With talk of another hybrid issue by CBA’s Colonial to boost its tier-one capital ratio, it is timely to review previous issues, especially on the back of the hybrid overload from the big banks in 2016.
It's remarkable to recall that within only 18 months, CBA issued a hybrid with a margin of 2.8%, then another at a much wider 5.2%, an extraordinary difference for a security with the potential for no (ie perpetual) maturity. The two issues represent the recent peak and trough of the margins.
Issuing bank hybrids (also known as preference shares or capital notes) instead of ordinary shares is attractive to banks to boost tier one capital without dilution of shares and earnings ratios.
Retail investors have actively sought hybrid securities in the past few years in response to the low-rate environment, especially hybrids issued by the big four banks. After some weakness in prices in recent years, hybrid securities have recovered to a healthy degree, but some remain below their face value, particularly CBA PERLS VII (ASX:CBAPD) issued in 2014. This is in stark contrast to the follow-up CBA PERLS VIII (ASX:CBAPE) issued in early 2016 that has traded at a premium since listing, reaching a high of $108.25 on 10 January 2017.
What happened to PERLS VII?
CBA PERLS VII was issued at the peak of hybrid issuance and due to demand was priced at the lower end of the margin above the Bank Bill Swap Rate (BBSW). The margin was a record low of 280 basis points (2.80%). The issue, which raised around $3 billion, was oversubscribed due to retail demand, with investors receiving a franked yield a little over 5% pa based on BBSW at the time. Retail investors have viewed hybrids as a fixed interest-type source of income, higher yielding than bonds and cash, and with lower volatility than the underlying shares.
However, PERLS VII has traded as low as $85.29 (issued at $100), generating massive capital losses for anyone who sold, in a security many expected to be price stable. It has since recovered to around $95.
After the CBA PERLS VII transaction, headwinds included:
1. Interest rates cycle bottoming: Rising rates highlighted the low issue margin of 2.8%, creating concern that CBA may decide not to redeem the PERLS at first opportunity due to their inexpensive funding source.
2. CBA high share price: There was the risk of the high price of CBA shares at the time of the issue falling closer to the 50% of the price level used as the benchmark which prevents conversion into shares. Then the PERLS become perpetual.
3. CBA high dividend yield: CBA’s gross dividend yield on its shares at the time was 7.7% pa compared to the yield on PERLS VII of say 5.4% pa, so the yield pickup increased the appeal of shares compared to hybrids.
What changed with PERLS VIII?
In early 2016, CBA PERLS VIII raised a much lower amount of $1.45 billion despite the margin of 520 bps (5.2%), an incredible change from less than two years earlier. The initial return of 7.5% pa (5.2% above BBSW) compared well with the gross dividend yield on CBA shares which was 8.08% pa at the time. The yield pickup of 58 bps for shareholders was much smaller than the previous PERLS issue.
When the PERLS VIII was announced, the trading margin was below other bank hybrids’ margins in the secondary market with shorter maturities. CBA was also worried that the poor experience on PERLS VII would weigh on the return to the market but the bank was buoyed by a pre-market offer by Unisuper to take 20% of the issue. Pricing at a healthy margin to allay concerns, the demand was strong although the size was not large. The institutional appetite drove CBA’s confidence that levels had reached a point where risk was rewarded, and the issue has traded strongly above par since launch.
Why retail investors like hybrids
Retail investors have been active purchases of bank issued hybrids, due to:
- Need for income: People living off their savings have a strong appetite for sources of income, and SMSFs in particular have moved strongly into hybrids.
- Replacement for banks shares: Hybrids have lower price volatility than underlying shares, and recently more comparable gross yields.
- Brand recognition: Investors feel comfortable investing in securities issued by the Big Four banks.
- Accessibility: Trading on the sharemarket increases the appeal compared to some other income sources.
Widening of margins over 2015 drove down prices, reaching a low (maximum margin) at the start of 2016. Hybrid prices in the secondary market have since been rising (margins falling, see chart below) and are closer to where they were trading pre-GFC (trading margin is yield to maturity less relevant swap rate).
Bank hybrids trading margins, 2016 versus 2017
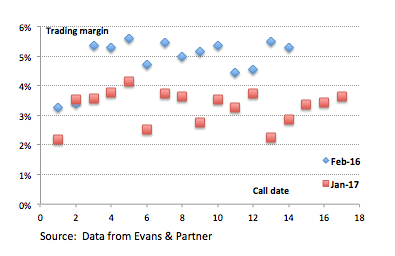
The dangers of fixed interest-like returns, but not fixed interest
Many new bank hybrid issues are ‘additional tier one’ (AT1) designed to be ‘perpetual’ instruments as required by the Australian Prudential Regulatory Authority (APRA). Hybrids differ from bonds and should not be considered a fixed interest replacement, as they do not have a fixed maturity, and distributions are discretionary. Hybrids do exhibit fixed interest-like returns, but in a falling market, can show equity-like volatility (CBA hybrids lost around 40% of their value during the GFC).
A better description for hybrids is ‘equity-paying income’. The equity part is the fact that holders of the securities would share in the losses if the company faces severe financial difficulties, and the fixed interest aspect refers to the regular distribution and limited upside if the company exceeds profit expectations.
Rosemary Steinfort is a Research Manager at DirectMoney.com.au. This article is general information and does not consider the circumstances of any individual.