Now is a good time to remember the lessons of history about growth shares versus value shares.
Imagine that your rich aunt has passed away and left you a parcel of shares, but you must make a choice, and there is a condition. The choice is between receiving either $1 million worth of Amazon shares or $1 million of Walmart shares. The condition is that you can never sell the shares. You can only receive the dividends from the chosen parcel in perpetuity. Which would you prefer?
This choice comes to mind because recently Amazon became a more valuable company than Walmart. The market capitalisation of Amazon is $244 billion versus $230 billion for Walmart (all figures in USD).
If we didn't know better, we might think that since the market value of the two companies is similar their profits must be similar. But in fact in 2014 Walmart's net income was $15.7 billion whereas Amazon lost $0.2 billion. In its whole 20 year history the cumulative profits of Amazon are less than $2.0 billion. In the last 50 days Walmart has made more money than Amazon has in the last 20 years.
Figure 1: Return premium of Value stocks over Growth stocks, US 1927-2013
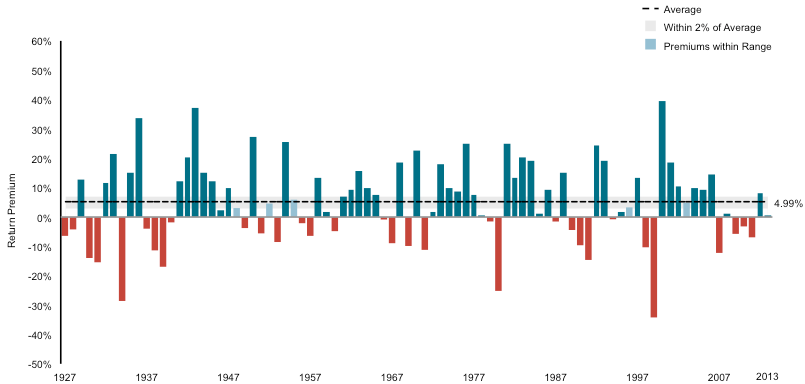
Source: Dimensional Fund Advisors
The graph shows, for each year, the return on a portfolio of the 20% of US stocks that have the strongest 'value' characteristics minus the return on the 20% of stocks with the strongest 'growth' characteristics. US stocks have 'value' phases (blue) when value stocks outperform and 'growth' phases (red) when growth stocks do better, but on average value stocks deliver much higher returns over time.
Give me the Walmart dividends
Obviously, the stock market is ignoring the difference in today's earnings and focusing on the higher expected growth in earnings of the two companies. The market sees a bright future of rapidly growing earnings for glamorous, high tech, disruptive Amazon and dim growth prospects for boring, old economy, sitting duck Walmart.
That may be so, but I will take the Walmart shares thanks. I want today's big Walmart dividends ($27,000 annually) versus the promise of large dividends from Amazon in the future.
We can't see into the future to which stock will outperform. But we can see into the past to the historic record of stock returns and that record is very clear - in the long run 'value' stocks like Walmart have higher returns than 'growth' stocks like Amazon.
Definition of value and growth
'Value' stocks are defined by their low share price relative to some objective measure of value. The share price of value stocks is low relative to:
- Dividends (a high dividend yield)
- Earnings (a low price to earnings (PE) ratio)
- Book value of equity (a low market value to book value ratio).
'Growth' stocks are the opposite to value stocks. That is, growth stocks have low dividend yields, high price-to-earnings ratios and high market value to book value ratios. High PE ratios are especially indicative of 'growth' stocks. Investors who will pay a high share price today per dollar of today's earnings must be expecting substantial growth in earnings in the future.
The graph above shows that, on average, across stocks and through time, value stocks outperform growth stocks by a lot. That is not only true for US stocks but around the world. There is no bulletproof theoretical explanation for why value stocks outperform growth stocks in nearly every country and through time (on average), but it is an undeniable regularity in the data.
The best explanation (to simplify somewhat) is that investors get too excited about stocks in new glamorous industries that are expected to deliver large dividends in the future. Those stocks on average don't deliver the expected dividends and then growth stocks underperform. Investors pay too much for stocks that promise large growth in dividends.
Value phases and growth phases
There are periods of multiple years in which excitement about growth stocks bids them up and they outperform boring value stocks that pay high current dividends but have low growth prospects. The US market may be in such a period now with digital technology stocks like Amazon, Facebook or Netflix.
So now is a good time to remember that investors who don't buy into over-hyped growth promises earn higher returns in the long run. That is an enduring lesson of not just the history of stock markets, but property market investments as well.
Dr Sam Wylie is a director of Windlestone Education and a Principal Fellow of the Melbourne Business School. Sam consults and teaches programmes for corporate and government clients and can be contacted on LinkedIn. This article is for general education purposes and does not address the needs of any individual investor.