The Year of the Dragon holds particular significance in Chinese culture. As the only mythical creature in the Chinese zodiac, it symbolises light, authority, and prosperity, promising good fortune.
While revered in China, Western folklore often associate dragons with darkness and destruction. The contrast between these interpretations underscores the uncertainty surrounding the year ahead and its potential implications for financial markets.
Western dragon
In financial market terms, the Western dragon symbolises a recession, casting darkness over the labour market and corporate profits, and wreaking havoc on valuations in risk assets such as equities and high-yield corporate bonds. Since the beginning of 2022, market consensus has repeatedly anticipated the emergence of the Western dragon from its hiding place. Poor leading economic indicators, contraction in bank lending, and elevated interest rates: something must surely break. Let's examine these factors individually.
Poor leading economic indicators
The Leading Economic Indicator (LEI) index is comprised of various inputs that typically precede changes in overall economic activity, including economic measures like employment and business activity. Since 1990, the LEI has turned negative on average 12 months prior to a recession. However, lead time varied to as short as six months (2020 recession) and as long as 19 months (2007 recession). Despite the LEI in negative territory for the past 20 months, a recession has not materialized. Why?
Figure 1: The leading economic index is heavily dependent on the manufacturing cycle
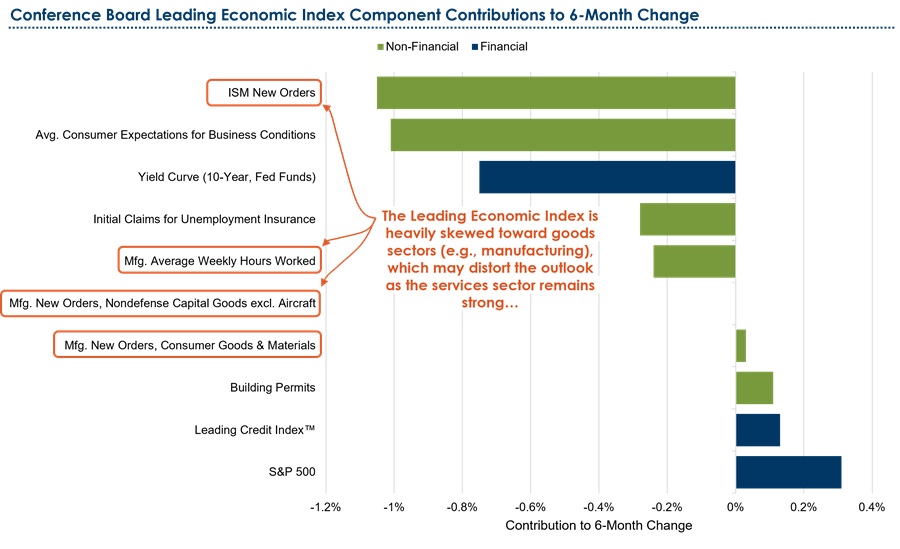
Source: Conference Board, Payden Calculations
The composition of the LEI index changes over time, with modifications to both inputs and weights based on past experiences involving the economic landscape. This makes sense as models should be adjusted to conform to changing environments. For example, the aggregated economic output (gross domestic product) in the US today is comprised of 80% services and only 9% manufacturing, a material change from nearly 30% of output deriving from manufacturing 40 years ago. In contrast, the LEI index currently includes ten measures in total, with four of those measures related to manufacturing. This discrepancy skews the LEI towards manufacturing, diverging from the actual composition of economic output.
Elevated real rates
Global interest rates have been rising for nearly four years, most notably in developed markets, at a pace unseen since the 1970s.
The natural response to such a rate hike is concern that it may be too restrictive and unsustainable, leading to an eventual breakdown. Undoubtedly, a few things have broken along the way: the cryptocurrency market in 2022, the regional banking episode in 2023, and the broader office sector within commercial real estate. This raises the question: Are interest rates too restrictive? The answer likely depends on your timeframe.
Using 10-year real rates in the US as an example, from 1990 to 2002, they averaged 3.8%. From 2002 to 2023, the average dropped to 0.9%. Since the beginning of 2023, they have averaged 1.7%, with current rates at 2.02%. Are these rates restrictive? When put in the context of the 2000s and 2010s, the answer is yes. However, in the context of longer- term history, the answer is no.
Eastern dragon
While the Western dragon has made several attempts to emerge from hiding, the Eastern dragon has been occupying the skies for multiple quarters, largely shining light and prosperity on financial markets. Global growth has remained robust, particularly in the US, as the Eastern dragon has been fuelled by a combination of fiscal stimulus, abating inflation, and a more balanced posture from global central banks. However, as the benefits from these factors diminish, the Eastern dragon must seek new sources of strength to continue its ascent in 2024. Let’s examine these sources.
Strong labour market
The global labour market has enjoyed robust health for several years, fuelled by the reopening of economies and the corresponding demand surge post-Covid. However, signs of labour divergence are emerging, particularly in developed markets.
When assessing the labour market wages should also be considered. Nominal wage growth remains elevated in most developed countries, with real wages rising as inflation declines. The result is more money in the pockets of consumers, providing a tailwind for consumption. This trend is particularly noteworthy in the US, where fiscal stimulus has been substantial and household leverage lower compared to other developed countries.
