Sustainable investing has gained traction as a way to implement personal values in portfolios and as a means to draw on material environmental, social and governance (ESG) factors in seeking to improve portfolio performance.
However, with the emergence of the COVID-19 pandemic, it was an open question whether sustainability might become an afterthought as companies grappled with a collapse in economic activity and investors sought to insulate themselves from market volatility.
Although this is an ongoing story, the result has thus far been one of surprising resilience. Instead of pulling away from sustainable strategies, investors have increased their exposure, with strong flows into ESG mutual funds and ETFs in 2020. ESG enjoyed a substantial performance advantage, with U.S. equity socially conscious funds gaining 7.1% for the year through August, nearly doubling the 3.7% return for all other U.S. equity funds.[1]
On the corporate front, the pandemic has prompted heightened focus on ESG, and 'doing the right thing' has helped many companies navigate the crisis. It could contribute to reputational and competitive advantages in the years ahead.
ESG lens on the pandemic
At a high level, how has the crisis focused attention on ESG? The impact has been substantial, if somewhat uneven across the three elements of environmental, social and governance factors.
Environmental issues were already central to sustainability, given increased concern about climate change and the carbon impact of companies and portfolios. With the pandemic lockdowns, the world got a brief glimpse at the environment without the smog from carbon-based transportation and industry, and some hope as to what might be achieved through a transition to sustainable energy. Moreover, the disruption to supply chains (already an issue tied to trade conflict) reinforced the importance of reliability and redundancies across operations.
In general, the shift toward digitisation may help businesses build out supply chains. The balance between efficiency and security will likely need to be monitored closely with an eye toward climate effects, potentially providing a leg up to companies with a detailed grasp of their environmental impact.
Social concerns have taken center stage during the crisis, as companies faced enormous pressure to downsize in the face of a drop-off in demand. Even as the economy slowly recovers, limitations to in-person interaction and travel are causing a slow-motion decimation of many once-thriving businesses.
Meanwhile, the disease and its economic fallout have disproportionately affected minority and lower-income communities. For companies, responding with sensitivity could have lasting impact, along with meaningful commitments to help correct societal inequities that have proven so divisive.
Finally, effective governance has been highly important, as companies have faced many issues in a compressed timeframe. Having board members with an array of relevant expertise, and who aren’t overcommitted elsewhere, is essential to take appropriate actions with precision and decisiveness. Allocating capital not simply for efficiency but in demonstrating broader commitment may be both the right thing to do and additive when it comes to company reputation.
Assessing the corporate actions that worked
From the early days of the pandemic, many businesses took steps to address issues associated with the health crisis and economic shutdown. Depending on the industry, they announced a wide range of actions related to the crisis, including layoffs, employee furloughing, extended paid sick leave, guaranteed wages and changes to capital allocation plans. Working with Neuberger Berman’s Data Science team, we were able to sift through third-party data to determine what customers and employees have said about these companies, and thereby infer potential performance implications.
In some highly affected industries like airlines, hotels and gaming, corporate actions widely classified as negative, such as layoffs and furloughs, resulted in varying outcomes on employment review and rating sites.
For instance, some airlines with high employee satisfaction going into the crisis saw a positive trend in their reviews and overall CEO satisfaction, with comments such as, “when COVID-19 hit, they worked hard to protect their employees both physically and financially.”
In contrast, those with low satisfaction saw a deterioration despite similar corporate actions. To us, this suggests that treating employees well in normal times can help create a more resilient organisation in times of crisis.
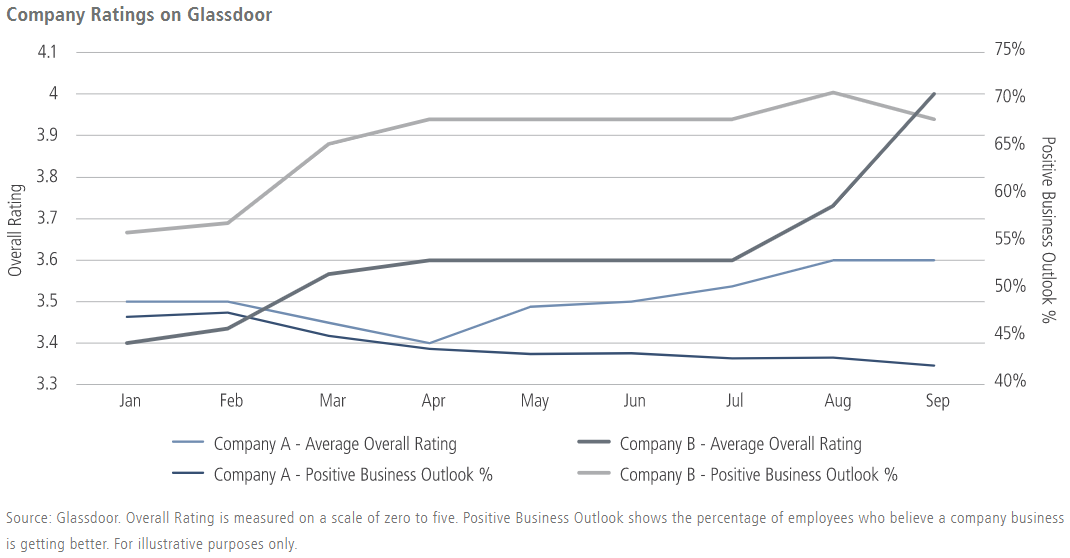
In gaming, the impact was clear-cut, with generous and responsible corporate actions leading to a marked increase in positive employment reviews, and vice versa. To illustrate, early in the crisis one casino operator (Company B in the display) continued to pay employees while its resort properties remained closed; the data showed positive employee reactions and reviews in response. Meanwhile, a competitor (Company A) saw a drop in ratings after announcing furloughs and layoffs, and a more modest subsequent recovery in ratings, as illustrated below.
