The big picture
The Reserve Bank of Australia's (RBA) most recent Statement on Monetary Policy reiterated that although inflation has picked up, price pressures in Australia remain considerably lower than in other countries. The near-term inflation trajectory was marginally upgraded, however, it is expected to remain within the RBA’s target band across the forecast horizon. The RBA expects core inflation to continue to drift higher and reach 2.5% over 2023. It also reinforced its stance “not to increase the cash rate until actual inflation is sustainably within the 2-3% target range”. The RBA has highlighted that the trajectory of inflation will be important, “with a slow drift up in underlying inflation having different policy implications to a sharp rise”. Over recent weeks, longer-term rates have increased back to pre-pandemic levels in anticipation of major central banks looking to raise rates.
At Charter Hall, we don’t pretend to know what the future holds in this space but, on balance, we subscribe with the views of the RBA that pricing pressures that have emerged across the market have largely been transitory and appear to be stabilising.
In this article, we examine the relationship between inflation and commercial real estate.
Inflation and commercial property
There are several inflation protections built into commercial property leases, particularly long-term leases. These generally include annual fixed increases, often at a given rate above the Consumer Price Index (CPI) rate. For example, a long-term lease in an industrial property might have annual rental payment increases structured at a fixed percentage plus CPI (e.g., annual rental payment increases of 3.0% would equate to a 0.5% fixed percentage plus 2.5% being the 12-month CPI rate).
Even when not linked to inflation, typical annual rent increases are set above the long-term outlook for inflation. For example, the average fixed annual rent increase across our two unlisted direct office funds average around 3.5%. Importantly, long-term leases that are either directly linked to inflation or set above long-term inflation averages can provide protection as they extend beyond short-term volatilities in inflation.
Leases may also contain expense pass-through mechanisms. With many of our lease arrangements, particularly triple-net leases, most of the expenses and capital works are ‘passed through’ which means the tenant is responsible for these expenses and capital works – not the landlord, providing protection for commercial property owners from any rising expenses.
A further protection for commercial property relates to supply, with higher construction costs slowing new developments.
Other factors that influence inflation and commercial real estate
Real estate occupier demand: Physical market drivers and real estate demand have a large impact on real estate asset performance. Elevated market vacancies can moderate rental growth, reducing the power of the inflation link for leases. However, higher quality assets typically have lower levels of vacancy, longer lease expiry profiles and stronger pricing power. These assets provide greater income stability and more robust investor demand, providing strong through-the-cycle returns.
The way in which we use real estate can also shift over time. For example, the pandemic accelerated the growth of online retailing, having opposing impacts on industrial and retail shopping centre sectors. Over the past year, industrial and logistics sector returns reached their highest level on record, significantly outpacing inflation. This can be contrasted with shopping centre retail returns, which were challenged by pandemic-related issues and compounded by structural longer-term shifts in online retail growth.
Economic growth: During some economic downturns, real estate has shadowed the negative performances of equities and bonds. During the early 90’s and GFC, the financial recession revealed severe asset mispricing and created liquidity challenges. Both inflation and real estate returns declined through this period.
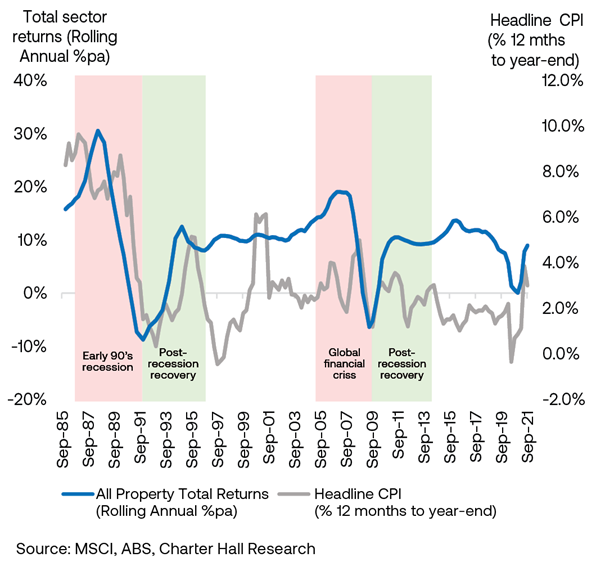
However, in an economic recovery, real estate returns and values typically grew in conjunction with the rebound in inflation. The inflationary growth that has transpired over recent quarters has resulted from the dramatic economic recovery underway. If post-recession recovery is like those in the past, then overall real estate returns should grow with inflation. The chart below illustrates the relationship between property returns and inflation; when there is growth in inflation, property returns also rebound.
