Over the years, the financial services industry has become needlessly complicated. Ultimately, investing still boils down to an exchange of capital today for cash flows tomorrow. Weaker balance sheets and income statements, dubious earnings assumptions and soaring bankruptcies demonstrate that a challenging investment environment lies ahead, but market pricing doesn’t reflect that outlook. Everything is rising in value because there is excess capital chasing too few opportunities.
Is that the role of financial markets?
Capital should be allocated more responsibly than that. The financial services industry of today looks quite different from a century ago, but its role in society has not changed. Back then, investing was the province of wealthy individuals and large institutions until companies such as MFS helped democratise markets and give small investors greater access to investments. At its core, investing is simple. It’s an exchange of capital today in return for a cash flow from a company or government in the future.
Against that backdrop, let’s take a look at what the price of risk is implying about future cash flows, though at this point it’s questionable whether the average investor even cares.
Weaker balance sheets and income statements
Long before the onset of the pandemic, worldwide profit margins had peaked and were contracting. Balance sheet quality was poor and deteriorating before the coronavirus spread around the world. Battling the spread of the COVID-19 forced a sharp curtailment of global economic activity in the first quarter, prompting companies to plug revenue gaps by issuing historic amounts of debt, materially weakening already fragile balance sheets.
At the same time, companies will incur incremental costs to minimise health risks for employees and customers, while many will also have to reorient supply chains to emphasise resiliency after many years of focusing more heavily on wringing out costs. This will weigh on income statements for those unable to offset higher costs with either higher prices or greater volumes. The resulting increased capital investment will lower return on working capital for years to come. In short, future cash flows are likely to underwhelm.
Fuzzy earnings maths
If companies are more indebted, have higher operating costs and greater output yet final demand remains below 2019 levels, how do the market’s implied 2021 operating earnings compute? Profits are not linear and the last few customers are always the most profitable. Scale matters immensely.
Absent revenue growth that is materially better than it was 2019, I honestly cannot make the earnings maths work.
Let’s look at this through a different lens. On annualised basis, the US economy contracted by a third this past quarter, a level materially worse than any quarter during the GFC.
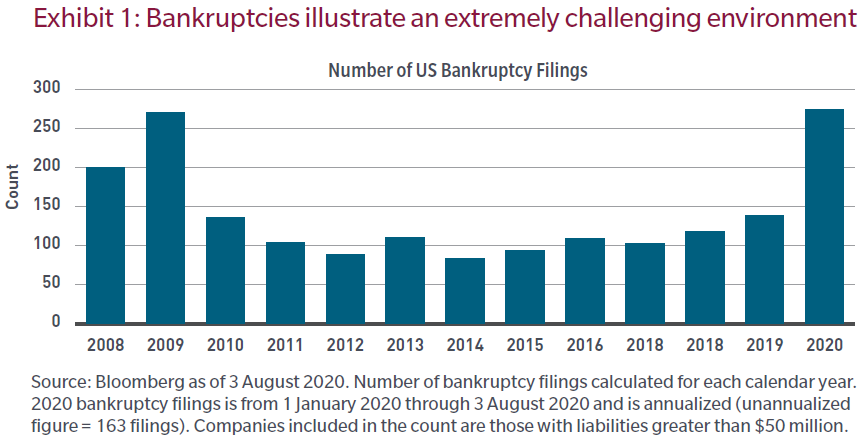
The graph above illustrates that the number of sizable bankruptcy filings is on pace to exceed any year since the GFC. This makes sense to me. The imbalance in the real economy leading up to the 2008 recession was over-leveraged financial institutions. The imbalance was largely concentrated in one industry. This allowed the subsequent earnings recovery to be historically fast because most other sector constituents did not require equity recapitalisation.
How is 2020 different?
