Around the world in the last two weeks, people have rushed retail stores to buy physical gold. Perth Mint has reported sales are at their highest level in five years, and they traded over the weekend to cope with demand. People are queuing across Asian cities in panic-like conditions, while the US mint has been forced to cancel sales of its gold coins. Buyers are responding to the rapid price fall to USD1,322 per ounce in mid-April, the lowest level for two years.
What is most extraordinary is that retail investors usually react to rapid market falls in the opposite way. When equity prices drop, investors usually panic from fear it will fall further. Inflows to managed funds are always at their strongest when the market is at its peak, and outflows at their highest when markets bottom. But something else is happening with gold.

Source: Compiled by Grant Williams of Mauldin Economics from various public sources.
A brief look at gold price history
Most of the time over history, one ounce of gold has been able to buy items worth the equivalent of around USD500 in today’s dollars adjusted for inflation. It has done so for much of the past 2,500 years through many societies. Occasionally the gold price (when measured in paper currencies) surges when paper currencies devalue, but it then falls back again in real terms. If bought below its long run level, gold can provide a hedge against the devaluation of paper, but if bought above the level it is speculation, not ‘investing’. It is not a matter of whether gold represents a store of value or some other safe haven characteristic. For an investor, it is only worth buying when it is cheap.
The gold price reached USD1,900 per ounce on 5 September 2011 in the midst of the US debt ceiling and credit downgrade crises. Since then it has fallen by more than 20%, including a 10% fall on 15 April 2013, triggered by fears that Cyprus and the PIIGS may have to sell their gold reserves to repay debts.
Gold may shoot up to USD4,000 or USD5,000 in one of two scenarios: (a) an extreme left wing outcome resulting in run-away US inflation leading to a breakdown of society; or (b) an extreme right wing scenario with a Tea Party-led Republican government bringing back the gold standard. These scenarios look remote. People who bought gold in the last bubble in 1979-80 are still waiting to get their money back in real terms after inflation 33 years later.
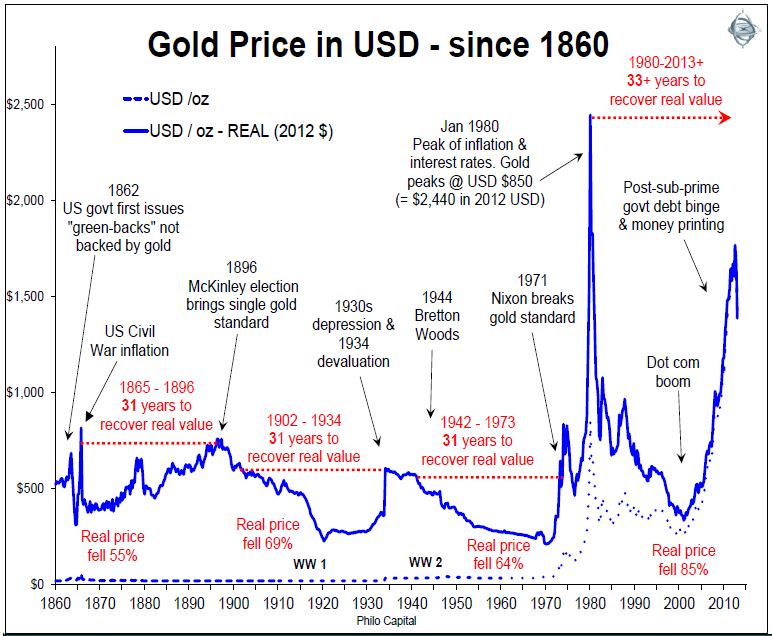
Investors cannot consider gold without also thinking about currencies and inflation, as the three are inextricably linked. Long term holding of gold makes sense as an inflation hedge or as a store of value if bought at or below the long term price around which it has oscillated for thousands of years. However, if paper currencies collapse, the nominal value of gold expressed in paper money terms can rise dramatically. So gold has most appeal if the investor’s home currency is about to experience massive hyper-inflation which destroys the value of paper money, which is unlikely in Australia in the near future. Or since the price of gold is expressed in USD terms, any expected rapid destruction in the value of a home currency may merit purchases of gold.
Of course, profits from short term trading are always possible as a more speculative bet, but long term portfolios are designed to look after long term needs, such as producing income and protecting wealth.
A copy of our comprehensive 2012 study of gold can be found here.
Ashley Owen is Joint CEO of Philo Capital Advisers and a Director of Third Link Investment Managers.