In last week’s article, we showed that the US Treasury defaulted three times on its treasury bills in 1979. They were ‘temporary’ defaults, but a default is a failure to pay debts promptly when due. Investors sued the US government in court for lost interest but they failed. The default crisis was a shock to Americans who thought that the US government would always pay its debts on time. The article was covered by Phil Baker in The Australian Financial Review, under the heading, “Think the US won’t default? It has before – three times”. Given the high profile of this issue, we thought it useful to take a quick look at what happened next.
Although the temporary defaults were a shock, they provided a catalyst that marked a complete turnaround of American fortunes, from the high inflation, high unemployment, high tax, stagnation of the 1970s, to the low inflation, low unemployment, low tax, booming 1980s. 1979 was the turning point and the start of the 1980s which saw the victory of monetarism and market capitalism over state-directed Keynesian, socialism and communism. In China, Deng Xiao Ping turned his back on communism as an economic system and started down the capitalist road, and within a decade the Soviet system and communist eastern bloc had collapsed.
The following charts are the same as in the previous article except they show the 1980s as well as the 1970s, illustrating how each of the measures turned the corner in the 1980s.
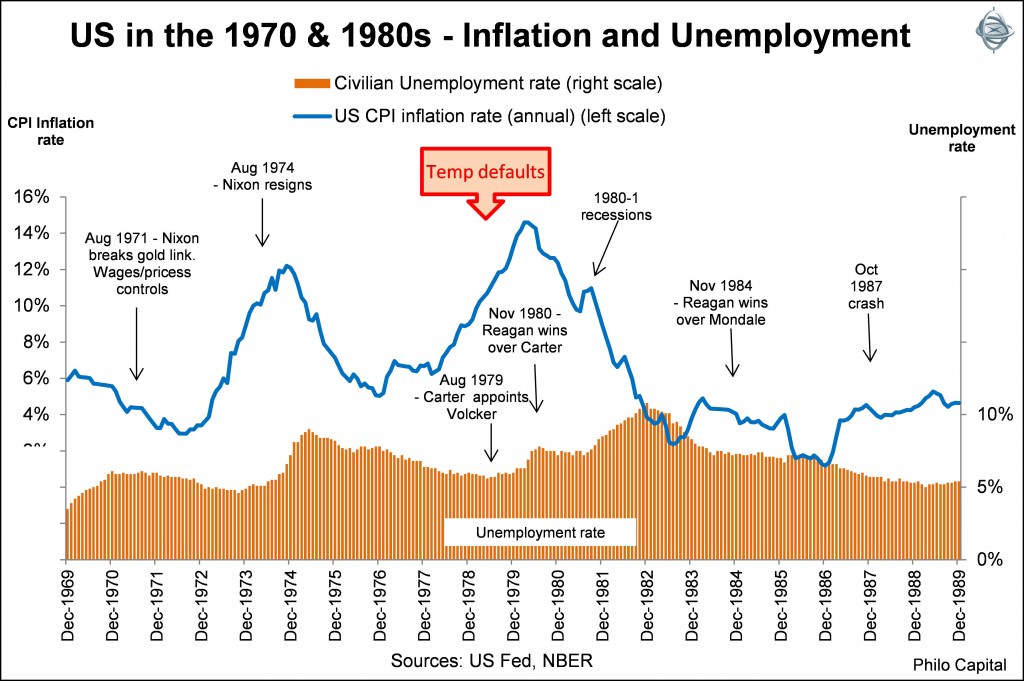
The first chart shows inflation and unemployment rising in the 1970s but both then falling in the 1980s following the 1979-1980 turning point.