The weak economic recovery following the GFC and the central bank stimulus undertaken as a result of the weak rebound created more widespread imbalances during the just-ended cycle. The accommodative monetary backdrop afforded companies with weak revenues to substitute borrowed cash flows for operating cash flows. Unlike 2008, the 2020 crisis is one of over-leveraged businesses across many industries and sectors. The pandemic is the excuse often used for weak financial results, while the cause was soft demand heading into 2020, balance sheet fragility and financial engineering. As a result, I expect more bankruptcies during this recession and a weaker-than-normal recovery in overall profitability.
Why are financial markets signalling otherwise?
The honest answer is: who knows? I can offer this perspective.
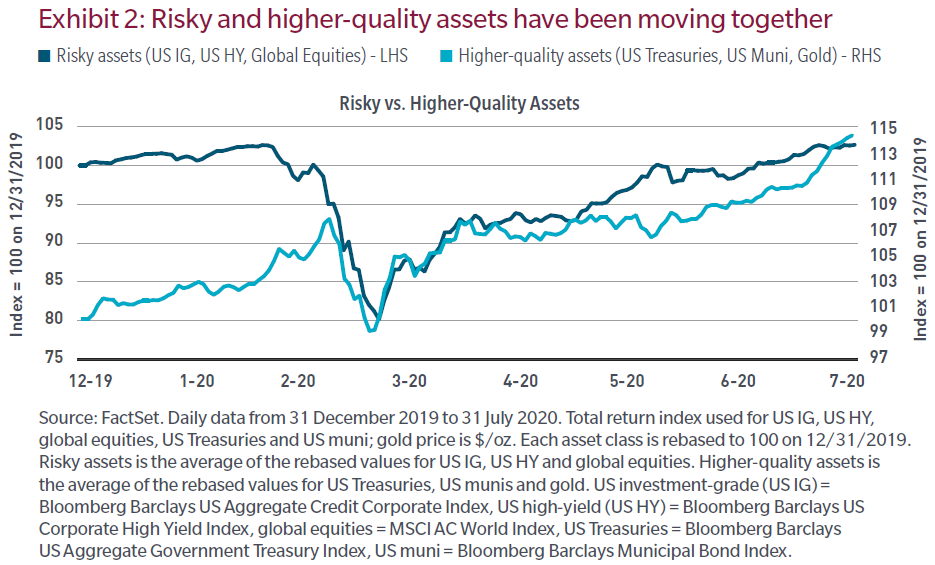
While there are numerous asset classes for investors to choose from these days: growth or value equities, large versus small capitalisation stocks, developed market corporate bonds or developing, etc., ultimately there is only one asset class: volatility. Most financial assets are effectively short volatility, as they benefit when markets anticipate increasing certainty and stability. Conversely, they suffer when conditions deteriorate.
Assets such as US Treasuries or gold, on the other hand, are effectively long volatility and benefit from greater uncertainty. But lately, as policymakers have injected capital into financial markets to fund operating losses and suppress the cost of risk, the correlation between short and long volatility assets has gone from negative to positive. Today, everything is rising in value because there is excess capital chasing too few opportunities. Is that the role of financial markets? Capital should be allocated more responsibly than that.
Patience and skilled security selection and a focus on fundamentals are more important now than ever as the outlook for future cash flow deteriorates.
Robert M. Almeida is a Global Investment Strategist and Portfolio Manager at MFS Investment Management. This article is for general informational purposes only and should not be considered investment advice or a recommendation to invest in any security or to adopt any investment strategy. Comments, opinions and analysis are rendered as of the date given and may change without notice due to market conditions and other factors. This article is issued in Australia by MFS International Australia Pty Ltd (ABN 68 607 579 537, AFSL 485343), a sponsor of Firstlinks.
For more articles and papers from MFS, please click here.
Neither Bloomberg nor Barclays approves or endorses this material, or guarantees the accuracy or completeness of any information herein. MSCI makes no express or implied warranties or representations and shall have no liability whatsoever with respect to any MSCI data contained herein.
Unless otherwise indicated, logos and product and service names are trademarks of MFS® and its affiliates and may be registered in certain countries.