Frustrated that inflation isn’t falling fast enough, major central banks have continued their monetary tightening, in some cases coming back to it after a brief hiatus. And as the lagged impact of these aggressive rate hikes ripples through the economy, the broad trend remains for slowing growth for the remainder of this year.
From May last year till now, the Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA) has lifted its policy rate by 4% to 4.1% to tame inflation. And as the RBA reiterated in its September policy meeting, Australia may continue to experience the below-trend growth in the future, as cost-of-living pressures and the rise in interest rates continue to weigh on domestic demand.
With the balance of economic forces tilted against capital markets, investors have been rushing out of risk assets into safer ones (Chart 1). According to Calastone, equity, multi asset and property funds saw major outflows throughout H1 2023, while fixed income funds added A$1.3bn. In addition, there were signs of investors flocking to cash after rolling out of riskier assets.
Chart 1: Australian investors are fastening their seatbelts*
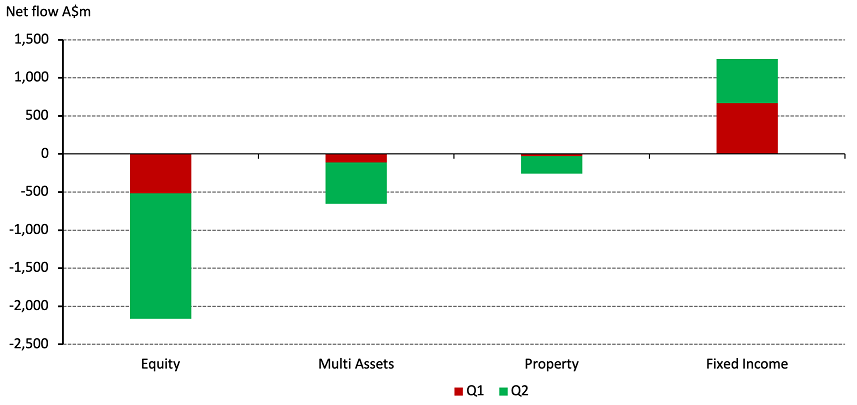
*As of 30 June 2023. Source: Calastone, World Gold Council
The risks for bonds
Fixed income assets currently seem like an attractive choice for investors. The sharp rise in bond yields since early 2022 and the rising possibility of rates peaking soon (Chart 2), after another rate pause in August, have improved the return potential in many fixed income sectors. And while flat to inverted yield curves make it less compelling to extend duration, a modest increase in duration could be prudent for investors seeking to hedge against a growth shock.
Chart 2: Investors are expecting lower rates than previous projections
Implied rates of Australian cash rate futures *
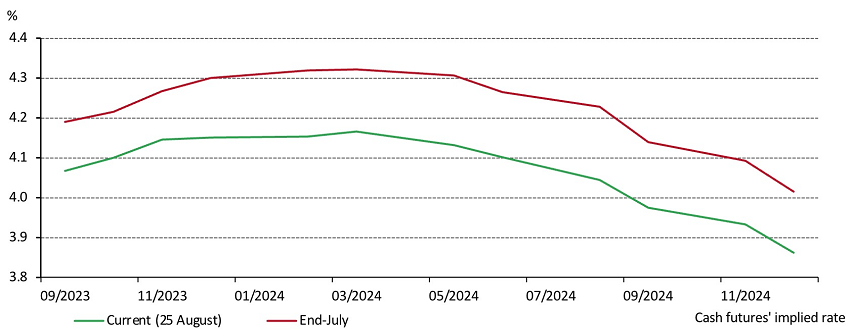
*As of 31 August 2023. Source: Bloomberg, World Gold Council
But there are risks associated with this view. Persistent inflationary pressure remains the primary obstacle to monetary easing and could even result in further tightening. Moreover, inflation volatility may be just one part of the medium-term inflation story. In fact, looking at the US experience, where we have data going back to 1870, inflation has tended to reappear in echoing waves at two and five years after it first spiked above 7% (Chart 3).
And the combination of short- to mid-term factors – such as surging unit labour costs and a tight rental market – as well as longer-term impacts from the green transition, deglobalisation and geopolitical uncertainties, indicate an environment in which there could be more frequent inflation shocks. The RBA also stressed in its latest policy meeting that sticky service inflation and the lag of monetary policy’s impact could provide further fuel for inflation to rebound.
