The $200 billion Future Fund is not alone in its enthusiasm for private market investments. One of the most significant financial trends since the turn of the century has been the explosive growth in private markets.
Private Equity is the cornerstone of the Future Fund’s illiquid portfolio, accounting for 16.8% of total portfolio allocations, second in size only to their global listed equities portfolio (including both developed and emerging markets).
Meanwhile, Calpers, Americas largest public pension fund, has announced an intention to increase exposure to private equity and private debt from 8% to 18% as we see the acceleration of a well-established trend: Morgan Stanley says US companies (the largest market for private investments) have raised more money in private markets than in public markets each year since 2009.
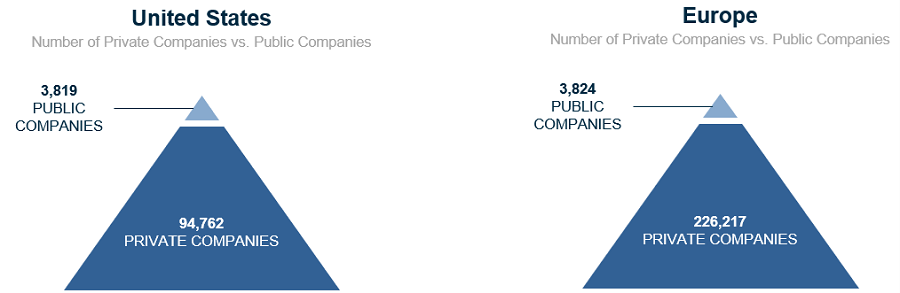
The magnitude of the ongoing opportunity is still emerging, as private markets are significantly larger than public markets, according to the S&P Capital IQ database.
Companies with revenues = US$15 million
Understanding Private Equity
Private equity refers to capital invested in companies that are not listed on public exchanges. Such investments can be made at any stage during the corporate life cycle.
The characteristics, risk, and potential return of private equity investments typically vary according to the stage at which the investment is made, with most investments being made once companies are more mature and validated:
Angel Investing is initial private funding support often backing little more than an idea and an entrepreneur.
Venture Capital is where managers actively work with early-stage or start-up investments to develop the business to raise further capital to fund commercialisation.
Growth Capital generally follows the venture capital stages as companies with viable business models and proven demand prepare for success on a larger scale. An increasing portion of growth capital funds customer acquisition.
Buyouts are the largest private equity segment. Transactions involve buying all, or a controlling stake, of a mature company with intention to improve its business and financial health, later reselling it for a profit to an interested party or conducting an IPO. Such transactions are often called leveraged buyouts as predictable future cashflows are ‘leveraged’ such that the acquisition can largely be debt financed, thereby bolstering investor returns.
Distressed funding is niche and generally involves acquiring the debt, equity or assets of a distressed business with the intention to restructure, recapitalise, and return to profitability.

Most private equity funds have an investment term of 10-12 years with only a small portion of the committed capital generally required upfront. The investments are typically made during the first five years with the realisations occurring later in the life of the fund.
What’s in it for investors?
Since the GFC, more companies have chosen to stay private rather than list on public exchanges as the regulatory burden for listed companies has become increasingly onerous and the funding options for unlisted businesses have improved.
Investors are attracted to private equity for:
- Proven ability to deliver strong risk-adjusted returns
- Resilience displayed during market turmoil
Private equity’s lower correlation with listed equities has become more relevant as investors seek to diversify away from heightened valuations in global equities, and anaemic cash returns.
The charts below illustrate how private equity has outperformed listed equity across time horizons and geographic regions. There is also greater variation in performance among managers when compared with listed equity funds, meaning investors who commit to top-tier private equity managers can expect to capture much greater levels of outperformance than the averaged-out returns displayed below.
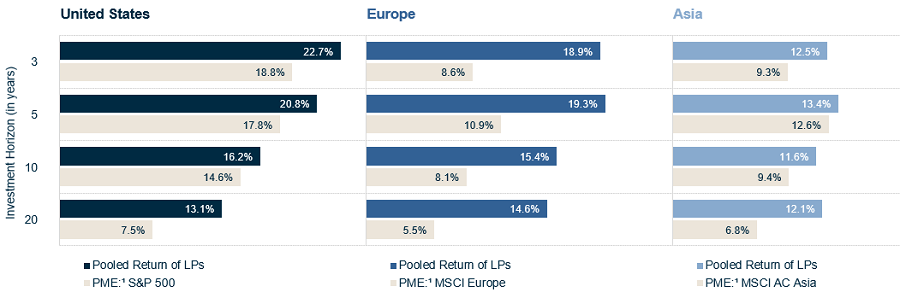
1 The Public Market Equivalent (“PME”) concept allows investors to compare the performance of private equity and other private markets investments (Private Equity) to other types of investments, such as public market indices (Public Equity). The methodology assumes buying and selling a given index according to the timing and size of the cash flows between the investor and the private investment. Performing this comparison requires the construction of a hypothetical investment fund that mimics private equity cash flows. This hypothetical fund purchases and sells shares of the index at the same time the private equity vehicle calls and distributes cash.
