This month marked the 10th anniversary of the launch of the original Apple iPhone. It was another reminder of how dynamic the global investment landscape has become in recent years. While Apple investors cheered the launch of the smartphone device, it would be difficult to think that they, or even founder Steve Jobs, would have appreciated at the time just how significant the device would be to some industries over the following decade.
The iPhone underpins market growth
The market capitalisation (cap) for Apple, already growing well on the back of the refreshed Mac and iPod offerings, was at US$105 billion at the time of the launch. A decade later, the business commands a market cap of more than US$750 billion. The equity value generated to shareholders over that period cannot be entirely attributed to the iPhone, but its introduction would prove to be a critical inflection point for both Apple and a multitude of other industries in bringing the internet into the consumer’s pocket. It is estimated there are over 700 million active iPhone users globally, while more than half of the entire world’s population has access to an IOS or Android smartphone device.
Opportunities and threats of new technology
Investors today are increasingly challenged by both the opportunities and threats that new technologies bring to established business models. The investment management community needs to continually review and re-test the potential for a company to be disrupted by an emerging entrant or identify an inherent opportunity in new business models. With more sophisticated technology, globally-connected communities and a venture capital industry that is willing to fund untested business strategies, the rate of change and the consequences of those changes continue to increase dramatically.
In the iPhone’s case, the impact from its introduction extended well beyond smartphone unit sales and broader industry market share. Entire industries have been created as a result of ready and easy access to the internet on a personal device. Telco operators, for one, have been huge beneficiaries from significant growth rates in data usage. Telstra, for example, has experienced a nine-fold increase in Australian mobile data consumption in the last five years alone, a trend that has been equally replicated on the global stage.
Global mobile data usage vs voice 2011-2016
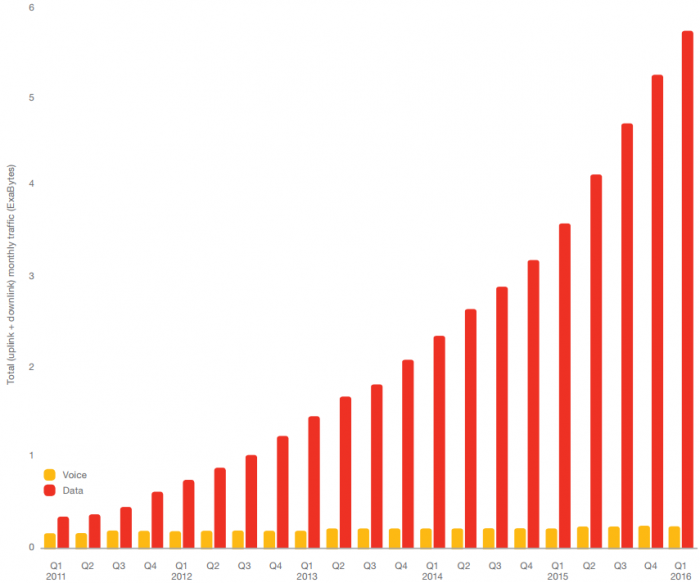
Source: Ericsson Mobility Report 2016
The smartphone also paved the way for an entire wave of new app-based business models such as Uber, SnapChat, WhatsApp and Spotify, all dependent on smartphone functionality. Using the latest available private valuation data, those four companies alone now have combined equity value of about US$120 billion, which is higher than Apple’s total market cap at the time of the launch.
The hyperbole is seemingly endless, from the enormous subsequent growth in active users for social media heavyweights Facebook, LinkedIn and Twitter to the estimated US$70 billion in earnings generated by the global app developer community since the launch of the Apple App Store in 2008. These are entire industries and companies that did not exist less than 10 years ago and for investors that were able to recognise the opportunities early, the returns have been exceedingly profitable.
Casualties are left in the wake
Momentous change also often brings with it inevitable casualties, where the products and companies that are unable to adapt are often ruthlessly left behind. In the iPhone’s case, manufacturers of digital cameras, personal GPS products and older-world mobile phones were unable to recover from the onslaught of multi-media smartphone devices. At the time of the iPhone’s release in 2007, Blackberry held about 50% of the mobile phone market in the US, with the company’s market cap peaking a year later just shy of US$80 billion. Ten years on, the company now trades with a market cap of US$5 billion.
Small and mid-cap providing opportunities
In Australia, there are ample opportunities to identify businesses that can benefit from emerging structural changes. While the larger cap end of the market tends to skew more toward older-world business that will likely view disruption as a threat, the emerging small and mid-cap company space has provided investors with opportunities to benefit from rapid and broad-based change.
The recent move by small and large businesses to host IT infrastructure in the cloud, for example, has created enormous tailwinds for the providers of external data centres and IT services. Where businesses once located their IT systems and servers on their own premises, cloud technology enables this function to be outsourced. NextDC (ASX:NXT) is a large provider of data centres and has seen its revenue more than double over the last three years.
For outdoor advertising, the introduction of digital screens and electronic billboards single-handedly revitalised an industry that before 2012 looked devoid of any meaningful growth. The ‘Out of Home’ media industry in Australia has seen revenues grow by more than 50%. After an initially shaky start to listed life, the share price of Ooh! Media (ASX:OML) has almost doubled since its ASX listing in December 2014.
OML revenue growth over ten years
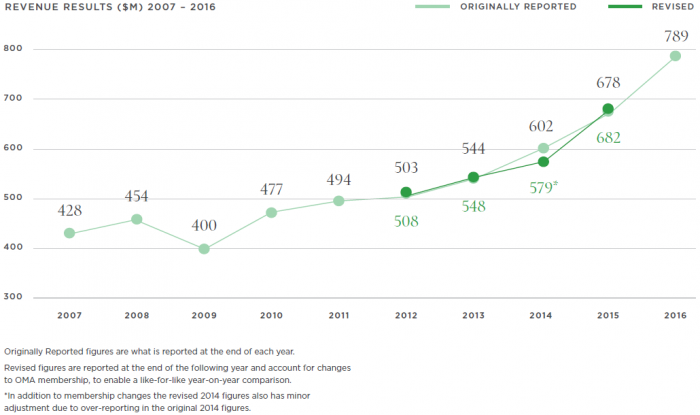
Source: Ooh! Media Limited 2016 Annual Report
The opportunities available from new technologies and new markets have also extended into the more traditional primary industries. The fortunes of dairy and infant milk formula provider A2 Milk (ASX:A2M) may have been less stellar without the emergence of cross border e-commerce retail websites (Tmall, JD.com) that opened up an entirely new market into China. A2 Milk generated just NZD$42.2 million in group sales in 2011 while that figure is expected to grow to above NZD$540 million at the coming FY17 results.
In an economic and corporate landscape that continues to evolve at an increasingly rapid rate, investors need to balance the threats of change to traditional business models with the opportunities available for new ones. One of the real pleasures of investing within the emerging companies space is the variety of businesses and industries available to leverage to these emerging trends.
Andrew Mitchell is Portfolio Manager and Co-Founder at Ophir Asset Management. This article is general information that does not consider the circumstances of any individual.