With all that said, the Eastern dragon should remain vigilant. Preliminary signs of labour market softening include a downward trend in overtime hours and a shorter aggregate workweek over the last few years.
Financial conditions
How should the Eastern dragon interpret current financial conditions? First, recent readings of real-time measures like the Goldman Sachs (GS) Financial Conditions Index remain below 30-year averages, indicating an environment favouring easing over restriction. Second, November and December 2023 witnessed the largest two-month easing in the GS Financial Conditions Index for several decades. Third, global monetary policy has shifted from a hawkish and hiking stance to one of leniency and easing (see chart below). This shift in policy should help mitigate disruptions in financial conditions associated with growth concerns or turbulence in the financial system’s workings. Finally, while varied in magnitude, global fiscal policies continue to be accommodative, especially in developed countries where austerity measures are deemed undesirable.
Figure 2: The global monetary tide shifts from policy tightening to easing
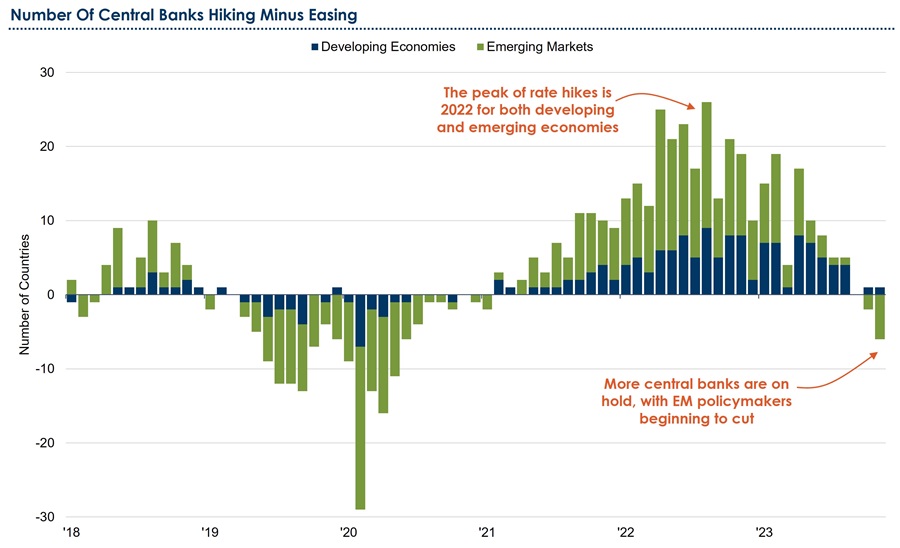
Source: Bank for International Settlements, Bloomberg
Implications for markets
The synergy of a robust labour market and a collective easing of financial conditions is poised to keep the Eastern dragon airborne for the first part of 2024, but we suspect a strong interconnection between the two dragons. The Eastern dragon’s growing strength heightens the chances of the Western dragon stirring from its slumber, as a stronger for longer market, coupled with favourable financial conditions and rising asset prices, increases the probability of economic growth, and by extension, inflation. This may curb expectations of continued loose monetary policy, leading to higher interest rates, diminished asset values, and tighter financial conditions. The resulting negative wealth effect could dampen consumption, weaken the labour market, and ultimately trigger a recession, awakening the Western dragon.
The current environment differs from the last 20 years given elevated yields in liquid public markets and an inverted yield curve. Credit spreads in most sectors are deemed fair at best and expensive at worst. Hence, investors may capitalise on market conditions by shortening maturity profiles, upgrading credit quality and transitioning from less liquid private markets to more liquid public markets.
Figure 3: Correlation Between Rates and Risk Assets: Inflation Matters
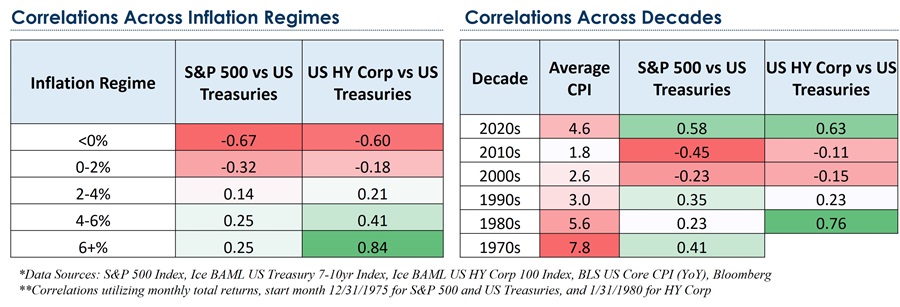
Source: Payden & Rygel, Bloomberg
Eric Souders is a director portfolio manager at Payden & Rygel, a specialist investment manager partner of GSFM Funds Management, a sponsor of Firstlinks. The information in this article is provided for informational purposes only. Any opinions expressed in this material reflect, as at the date of publication, the views of Payden & Rygel and should not be relied upon as the basis of your investment decisions.
For more articles and papers from GSFM and partners, click here.