Sources: MSCI, S&P and BURGISS
Overcoming the challenges of Private Equity investing
The benefits of investing in private equity have traditionally accrued to institutional, wholesale, and ultra-high net worth investors who are better placed to manage the traditional complexities associated with investments in the asset class.
This changed in 2019, when Pengana Capital Group listed the Pengana Private Equity Trust (ASX:PE1), a listed private equity vehicle specifically designed to enable everyday retail investors to overcome the many barriers in accessing private equity.
The LIC structure is most appropriate for listed private equity because it allows an investment manager to unitise illiquid underlying investments into shares and list on the market. This structure solves several challenges of private equity investing, including:
High barriers to entry: Private equity fundraisings are extremely exclusive with significant excess demand for top managers; PE1 partnered with US-based GCM Grosvenor to leverage existing access via a well-established private equity manager with long-standing relationships, which provides exposure to these difficult-to-access private equity opportunities.
Capital constraints and high minimum investment requirements: Typical private equity funds may require a minimum of $5-10 million for a single investment. PE1 provides access to a truly diversified portfolio of private equity investments across underlying investment managers, economic conditions, vintages, geographies, sectors, and strategies (PE1 has exposure to nearly 400 underlying companies).
Highly illiquid: Existing private equity vehicles lack liquidity with an average 10-year capital lock up. But the LIC structure means PE1 investors have daily liquidity on the ASX.
Complex cash-flow management: Traditional private equity funds require capital to be contributed on a drawdown basis and exhibit lumpy returns as investments are realised and funds wound up. Yet the listed investment trust structure allows for internally managed cashflows, with drawdowns and distributions managed by the portfolio manager. Distributions are further reinvested to gain new private equity exposures.
No regular distributions: Regular distributions are a challenge for traditional unlisted private equity, yet PE1 can target a 4% p.a. distribution paid semi-annually.
Why private equity is becoming more relevant
In its Global Private Equity Report 2021, Bain and Company shows that one of private equity’s enduring strengths is its ability to thrive during periods of economic disruption with downturns historically providing excellent investment opportunities. This is particularly evident when assessing the returns (IRRs in the 17 – 21% range) of funds established in 2002 and 2009 following the last economic downturns.
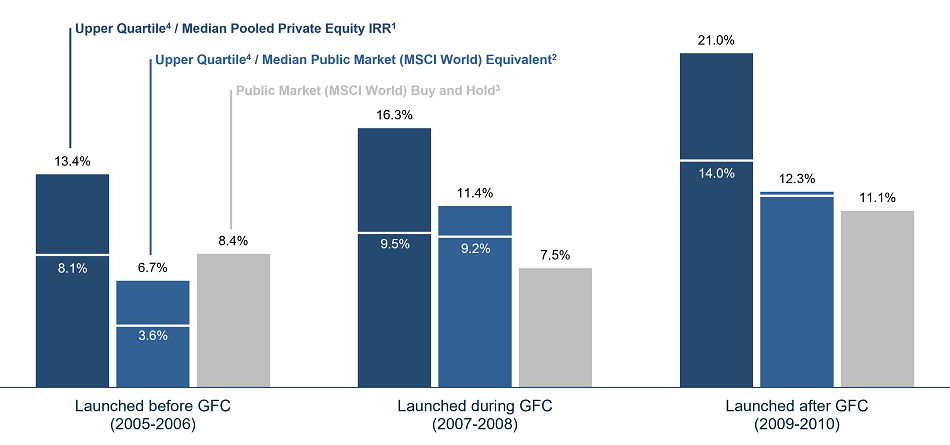
Source: BURGISS, MSCI.
All current evidence indicates inflation is likely to remain elevated, with potential for huge spikes following Putin’s invasion of Ukraine. Global interest rates could march steadily higher. This will put pressure on businesses with excessive leverage and valuations.
In the private markets, these characteristics are typically associated with the very large funds and mega transactions where the deal terms reflect the intense competition to deploy vast amounts of capital. Middle market transactions are typically completed with lower levels of leverage, and at lower valuations, which should provide a measure of additional protection in a rising rate environment.
The recent inflation shock presents a unique opportunity for private equity managers to offer solutions to high quality businesses that require continued financing and structuring them to include strong downside protection for investors while preserving meaningful upside.
Russel Pillemer is co-founder and Chief Executive Officer of Pengana Capital Group, which operates the Pengana Private Equity Trust (ASX: PE1). This article is general information and does not consider the circumstances of any investor.