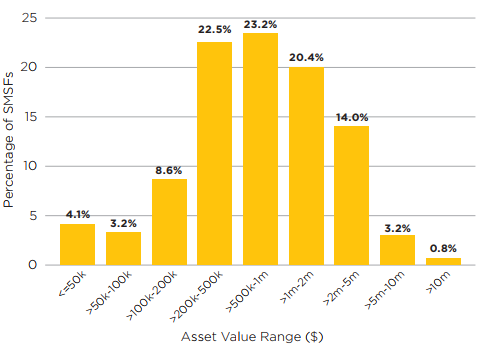
Class also provides the asset value ranges of SMSFs, showing some very small and very large balances but two-thirds in the $200,000 to $2 million bands.
Where the first chart above reports listed shares at 29%, like the ATO data, the vast majority of these shares are listed on the ASX. It is the unlisted trusts category at 17.7% of assets and the listed trusts at 4.5% of assets where the global equities lie. In these SMSFs, managed funds comprise 11.5% of assets, with 32% of SMSFs holding some type of managed fund.
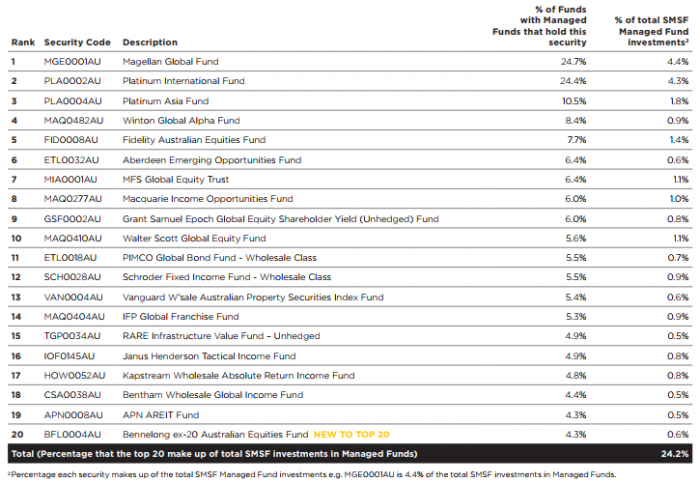
The asset exposure of the Top 20 managed funds is 58% international equities, 10% Australian fixed interest, 9% cash, 8% global fixed interest and 5% listed property. Only 8% is Australian equities. A 58% allocation of the 11.5% in managed funds places 6.7% in global assets.
As shown below, the Top 20 managed funds are prominent in many SMSFs, with about a quarter of SMSFs with managed funds holding investments with either Magellan or Platinum.
Direct equities by security
The Class data reports the largest asset allocation is to listed domestic equities (including listed trusts) at 37% of SMSF assets, with a place in 68% of all SMSFs.
The domestic listed assets comprise:
- Shares 78.5%
- Debt and hybrids 9.0%
- Stapled securities 6%
- ETFs 5.9%
- Other listed trusts 0.6%
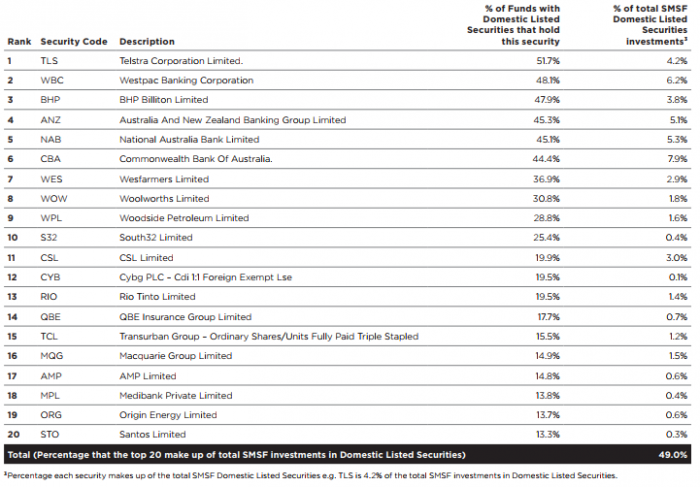
The following table shows the Top 20 shares in SMSF portfolios. Over half of all SMSFs that hold domestic shares have experienced the Telstra pain of a halving in the share price and cut in dividend. The banks make up over half the investments in the Top 20, with Westpac overtaking BHP in the last quarter.
Graham Hand is Managing Editor of Cuffelinks. Exclusive access to the Class SMSF Benchmark Report for June 2017 was provided by Class Super.