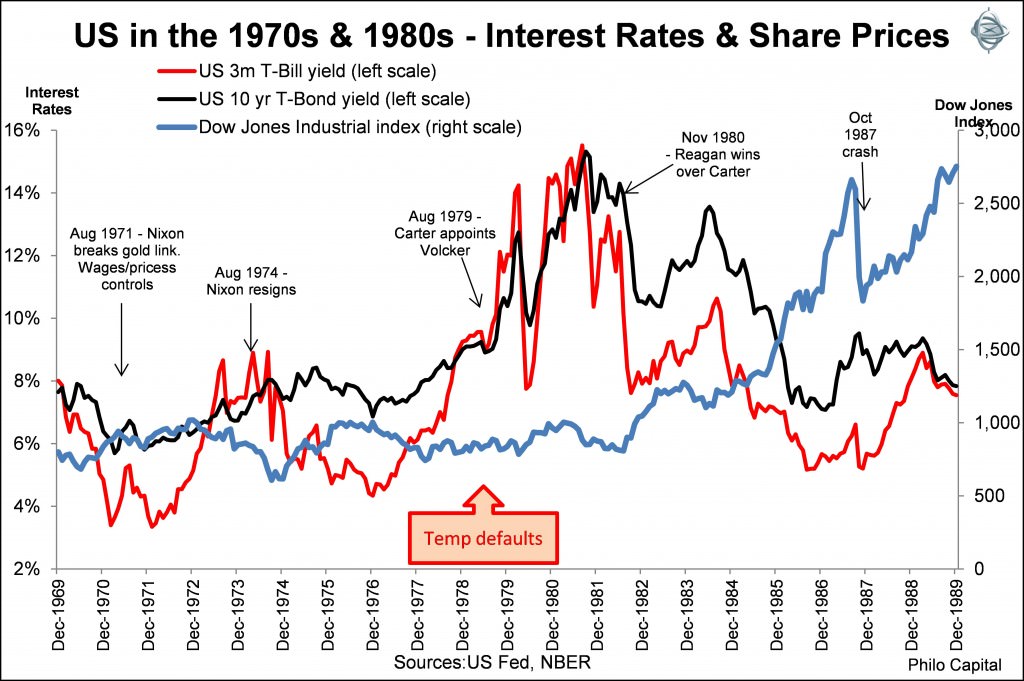
The next chart shows short and long term interest rates rising in the 1970s but then falling in the 1980s. It also shows how the stock market shrugged off the default crisis and turned the corner, shifting from the stagnant 1970s into the booming 1980s.
The final chart shows oil and gold prices rising in the 1970s, but then collapsing in the 1980s. It also shows how the US dollar ceased its 1970s decline, turning into strength in the 1980s. The dollar returned to such strength in the early 1980s that the US had to engineer a major international intervention, the 1985 Plaza Accord, to prevent its further rise.
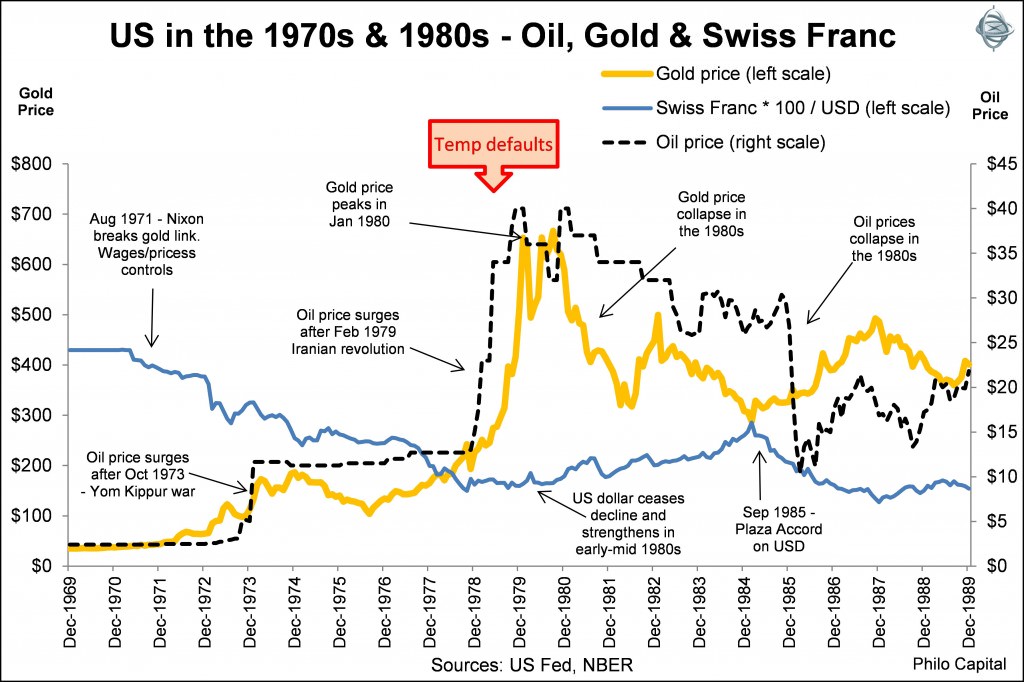
It shows how the US dollar was then, and still is, the global ‘safe haven’ currency. The US dollar strengthens in crises, even when US is the cause of the crisis, as it was in the 1979 treasury default crisis, the 2008 sub-prime crisis and even in the US credit rating downgrade in 2011.
Thus the deep financial, economic and political crises that came to a head at the end of the 1970s became the dawn of a brand new era of growth and prosperity for Americans.
Or so it seemed. The 1980s boom under Reagan was financed by a massive build-up of government debt, in which the US went from being the world’s largest creditor nation to the largest debtor nation, and the prosperity was built on a mountain of debt. It was good while it lasted, but it led to the 1995-96 government shutdown crisis as we described here.
Ashley Owen is Joint Chief Executive Officer of Philo Capital Advisers and a director and adviser to Third Link Growth Fund.