Contributing authors: Jonathan Lemco, Asawari Sathe, Adam J. Schickling, Maximilian Wieland, and Beatrice Yeo, from the Vanguard Investment Strategy Group’s Global Economics Team.
The last 12-plus months have emphasised that the COVID-19 pandemic would accelerate trends already in place. One of these trends is the shortening, and in some cases the reshoring, of supply chains, as business leaders question whether their supply chains have been stretched too far and become too complex.
Such a trend raises a natural question: Is globalisation dead?
New Vanguard research, The deglobalisation myth(s), concludes that, no, globalisation isn’t dead. Instead, global trade growth is likely to slow, as it’s been doing since the GFC. This slowing in global trade growth, what we term ‘slowbalisation’, is unlikely to turn into a contraction in global trade. What’s more, the implications for investors are only modest.
A slowbalization scenario is the most likely outcome
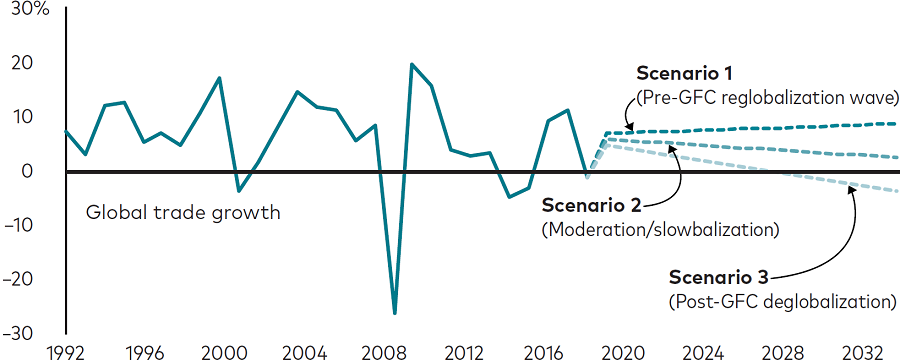
Sources: Vanguard calculations, using data from the World Bank, the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development, and the KOF Swiss Economic Institute.
The allure of global trade is understandable
Companies that produce goods or provide services want the largest possible markets for their outputs. But a structural expansion in supply chains, which boosted gross trade in the 1990s and early 2000s, started to slow even before the GFC. A turn toward protectionism - government policies that favour domestic industries - over the last decade in the face of rising inequality in developed economies is likely to similarly tap the brakes on global trade.
We note that other aspects of globalisation, including international capital flows, knowledge sharing, and geopolitics, carry potentially significant economic, societal, and environmental consequences. Our latest research focuses on just one aspect of globalisation that addresses a specific concern of investors: the trade of goods and services.
The concern is that slowing global trade growth may reduce corporate earnings and profit growth and, by extension, weigh on equity prices. After all, a globalisation wave that began in the 1990s coincided with a six-fold increase in S&P500 Index earnings per share and more than a doubling of profit margins, contributing to almost 90% of the index’s price return over most of three decades.1
Risks to investors may not be as great as they seem
But we contest the view that globalisation has been the central factor in the expansion of these return drivers. Our research demonstrates an inconclusive or weak relationship between earnings growth and changes in trade dependency. And it shows that industries with the greatest increase in profit margins since 1990 - finance and insurance, and office and computer machinery are examples - have experienced only modest changes in trade dependency.
Trade tensions that precipitated sharp bouts of market volatility just a few years ago underscore the importance that investors ascribe to global commerce with few impediments. No doubt, geopolitical risks are ever present and worthy of attention. But our new research quantifies risks related specifically to a future of slowing global trade growth, and we believe that these risks to investors aren’t as large as they’re sometimes portrayed.
Rather, we emphasise conclusions shared by our new research and our December 2020 research A Tale of Two Decades for U.S. and Non-U.S. Equity: that corporate earnings growth hasn’t been a major contributor to U.S. equity outperformance in the past and that we shouldn’t expect it to have a meaningful impact on future outperformance or underperformance.
Valuations, or the price investors pay for earnings, represent the most important signal for future asset returns.
1 The average annual S&P 500 Index price return from 1990 to 2018 was 7.4%. Three factors make up this return: valuation expansion/contraction (dollar paid per dollar of earnings), earnings growth from revenue growth, and earnings growth from ratio of earnings to revenue (profit margins). Contributions from these factors were 0.8%, 3.7%, and 2.9%, respectively.
Vanguard is a sponsor of Firstlinks. This article is for general information and does not consider the circumstances of any individual. For more articles and papers from Vanguard, please click here.