Maintaining pay supported employee sentiment
Other industries required management teams to quickly adjust policies. In the case of one home improvement retailer, for example, initial criticism from employees on sick leave policy was quickly addressed by specifying that paid leave was for all employees who needed it regardless of whether or not they felt sick. Subsequently, the company temporarily raised hazard pay rates and initiated a second round of bonuses to all hourly associates.
Despite a potential lack of accommodative policies at the early onset of COVID-19 relative to peers, the company made constructive real-time decisions after that point, with a commitment to the support and safety of their employees. We believe a flexible approach that is open to employee feedback is critical in difficult circumstances.
Materiality in action
A key benefit of ESG research is to identify factors that could have a material impact on their operational and financial results. To illustrate, data security can be particularly relevant to technology companies while carbon footprint is a fundamental issue for energy firms.
Some time ago, we created the NB Materiality Matrix (excerpted below) to highlight such linkages, while drawing on our proprietary ESG 'Sustainability Score' rating system to pinpoint likely impacts at the company level. During the crisis, we have found that many of the factors we previously identified as material appear to have become even more important. Some examples follow.
NB Materiality Matrix: Select industries
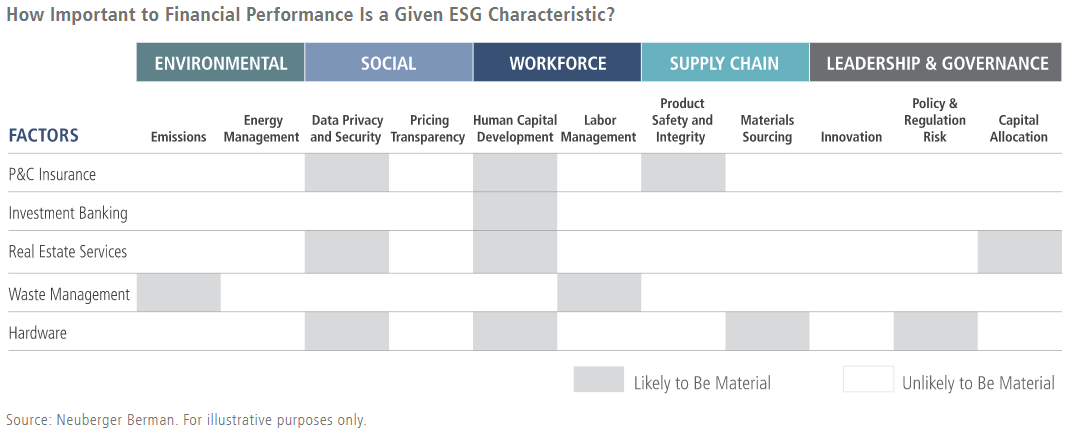
Labor management. Labor relations are a key issue when looking at waste management. Provider W carries an above-average environmental and social score within our proprietary ratings. Given the nature of its core business (solid waste management services), it provides an essential service. The company has worked to meet its customer commitments and minimize trash pickup service disruptions in a responsible manner. It took the initiative to raise pay for frontline employees, provide paid medical leave benefits, and enhance internal safety protocols.
Customer relations. Maintaining strong relationships with customers has always been important to the financial services industry but have now come further into focus. Big banks have largely been viewed as partners and a critical transmission mechanism for government stimulus programs. Many have processed an unprecedented volume of loans very quickly. However, we have seen significant divergence in their performance in scaling up disbursement operations. Some institutions have been criticized for acting too slowly, or favoring particular clients, while others have performed better. These institutions have also supported consumers and businesses in this crucial period through various forbearance programs.
Data security. Challenges around data security have always existed, but are garnering even more attention during the pandemic given that many businesses are being required to operate digitally. As a global technology provider, Company C has understood its responsibility to ensure that its products and services deliver value in a secure manner, such as through its videoconferencing platform. According to our proprietary ratings, Company C scores above the group average on privacy and data security, and has set a standard for creating a trusted partnership with its customers.
Capital allocation. Capital allocation decisions are among the most important factors around which we can engage with companies, especially during a crisis. Company R, a real estate investment trust, set what we consider a strong example for peers through the pause on its share-repurchase program, where all previously generated profits would be allocated to its nonprofit foundation and COVID-19 relief efforts.
Good governance and resilience in crisis
The crisis has shed light on the strength of ESG as an assessment tool, and the role to be played by responsible investors. Stakeholders have long memories and as conditions normalise, employees will likely remember how they were treated, as will customers, suppliers and investors. Relationships built on trust are likely to support nimbleness of operation, and the ability of companies to survive and emerge stronger than ever.
The tools we use to assess corporate actions have not changed. However, the gauges of transparency, responsibility and sound practices that might have drawn more subtle signals in prosperous times often simply flash red in times of crisis. Paying attention to these signals may be more crucial than ever.
As we peer over the horizon, we believe strong governance and sustainability practices will increasingly matter and may influence resiliency in future crises.
Jonathan Bailey is Head of ESG Investing at Neuberger Berman, a sponsor of Firstlinks. This material is provided for general informational purposes only and nothing herein constitutes investment, legal, accounting or tax advice, or a recommendation to buy, sell or hold a security. You should consult your accountant, tax adviser and/or attorney for advice concerning your own circumstances.
For more articles and papers from Neuberger Berman, click here.
[1] Source: Morningstar Direct. Reflects performance of funds’ oldest share class. Includes U.S.-domiciled open-end funds, where the Global Broad Category is equal to equity. U.S. equity funds include Large Blend, Large Growth, Large Value, Mid-Cap Blend, Mid-Cap Growth, Mid-Cap Value, Small Blend, Small Growth and Small Value Morningstar universes.