Bonds have been an exceptionally rewarding asset class for nearly four decades. They have also proven to be a reliable diversification tool, particularly when deployed with stocks in a so-called '60/40' portfolio. But expecting a repeat performance in the decades to come reminds us of the late financial historian Peter L. Bernstein’s comment that: “There is a difference between an optimist and a believer in the tooth fairy.”
As can be seen in the chart below, this extraordinary period of performance has been unusual in the context of longer-term history. Bonds have benefitted from a favourable tailwind that stretches back to the early 1980s. Recently, the tailwind has been reinforced by the unprecedented actions of central banks following the GFC. To avoid a deflationary debt spiral, the Federal Reserve and other major central banks intentionally drove bond yields to historic lows and even into negative territory in some instances, sending bond prices to new highs.
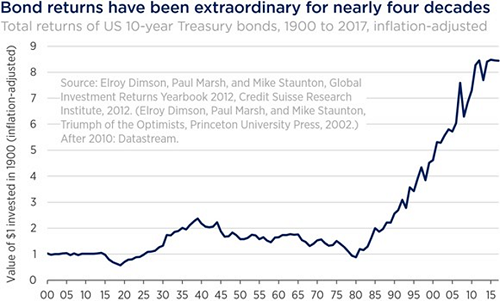
government bonds
Prospective returns for many bonds now appear limited
In addition to nosebleed prices and rock-bottom yields, the risks embedded in the bond market would appear to be well above average when we observe cuts in taxes and a ramp up in fiscal spending at a time when government debt is already at or near all-time highs. Governments and central banks are desperate to inflate away these debt burdens. Sustained negative real yields imply sustained negative real returns to holders of these nominal assets.
We also ask ourselves: “Who is the marginal buyer of bonds at these yields if central banks are stepping back?” Historically it might have been large governments recycling their enormous current account surpluses. If a country exports more than it imports, it needs to do something with the difference, and exporter countries have often been major buyers of importers’ bonds. But the reduction of international trade imbalances is now top of the political agenda.
In addition to political will, there are forces at work that should lead to a more natural reduction of the global gross trade surplus. Examples include the seismic shifts in China, where supply-side reforms have the potential to substantially boost imports, and in the US, where the shale oil and gas revolution is beginning to impact the export picture.
The bond sell-off that spooked investors in February this year was driven by greater-than-expected wage growth in the US. It could be a sign of more volatility to come. Negative returns are likely if interest rates continue to rise as quantitative easing begins to unwind. When yields are low, bond prices become extra sensitive to any change in yield, adding a layer of risk.
Rise in correlation reduces diversification benefits
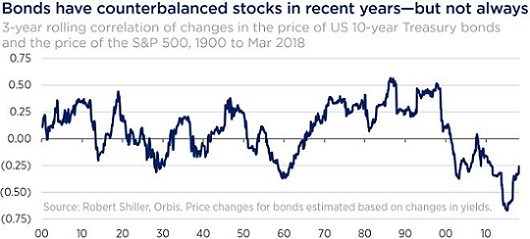
Worse, there are signs that stocks and bonds are now moving together, negating the diversification benefit bonds are expected to provide. Taking a longer-term view of history, the following chart shows that the strong anti-correlation between US stocks and bonds (the negative numbers) since the late 1990s is quite unusual. History suggests that investors should expect bonds and stocks to be more correlated in the future with the possibility of high correlations in a rising interest rate environment. It also suggests that investors might question the traditional diversification role played by long-dated government bonds in a balanced portfolio.
Yields for long-term government bonds can be broken into a few components: inflation expectations, the expected path of real interest rates and the term premium. This latter component can be thought of as the compensation offered to investors for taking on a long-dated risk. It should always be positive, but today, term premiums in most developed markets are near zero, and some, astonishingly, are negative. A negative term premium implies that investors are paying for the privilege of taking on term risk. This is highly unusual, if not nonsensical. Yields can be low for good reasons, but it’s hard to imagine a good reason for the term premium to be negative. This looks like a real inefficiency — a mispricing.
One culprit is quantitative easing (QE), the process where central banks buy bonds and other assets using newly-printed money. Large price-insensitive buyers of government bonds are bound to create price distortions. In this environment it makes sense for governments and companies to borrow long term, and this is what we have seen. Ireland and Austria have issued bonds that mature in 100 years.
Today's prices force a rethink
One definition of risk is that “more things can happen than will happen”, and purchasers of these bonds have 100 years’ worth of potential surprises to look forward to. For taking on this enormously long-dated risk, investors receive a paltry 2% per annum. Relying solely on long-term government bonds to manage risk at today’s prices strikes us as imprudent at best.
Graeme Forster is Portfolio Manager at Orbis Investments, a sponsor of Cuffelinks. Commentary is adapted from Orbis quarterly reports and reflects recent views. The information provided in this article in general in nature and does not take into account your personal objectives, financial situation or needs.
For more articles and papers from Orbis, please click here.