CPI and Unlisted Total Sector Returns (Office, Retail and Industrial & Logistics)
Allocations to real estate
This economic recession didn’t originate from the financial sector. As such, the real estate sector didn’t face the same issues relating to liquidity and the underlying confidence in asset valuation seen during past economic crashes. The global allocations to real estate, particularly across the Asia-Pacific region, continued to increase over the past year. This generates increased investor demand for commercial real estate assets across Australia.
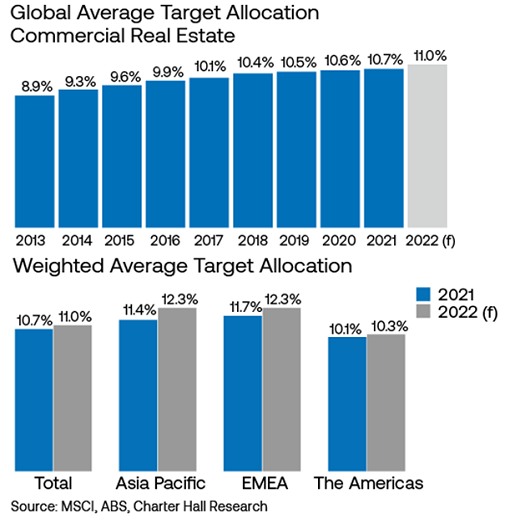
Inflation and commercial property
Real estate provides low correlation to other investments such as hedge funds, venture capital, private equity, private debt and other hard asset classes such as infrastructure1. Investors seek real estate for the potential benefits of reducing volatility and potential risk.
These factors have already translated into increased investor demand. Investment volumes in Australia across the industrial sector reached $18 billion over the year – well above the long-term average of $4.7 billion. Similarly, transaction volumes for the office sector climbed to $15.9 billion over the past year, the highest level since 2019.
How has commercial real estate performed in periods of elevated inflation?
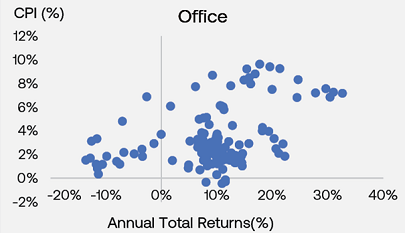
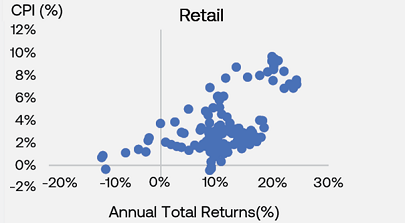
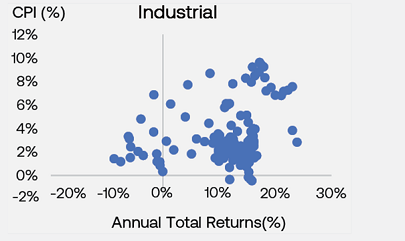
The charts below show how in periods of higher inflation, annual returns of commercial real estate also tend to be high and elevated, regardless of the underlying property sector.
Commercial real estate has historically provided a solid hedge and performed well in periods where inflation increases against the backdrop of economic expansionary periods. Other external market factors can also have larger influences on investment performance, including investor demand.
Outlook
Moderate inflation poses little risk to commercial property. We focus on strategies that assist in offseting the potential negative impact of rising inflation, including a focus on long leases with fixed reviews, interest rate hedging and high quality assets.
Steven Bennett is Direct CEO and Sasanka Liyanage is Head of Research at Charter Hall Group, a sponsor of Firstlinks. This article is for general information purposes only and does not consider the circumstances of any person, and investors should take professional investment advice before acting.
For more articles and papers from Charter Hall, please click here.
1. (PERE 2022) 'Look Ahead 2022 : Five reasons real estate allocation will rise next year' Charts show quarterly returns between the periods of 1985 and 2021.
Source: MSCI, ABS, Charter Hall Research