Chart 3: Inflation cycle in the US since 1870
US inflation experienced multiple bounces after the first spike above 7%
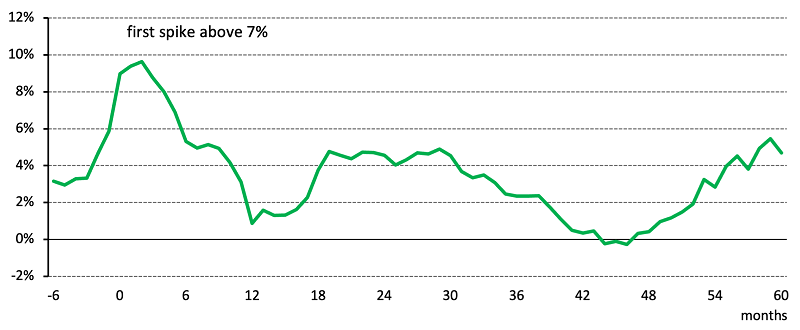
*Based on monthly US CPI y/y growth between January 1872 and June 2023. Source: Bloomberg, World Gold Council
Such an environment would require ongoing and fairly dramatic adjustments to monetary policy from the RBA, which in turn could introduce volatility, potentially below-trend growth, and the possibility of negative returns in Australian fixed income allocations.
Why a gold allocation makes sense
Against this backdrop there are advantages to diversifying the sources of safety in an investment portfolio beyond just high-quality government bonds.
Here's why gold can be a useful addition to portfolios:
1. Diverse sources of demand make it resilient and give it the potential to deliver solid returns in various market conditions (Chart 4). That's evidenced by recent gold performance: following a strong 2022 (+7%), gold in AUD capped another gain of over 12% during the first eight months of 2023, once again outrunning other major assets.
Chart 4: Gold and bonds can together be a potent portfolio diversification strategy
Returns from equities, bonds and gold during negative quarterly GDP growth in Australia, 1985 to 2023
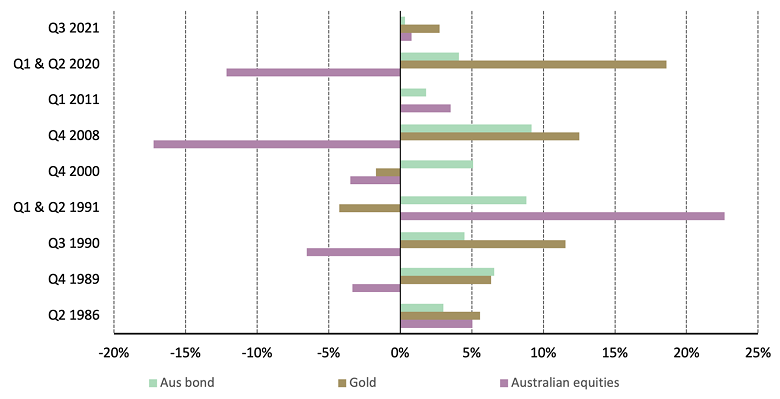
*Data from Q4 1985 to Q2 2023. Based on LBMA Gold Price PM, Bloomberg AusBond Composite Index and MSCI Australia Index. All calculation in AUD. Source: Bloomberg, World Gold Council
2. Gold is a particularly useful hedge against stagflation, a combination of stubborn inflation and slowing economic growth. During past periods of stagflation, gold in AUD has delivered a 27% annual average return, significantly outperforming other assets.1
These characteristics underscore our belief that gold has a key role as a strategic long-term investment and as a mainstay allocation in a well-diversified portfolio alongside equities and bonds. Looking ahead, gold and government bonds are likely to perform differently. That feature alone should appeal to investors, particularly those of Self-Managed Super Funds, and could be key to managing the potential risks ahead.
1 Based on data between 1973 and 2022, all calculations in AUD. For more please see: The relevance of gold for Australian investors in 2023 | World Gold Council
Jeremy De Pessemier is an Asset Allocation Strategist, and Ray Jia a Senior Analyst at World Gold Council, a sponsor of Firstlinks. This article is for general informational and educational purposes only and does not amount to direct or indirect investment advice or assistance. You should consult with your professional advisers regarding any such product or service, take into account your individual financial needs and circumstances and carefully consider the risks associated with any investment decision.
For more articles and papers from World Gold Council, please click here.
