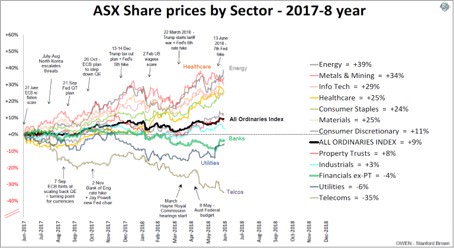
The broad Australian share market posted total returns (including dividends) of 14% for the 2017-2018 year. This was the sixth straight financial year of positive total returns (although the 2015-2016 year was line ball following the commodities price collapse). Here is a chart of the main sector price indexes over past 12 months.
Click to enlarge
Winners and losers by sector
The sectors that dragged down returns were the banks, telecommunications and utilities. They account for nearly half of the total market value. The main culprits were the banks (‘Financials ex-property trust’ sector above). All of the big dinosaur banks were down heavily with CBA the worst, down 12%. Macquarie, which is more of an asset manager than a bank, is the only local ‘bank’ with any global or even regional potential and was up a strong 40%. AMP was down another 30% for the year and is now more than 80% below its listing price 19 years ago.
Telstra fell another 39% over the year as it cut dividends and faces more cuts in coming years. Its share price is now 70% below its dot-com peak 19 years ago. Both AMP and Telstra were sleepy old institutions prior to their stock market listings but both were crippled by disastrous spending sprees undertaken by their imported American CEOs in their early years as listed companies. They have both been plagued by poor management distracted by cleaning up the messes of the past. Unfortunately, hundreds of thousands of retail investors were caught up in the hype drummed up for their listings in the late 1990s boom and many are still clinging grimly to their shares today.
Most other sectors of the market had a great year. Resources were the best, benefiting from rising commodities prices and finally a weaker Australian dollar. Miners were up strongly virtually across the board, led by BHP and RIO (up 45% and 32% respectively). Fortescue was the only major exception. In the Energy sector, all of the major oil, gas and coal stocks were up strongly on higher oil prices.
The Tech sector also rode the global tech boom. Computershare was up 30%, Carsales and REA both up 30+%. Healthcare stocks were aided by global healthcare strength, with CSL, Cochlear, Fisher & Paykel Health and especially Sirtex up strongly.
Although the overall Australian share market is not overpriced on a variety of valuation measures, our outlook for returns is rather subdued. The banks are facing a housing and construction slowdown, rising compliance costs, and management severely distracted by the fallout from the Financial Services Royal Commission. Falling housing prices, credit restrictions and rising mortgage interest rates risk hurting local demand for products and services, while exporters face lower global demand if the trade war escalates
Impact of a falling Aussie dollar on global equities
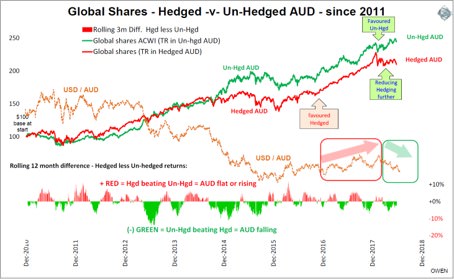
One of the big impacts on investment portfolios this year has been the Australian dollar, and how much of the currency risk in international share holdings was ‘hedged’ or ‘unhedged’.
Some global share funds have the currency risk ‘hedged’ (like the Exchange Traded Fund ‘VGAD’ and the Magellan Infrastructure Fund) while others leave the currency risk ‘unhedged’ (like the ETF ‘VGS’ and the MFS Global Fund). The decision on how much hedging to use can make a big difference to portfolio returns.
In the chart below, the red line shows returns in Australian dollars from global shares when the currency risk is hedged, and the green line shows returns when the currency is unhedged.
Hedged returns do better when the Aussie dollar is rising or flat (usually in booms), and unhedged returns do better when the Aussie dollar is falling (usually in busts). The lower section shows the relative returns between hedged and unhedged - positive red bars when hedged returns are beating unhedged (AUD rising or flat) and negative green bars when unhedged is winning (AUD falling). The orange dotted line running through the middle of the chart shows the US Dollar / Aussie dollar exchange rate.
Click to enlarge
This calendar year, the US dollar has risen and Aussie dollar has fallen. Hedged returns (red) have been flat as global shares have stalled, but unhedged returns (green) have continued to rise. It shows how performance of global shares for unhedged Australian investors can be affected as much by the currency as the underlying funds, companies or markets.
Ashley Owen is Chief Investment Officer at advisory firm Stanford Brown and The Lunar Group. He is also a Director of Third Link Investment Managers, a fund that supports Australian charities. This article is general information that does not consider the circumstances of any individual.