Demographers, economists and policy makers are increasingly concerned about the ageing population and increasing number of people aged over 45 who will start to transition into retirement over the next 20 years. In 2020-21, 39% of the Australian labour force were aged over 45 versus 32% in 2000-01.
Intergenerational reports prepared for Commonwealth and State Governments highlight challenges with the ageing population and the rise in the number of people who may choose to retire. This will have significant impacts on the labour force, consumption patterns and public finances and in turn on economic growth.
There does not exist an accepted approach for measuring the age of retirement. There is data on people accessing superannuation or aged pensions, but this doesn’t account for people who are still working. Sample surveys ask respondents if they are retired or likely to retire at a single point in time, but this does not capture the dynamic nature of the transition into retirement.
Without regular data on people’s transition into retirement, it is difficult to develop policy and programmes to deal with the challenges of an ageing population. To fill this void, KPMG has prepared an age of retirement dataset. To measure the age of retirement, KPMG has used the same approach as measuring life expectancy. That is, for a person aged 45 today, at what age are they expected to retire? The expected age is based on changes in the probability of remaining in the labour force for each year.
Expected age of retirement
In 2020-21, men aged 45 were expected to retire at age 65.2 and woman were expected to retire almost one year earlier at 64.3. Tables 1 and 2 present the expected retirement age for women and men for selected years between 2000-01 and 2020-21. Over this period the expected retirement age for woman has increased by 2.6 years and 2.0 years for men.
The increase in the expected age of retirement has been driven by a range of factors including:
- A shift towards service-based jobs and away from more physically demanding jobs
- Overall increased labour force participation among women due range of policy measures that have helped women strengthen their links to the labour force during their 20s, 30s and early 40s. This includes paid paternity leave (for both men and women), access to affordable childcare / early childhood education and more broadly increased focus on gender equity within the society and in public policy.
- Strong labour market conditions helping to retain older workers in jobs
- Changing social attitudes towards older workers
- Increasing trend towards part-time work amongst older workers.
The small increase in the expected retirement age for men is likely related to a strong labour market (due to closed borders limiting skilled immigration) which has encouraged older men to remain in the labour force for longer. Given the adverse impact of COVID-19 on female-dominated industries (e.g. retail and hospitality) the increase in the expected retirement age was not as noticeable as it was for men.
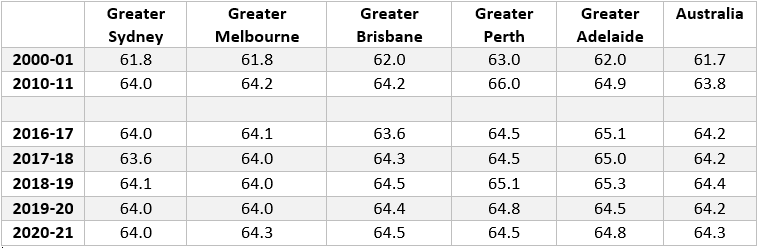
Expected age of retirement of women (selected years)
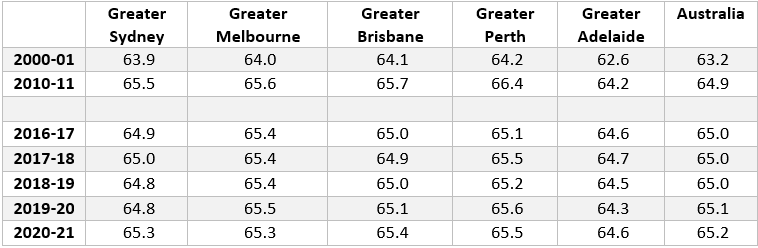
Expected age of retirement of men (selected ages)
City comparison
Comparing the major Australian cities, women in Australia’s largest cities of Sydney, Melbourne and Brisbane retire earlier than their counterparts in Perth and Adelaide. This may be driven by the relative cost of living, especially in Sydney and Melbourne which encourage older people to shift out of the city as they age to a lower cost regional area.
Over the past two years the expected age of retirement in the major capital cities has started to converge. This convergence is more noticeable for the expected retirement age of men, with increases in Sydney, Brisbane and Adelaide and small falls in Melbourne and Perth.
These movements are reflecting different economic trends in those cities, with a strong labour market in Sydney during 2020-21and a weaker labour market in Melbourne due to COVID-19 lockdowns.
Implications of later retirement
The length of retirement has implications for both individuals’ personal finances, and for government spending. An increasing age of retirement indicates that businesses will be able to access skilled labour for longer, although the data suggests that older workers would prefer to work part-time. This presents an opportunity for both workers and businesses to come together to retain skilled workers and provider older people with income, social interaction and intellectual stimulation.
In addition to those older people who are maintaining links to the labour force, there appears to be a cohort of older people who are moving away from the major cities into the regional area. COVID-19 may have accelerated this shift of people to regional areas.
This has the potential to create housing affordability problems for ‘local residents’ in regional communities. This can be addressed by strategic land use and infrastructure planning to take advantage of a growing population. Aged care and health service providers will also have to plan and build capability to deal with the increasing demands of a larger and older population.
There is also the need to continue to maintain momentum on gender equity. Ongoing business support and policy changes to further advance gender equity will help reduce the retirement gap between men and woman. This includes provision of more affordable childcare / early childhood education, more generous paid paternity leave for both men and women and reducing the distinction between primary and secondary carers between parents to name a few. These actions will help bring the retirement age of women in line with men.
Increasing the length of woman’s working careers will provide significant productivity dividends for the economy. It will also help to address the gender superannuation gap. KPMG analysis has found that in the years approaching retirement, the gender superannuation gap between men and women can be between 22% and 35%. The median superannuation balance for men aged 60-64 years is $204,100 compared to $146,900 for women, a gap of 28%. For people aged 55-59, the gender gap is 33% and in the 45-49 age group the gender gap is 35%.
Analysis is based on labour force participation data, five-year age groups from the Australian Bureau of Statistics Labour Force Survey, calibrated using detailed labour force survey data from the Census of Population and Housing.
Also see Wood, D., Griffiths, K., and Crowley, T. (2021). Women’s work: The impact of the COVID crisis on Australian women. Grattan Institute.
Terry Rawnsley is a Director, Demographics & Urban Economics, Planning & Infrastructure Economics at KPMG. This article is general information only.