The Federal Government's 2023 Intergenerational Report features an ageing population and rising demand for aged care as key themes impacting our economy and society over the next 40 years. These trends reinforce the need for Australians to consider their aged care needs rather than wait for a crisis before becoming aware of their aged care options, how to access care, and the financial decisions that need to be made.
What the report says about aged care
The report singles out the care and support sector as one of the major growth sectors over the next 40 years. It estimates that those aged 85 years or older will triple during this time, and the care sector will need to accommodate the needs of these people.
The Government predicts that ongoing budget deficits will limit its ability to fully fund the increasing cost pressures of aged care. These increasing costs are likely to see people fund a greater portion of their care needs where they have the financial means to do so. Australians need to plan ahead for their aged care needs and consider the costs and financial decisions associated with accessing aged care support. Aged care considerations should be a key part of their retirement planning.
Australia’s population is projected to grow from 26.5 million in 2022–23 to 40.5 million in 2062–63. The number of people aged 65 and over is expected to increase substantially and represent 23% of the population (around 1 in 4 people).
Longer life expectancies should result in Australians spending more years in full health. But on the flip side, we will also have an increased number of years in ill-health, which will accelerate government spending in health and aged care as well as the demand for aged care services and advice.
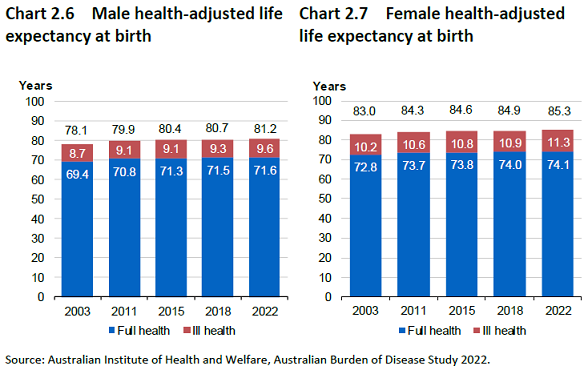
The average number of years that a person lives in ill-health has been steadily increasing in the last decades and this trend is expected to continue.
Funding for aged care
Most Australians who reach old age will need aged care services. The Australian Government provides funding for residential aged care and a range of community care – including home care – services.
The major aged care services subsidised by the Australian Government include:
- Home support services through the Commonwealth Home Support Programme and Home Care Packages, and
- Residential aged care services that provide 24-hour care and accommodation for older people who are unable to continue living in their own home.
Currently, people aged 65 or older currently account for around 40 per cent of total Australian health expenditure, despite being about 16 per cent of the population.
Australian Government spending on aged care is projected to grow from 1.1% of GDP to 2.5% in 2062-63 with the older population accounting for around 70% of the projected increase in real spending on aged care per person.
Spending on residential aged care will increase the most although spending on community care should also rise significantly. Aged care spending per person will also increase.
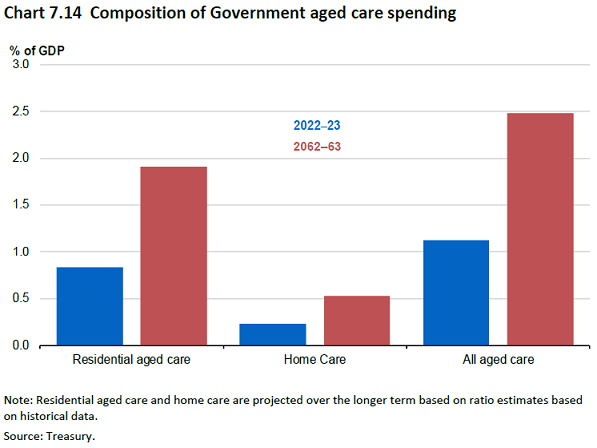
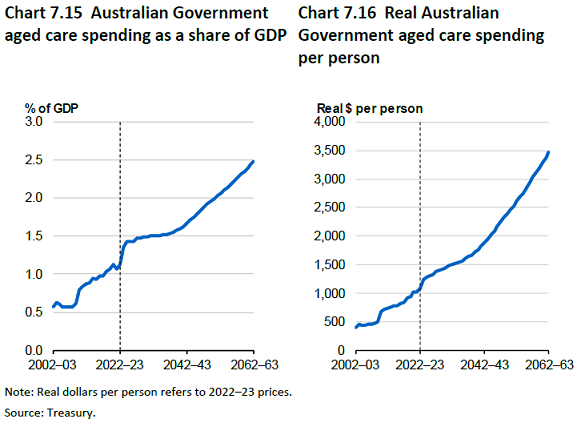
Australians need to consider the aged care options and strategies for themselves as well as their family members, particularly where they have caring responsibilities for an older family member. People who hold enduring powers of attorney for an older family member and are responsible for making financial and health decisions for them need to ensure that they have the resources and support to make informed decisions.
Assyat David is a Director of Aged Care Steps. This article is based on the author’s understanding of the relevant legislation at the time of writing. This information is of a general nature only. The author has not taken into account the goals, objectives, or personal circumstances of any person.