Global markets have entered a difficult period as fundamentals turn and the spectre of inflation remains on the horizon. As global economies faced myriad difficulties over the past couple of years, governments responded by supporting their economies through various crises with large amounts of debt. That, in turn, has meant the equilibrium level of interest rates has continued to get lower and lower.
But while higher inflation is now driving interest rates back up, it is unlikely they are headed back to where they were previously and ultimately, we are still living in a low-rate world.
Highly indebted governments (and consumers) can not afford rates to reach levels much above 3%. If they do get too high, the risk is that economies will be pushed into recession again.
All of this means it is a tough time for growth managers, and growth equities have been under pressure for some time. In fact, many of the problems in global equity markets were apparent as early as March of last year.
Investors need to remember that in any market environment, earnings growth drives stock prices. It's not an equity market. It's a market of stocks. So those companies producing great earnings growth can continue to do so through any cycle. It may not happen in a straight line, but it will happen.
Identifying big technological and structural changes in society are a key component in recognising opportunities. One of these areas that we are focused on is High Performance Computing. But more about that later.
Market outlook
First let’s assess the current market outlook. As outlined above, we still believe the big picture is a low-rate world continuing to underpin high asset prices in the medium to long term.
In the short term, inflation is causing interest rates to go up. And expectations around interest rates have changed rapidly in the last 12 months alone. In March 2021, the US Federal Reserve was forecasting no rate hikes for the next three years. By December, estimates had increased to three rate hikes, rising to seven by March, with latest estimates at close to 10.
A simple way to think about markets is that if you take the earnings yield of the S&P 500 and subtract the US 10-year bond yield, you need to get a carry, or positive return, for taking the risk of owning equities, in the same way you expect a carry for the risk of owning a house or for owning high yield credit.
That carry has remained roughly the same at 3% for a long period. Markets might have gone up a lot, but interest rates have gone down a lot too, which means the market has not gotten more expensive for a number of decades.
We're now seeing that equity risk premium move below 300 basis points for the first time in a long while and that is creating volatility in equity markets. Fortunately, as long as you assume that interest rates won't get much above 3% in the long term, that equation will work itself out over time.
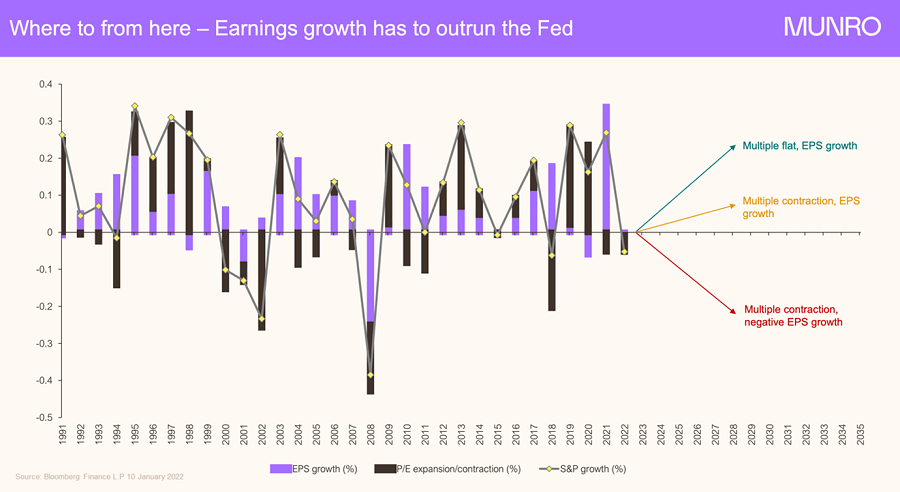
The above chart shows the different movements in S&P 500 earnings per share (EPS) growth, price-to-earnings (P/E) multiples and index growth over the past three decades. There are varying periods of P/E multiple expansion/contraction, EPS positive or negative growth and market movements.
