Determining the value of gold can at times make potential investors hesitant. Being unable to judge what the price might do reduces confidence in making an informed decision. Gold in Australian Dollars (AUD) breached A$3,000 this year dipping slightly by the end of the first half of 2023, before reaching a record high in the last week. Now sitting above A$3,100, the geo-political events over the last three weeks demonstrate how hard it is to time the market. So, when is the right time to buy, or even increase, a gold allocation into a portfolio?
The global gold market is valued in US Dollars (USD). Gaining insight into such aspects as US real rates and the strength of the USD can help indicate what the price might do in the short to medium term. However, the gold market is much deeper and broader than just these two factors. Its demand is boosted by both economic growth and uncertainty. Since gold is a global asset, demand tailwinds from one region may counteract headwinds from another. These counterfactors pose their own challenges but also give gold its core characteristics as a unique investment.
Factors influencing the gold price
Without interest or dividends, typical discounted cash flow models fail when assessing gold. So too do other valuation tools often used for shares and bonds. Gold does not have any expected earnings or book-to-value ratios. But there is a good reason why it does not pay a coupon: with no issuer; it carries no credit risk. Its price is determined by the intersection of demand and supply, (with Australia being one of the world’s largest suppliers). Understanding these drivers, can give more assurance into what determines performance.
There is often a misconception that positive economic growth is bad for gold. The recent inflation figures from both the RBA (5.2%) and the Fed (3.7%), as well as other major economies has been encouraging. While these Consumer Price Indices (CPI) numbers have ticked up slightly, the consensus view is that we’re reaching late stages of the inflation cycle, with rates close to peaking. Eventually, there be come a time when talk shifts to rates decreasing to help kickstart local economies, and thereby enhance consumer spending.
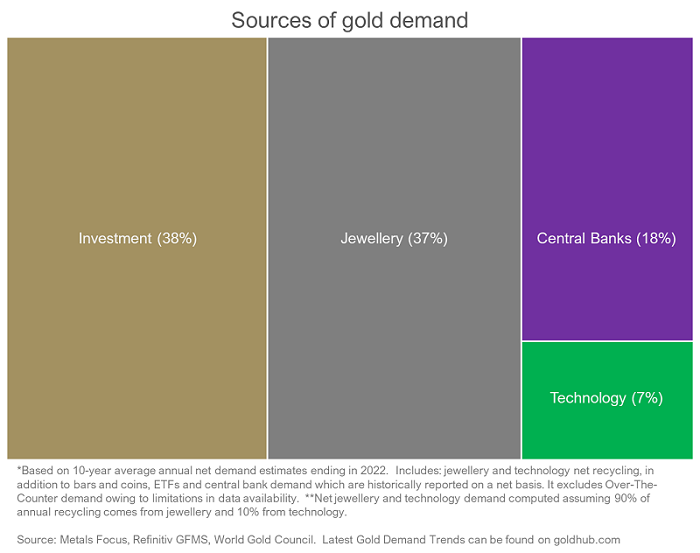
As almost half (44%) of gold’s demand originates from the jewellery and technology sectors, economic improvement generally results in increased appetite for such items. This is where regional demand tailwinds are relevant. Consumer demand, while global, is heavily weighted towards China and India who account for over half of jewellery demand.
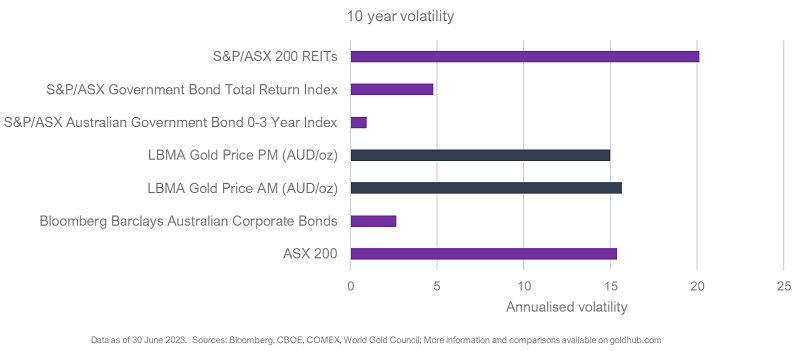
Investment demand (38%) can over the short term, exert strong pressure on gold’s price. This type of tactical demand from physical markets, exchange-traded securities and over-the-counter (OTC) products has historically experienced increases during periods of economic and political uncertainty, and falls as confidence grows. As gold is one of the most active daily traded assets, there is a tendency to suggest that it is highly volatile. Yet, in reality, over the medium to long-term, it is less volatile than Australian Real Estate Investment Trusts, and on par with the ASX 200.
Central Banks account for almost a fifth (18%) of gold demand to help diversify reserves. In the past, many have been forced to print more money. This increase in supply, while helping to stave off economic turmoil, carries the cost of devaluing the currency. Gold, by contrast, is a finite physical commodity whose supply can’t easily be added to. It is a natural hedge against inflation.
But diversification matters
All prudent investors will be mindful that protecting long-term investments is fundamental. When determining an investment strategy, questions over protection are generally focused upon;
- Is the portfolio diversified enough?
- Are the right defensive assets in place?
- Does the portfolio have liquidity available?
There is no standard diversification model. Investment appetite, fund life stages, and personal sentiment can result in allocations varying from one portfolio to another. But, according to a recent Calastone report, Australian investors fled managed international equity, property and mixed asset funds at a record level during Q2 2023. Fixed income funds were the beneficiaries. Given the higher interest rate environment, this is not too surprising. Many investors look upon these products as fulfilling a traditional role of diversification, offering protection during periods when risk assets have come under pressure. In the main, fixed income products certainly help, but they are not absolute.
When inflation is below 2%, the correlation between global equities and treasuries has been negative, providing diversification. At levels above 2%, this relationship has historically started to break down.
The right gold allocation
Understanding the broader drivers of gold’s price can improve investor confidence, and unlike some other defensive assets, gold has various demand sources, which complement the other over different economic and market conditions.
The answer to when there is a good time to buy gold depends upon the investor’s strategy and objectives. A diversified portfolio needs the insurance over the medium to long term to help ride out unforeseen market events. Gold can help achieve that, but can also stand its ground in calmer times (if history is anything to go by). Therefore, there is never a bad time to think about the right allocation.
Jaspar Crawley is Head of Institutional Investor Relationships, APAC ex-China at World Gold Council, a sponsor of Firstlinks. This article is for general informational and educational purposes only and does not amount to direct or indirect investment advice or assistance. You should consult with your professional advisers regarding any such product or service, take into account your individual financial needs and circumstances and carefully consider the risks associated with any investment decision.
For more articles and papers from World Gold Council, please click here.
