Australians have long liked bank deposits, a traditionally simple and safe investment and a $2 trillion market. However, upcoming bank regulations mean investors will not be able to simply break a bank term deposit investment. They will need to give 31 days’ notice and may forgo interest. The regulations may also favour rates given to individuals while small businesses and others, including SMSFs, may be worse off.
For investors who want a degree of safety and access to funds, an Australian dollar corporate bond fund may make more sense. It’s a little riskier, but bond funds typically generate better returns than deposits with ready access to funds.
Consequences of revised liquidity regulations
Soon after the GFC, the Basel Committee on Banking Supervision released a revised set of guideline regulations for banks around the world. These rules were significantly adopted in bank liquidity measures imposed by the Australia Prudential Regulation Authority (APRA).
Specifically, the Net Stable Funding Ratio (NSFR) encourages banks to retain a minimum level of ‘stable’ funds to help ensure they can withstand a sudden outflow. Australian banks will need to comply with the NSFR by 1 January 2018.
The NSFR is defined as the ratio of: the amount of available stable funding (ASF) to the amount of required stable funding (RSF). The ASF is weighted from 0% to 100% to reflect the likely stability of the funding. Retail and small business deposits are considered more stable than other sources.
These rules will therefore encourage banks to take deposits from retail and small businesses as well as longer-dated deposits. This should benefit individual direct investors who want to deposit their money for a reasonably long period, and receive relatively higher interest rates.
For everyone else, including SMSFs and larger businesses, it is bad news for two reasons:
- investments from these sources become relatively less attractive to banks and could reduce the interest rates received, and
- term deposits will become illiquid. Previously, depositors could call a bank, request a break in the term and the bank would typically pay on the spot with full interest accrued, or perhaps some adjustment. Now, 31 days’ notice will be required and interest earned to that date may evaporate.
For example, in Australian Prudential Standards (APS) 210, Attachment A, page 19, APRA specifically defines retail as from ‘a natural person’. A ‘legal entity’ such as an SMSF falls into the wholesale deposit category.
“… ‘retail deposits’ are defined as deposits placed with an ADI by a natural person. Deposits from legal entities, sole proprietorships or partnerships are captured in wholesale deposit categories.”
In fact, APRA goes further and explains why SMSF deposits are less stable:
“APRA considers SMSF depositors to be self-selected, financially sophisticated individuals, which is an indicator of a greater propensity to withdraw funds in a stress situation. As such, SMSF deposits are appropriately categorised as less stable.”
Collapsing yields
Yields have fallen for deposits, bonds, equities, and just about every asset class in Australia over recent years. In a higher-yielding environment, a 1 or 2% difference in returns did not make much difference to relative long-term returns. Nowadays, it has a huge impact.
The graph below shows the accumulated total returns of two types of investments: a 12-month deposit of 2.3% compared to the running yield of a corporate bond fund such as Spectrum’s at 4.1%. Both are presumed to keep the same yields over the period.
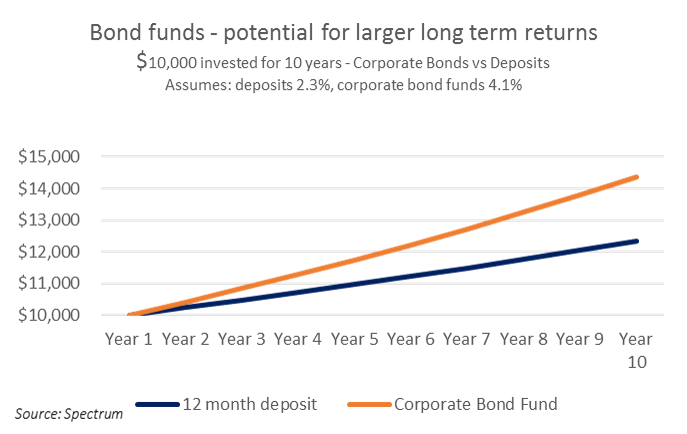
$10,000 invested in the bond fund would theoretically generate around $4,400 in income over 10 years whereas the deposits would generate around $2,300.
Bonds versus deposits: back to normal
Post GFC, Australian banks were told by regulators and rating agencies that they relied too much on international bond investors and that their balance sheets required more local deposits. The banks responded by paying up on deposits to bring their yields near those of a 3 year ‘A’ rated corporate bond.
As the graph below shows, there is now a more normal yield premium for corporate bonds over bank deposits. This reversal to ‘normal’ helps investors, in general, get better returns from a corporate bond fund compared with bank deposits.
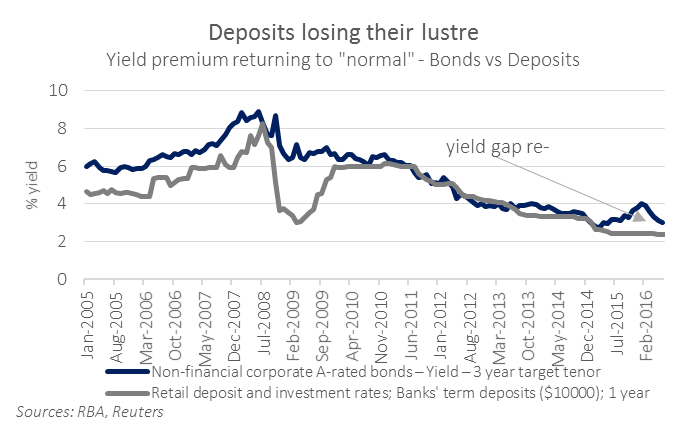
The growing $600 billion SMSF sector holds about $160 billion in bank deposits, while little SMSF money is invested in bonds, and many appear to use deposits as a proxy for bonds. This made sense in the past, but not anymore, particularly because SMSFs may now get worse deposit rates than an individual.
Liquidity or return
For many bank depositors, it now looks like they can either have yield or liquidity but not both. Corporate bond funds offer higher returns and the ability to sell at short notice.
This is not to say there will not be nuanced competition for deposits. The new regulations mean that not all deposits are equal in satisfying regulations. This means it is highly likely there will be differential deposits pricing depending on who and for how long the deposits are for.
The NSFR will only be applied to larger, more complex banks or authorised deposit-taking institutions (ADIs). Smaller ADIs with balance sheets comprised predominantly of mortgage-lending portfolios funded by retail deposits are likely to have stable funding in excess of that required by the NSFR. Regulators see limited value in applying NSFR standards to these entities.
Damien Wood is a Principal at Spectrum Asset Management, and manages the Spectrum Strategic Income Fund. Spectrum and the author have investments in either securities mentioned in this report or comparable securities. This article is for general information purposes only and does not consider the circumstances of any individual.