We believe the most likely scenario for the year ahead is P/E multiple contraction and EPS growth. That is slower EPS growth this year and P/E contraction, and potentially reduced growth next year with more P/E contraction.
However, the worst-case scenario outcome – of P/E contraction and negative EPS growth – would require a large proportion of big US companies to simultaneously experience earnings contraction, something that is highly unlikely.
Area of interest – the fourth era of computing
Investors invest in equities – not economies – and equities are driven by structural earnings growth, and this is why we like to identify key areas of Interest and structural change.
Semiconductors are one such area. Semiconductors have gone from a zero per cent market, or zero per cent business, nearly four decades ago, to half a trillion US dollars today. Semiconductors now are on their way to becoming a $US1 trillion business as we head into the fourth era of computing, or the artificial intelligence (AI) era of computing.
As every single device in the world becomes connected to the internet - your fridge, your garage, your security system, your airport parking, etc – a multitude of data is going to go up into the cloud. Once there, it needs to be processed at incredibly fast speeds with AI in order to create predictive outcomes. This is already happening to some extent with, for example, streaming service recommendations.
But all this high-speed data processing is going to require more GPUs or graphic processing units to create accelerated computing. We are forecasting that the server market has the potential to grow from roughly $US25 billion per annum today to nearly $US250 billion, or by a multiple of 10, by 2035.
There are only three or four companies worldwide that are in this highly focussed world of high-performance computer architecture and one of our favourites is semiconductor company AMD (Advanced Micro Devices). As a growth stock, it’s obviously not currently popular, but it’s going to get very exciting very soon.
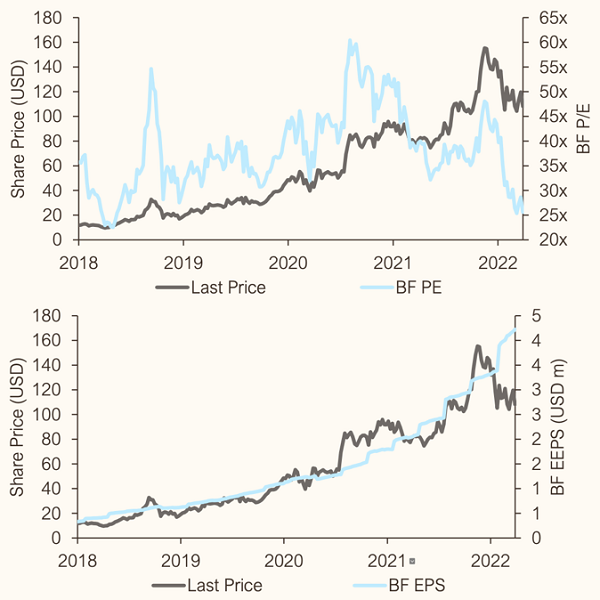
Source: Bloomberg Finance L.P 1 April 2022
As indicated in the above chart, AMD’s earnings growth has grown structurally over time and will continue to grow as more and more companies invest in this product. Not so long ago you had to pay 30 times earnings for AMD, but you can now buy it at 18 times earnings, even though it’s growing its earnings at 35% this year. We forecast it will grow its earnings at 30% next year as well as it really is one of the great growth opportunities of the future.
Final word
There is no doubt it’s a tough time to be investing in growth stocks but by continuing to identify the structural areas of interest, such as accelerated computing outlined above, growth fund managers and investors can take advantage of lower prices and be well positioned when the market and interest rates do return to some level of normality.
Nick Griffin is Chief Investment Officer at Munro Partners. Munro is a specialist investment manager partner of GSFM Funds Management, a sponsor of Firstlinks. The information included in this article is provided for informational purposes only. Munro Partners do not represent that this information is accurate and complete, and it should not be relied upon as such. Any opinions expressed in this material reflect our judgment at this date, are subject to change and should not be relied upon as the basis of your investment decisions.
For more articles and papers from GSFM and partners, click here.