Regular equity income can help manage longevity risk and exposure to rising prices but finding quality income in equities is not as simple as it seems.
Investors in the later stages of their accumulation phase, approaching retirement and in retirement can benefit from the use of equities as part of their overall income plan. With a rolling 10-year dividend yield of 4.2% excluding ranking (Source: S&P Dow Jones, S&P/ASX200), Australian equities can provide a vastly more attractive income than many alternatives.
Investors face two major risks that impact how much money they have to fund retirement, and how long it will last: longevity risk and the risk of inflation. In simple terms, longevity risk is the risk of outliving your money. Inflation risk is the risk that rising costs (such as healthcare) reduce the purchasing power of your money each year. An equities approach to income can help outpace those rising costs and provide long-term capital appreciation to help replenish funds.
Why does active dividend income investing work?
An active dividend investment approach can add value to a portfolio and generate outperformance through investing in quality companies with strong dividends and dividend growth. The focus is on companies with sustainable earnings growth, maximising the benefits available through the tax and imputation system and tactical allocation to capture a greater share of dividend income.
Markets are not perfect. The first and most fundamental reason that an active approach to income investing works is the fact that the market is relatively inefficient, particularly in the short term. However, some inefficiencies can be traps.
The risk of chasing yield for yield’s sake
Many income investors assume the relationship of current dividend yield to future earnings growth is linear, that is, the higher the dividend yield, the higher the future earnings growth from which dividends are paid. This assumption does not actually hold in the market.
Figure 1: The highest dividend yields do not equate with earnings growth the year ahead
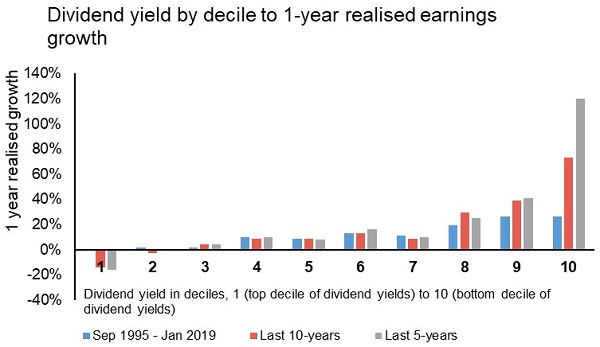
Source: Ausbil, Macquarie Equities.
On average, the top dividend yield companies actually see low, or even negative, earnings growth going forward compared to companies in the 4th to 7th decile of companies, as illustrated in Figure 1. This has been true for the last 20 years.
An active approach does more than simply chase the highest yield, as would a passive approach to yield. An active dividend income strategy can increase income from companies whose dividends are healthy, but maybe not the highest, because they are also investing earnings into a growing business, hence into better earnings growth in the year ahead.
Another quirk of dividend investing is that the highest yielding stocks are more volatile, as illustrated in Figure 2.
Figure 2: The highest dividend payers are also the most volatile
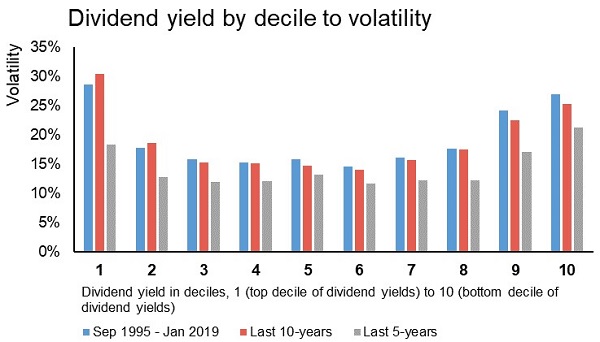
Source: Ausbil, Macquarie Equities
Top decile dividend yielding companies tend to show higher volatility in returns, on average. An active approach seeks to reduce portfolio return volatility by not chasing yield for yield’s sake.
Finally, top dividend paying securities may not be good value-for-risk, as illustrated in Figure 3.
Figure 3: Top dividend paying securities may not be good value-for-risk
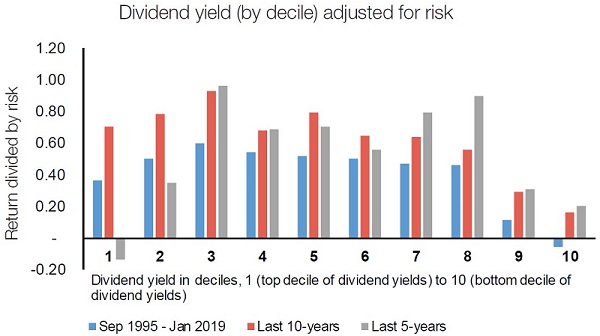
Source: Ausbil. Macquarie Equities
Chasing the highest dividend yield companies can provide poor value for risk taken when compared to the market. Lower decile stocks by dividend yield demonstrate a better performance for risk than for the top decile of dividend yield companies.
High dividend payout ratios may also be indicative of a lack of equity reinvestment opportunities for a company into growing its own business. A company with a sustainable dividend profile usually seeks to reinvest some earnings into their business, into positive return projects that can generate earnings growth in the future. A classic example of a high dividend paying company compared to a company which has reinvested some earnings into productive opportunities for reinvestment is the difference between Telstra and CSL.
Figure 4: The dividend journeys of two different companies
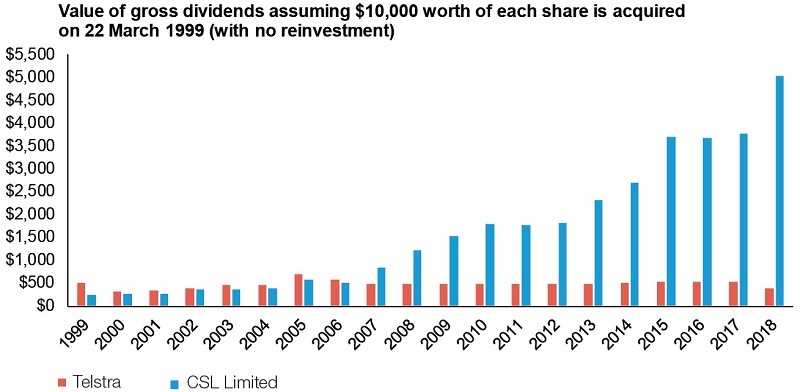
Source: Ausbil
It’s not only about dividend yield
Telstra was long considered a key dividend paying stock but the burden of being the largest telco, legacy systems and infrastructure cost, rapid change and limits to growth have seen Telstra lose its status. By contrast, CSL has steadily transformed itself from also being government owned, as the Commonwealth Serum Laboratories, into a global leader in biotechnology. It has balanced the payment of dividends with significant reinvestment into areas that can generate future growth in earnings, as illustrated in figure 4. Of course, these relationships may change over time, but it can take a long time for a company to change its course.
Astute active dividend income approaches can seek dividend yield while avoiding companies with no opportunity to reinvest to improve earnings and returns. With active dividend income approaches, investors like SMSFs, retirees and investors approaching retirement can diversify away from traditional sources of income, like fixed income and term deposits, for a longer-term approach, diversified across high-quality Australian companies. They can do this in equities without sacrificing the potential for long-term growth.
Michael Price is Portfolio Manager of the Ausbil Active Dividend Fund at Ausbil Investment Management. This report contains general information only and the information provided does not constitute financial product advice. It does not take account of your individual objectives, financial situation or needs.