Now is a great time to be an older Australian in the workforce. With full employment, the demand for local, skilled workers is at a record high.
It’s becoming more comfortable to work as well. Since COVID, flexible work arrangements have become commonplace and are widely accepted by most employers. In addition, most older Australians want to work longer than previous generations did, transitioning into retirement over time.
But, despite these opportunities and good intentions, most older Australians are not actively planning for the final chapters of their working life.
In our new study, New Life, Old Life, we find that the runway to retirement is shorter than expected – most of us don’t work for as long as we intend to. Sometimes the reasons are out of our control; sometimes, they’re not.
Whatever the conditions that bring about our retirement, there are always things we can do to prepare and improve our circumstances – and, more importantly, our quality of life.
Opportunities for older workers
The pandemic has accelerated the changing landscape of work in Australia. Knowledge-worker industries have shifted from the traditional nine-to-five, office-based model to a more flexible working arrangement, with remote working usually a component.
The outcome is that many jobs can now be performed from home without a peak-hour commute or dedicating an entire day to the office.
These new ways of working present an opportunity for older Australians in the workforce, especially those with higher education or skill backgrounds.
In addition, there is a unique mix of factors that are currently providing opportunities for older knowledge workers. Since the start of the pandemic, Australia’s strict border controls have seen a negative net overseas migration.
Specifically, 112,900 more people left Australia than arrived between March 2020 and September 2021. Since then, net migration has rebounded but is still not at pre-COVID levels.1
Figure 1: Net overseas migration dipped markedly when borders closed
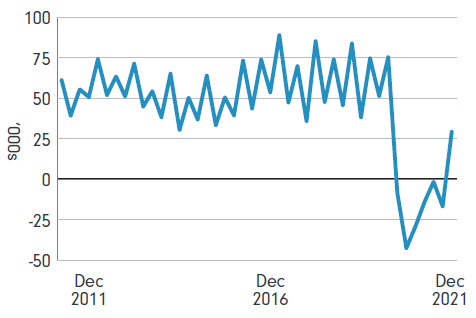
Sources: ABS National, state and territory population, December 2021; and Scanlon Foundation Research Institute
This lack of migration to Australia has stifled Australia’s supply of skilled workers. With the economy still growing, the unemployment rate in Australia is at historic low levels – 3.4% in October 2022.
This is great news for older Australians planning the wind-down phase of their careers.
The low unemployment rate, combined with the lack of skilled workers, means there is a real opportunity for older workers, who may have been overlooked in the past, to continue contributing to the workforce.
Figure 2: Australia’s unemployment rate is at a historic low
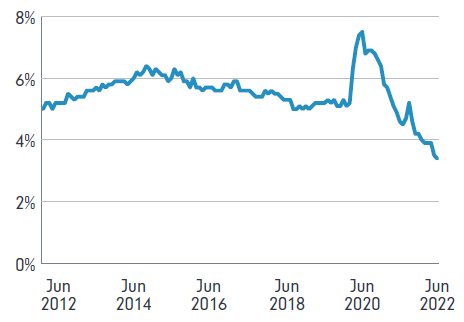
Source: ABS Labour Force Status Aug 2022
Moreover, the pandemic has led to a rethinking of what work means and what is really important in life. Workers now have higher expectations of their employers, demand work-life balance and flexibility, and feel it is the responsibility of businesses to take societal action.
The Return on Action Report Australia, commissioned by Atlassian, found that in the year to March 2021, 29% of workers have experienced an improvement in work–life balance and 26% work more flexibly than a standard nine-to-five workday.
Almost two-thirds (64%) agreed that their employer has been supportive of flexible and remote working.
The runway is shorter than expected
Older Australians often intend to take advantage of the new ways of working, but it doesn’t work out that way.
The average age at which Australians plan to reduce their work commitments and transition into retirement is 62.5 years, and the average age we would like to retire fully is 64.8 years.
But the reality is different. The average age at which Australians start reducing their work commitments is 61.4 years, and the average age we fully retire is 63.4 years.
These averages reflect the fact that one in three older Australians who planned their retirement did so earlier than they intended.
The top three reasons for retiring earlier than planned were that they were suffering from personal health issues (two in five), they were required to care for someone suffering from health issues (one in eight), or they were made redundant and lost their job (one in eight).
Therefore, it makes sense that one in four retirees report feeling out of control at retirement.
The sooner you start planning, the better
If there’s a risk you may be forced into an earlier retirement than intended, it makes sense to start planning early. The good news is that pre-retirees are the most open to receiving advice.
Four in five pre-retirees currently receive advice, have received advice in the past, or would consider receiving financial advice. And, of the pre-retirees who have never received financial advice, three in five are open to it.
The preferred professional to seek advice from is a professional financial adviser. More than twice the number of respondents would seek professional support from a financial adviser than an accountant.
And professional financial advisers are preferred over employers as a source of information, by a factor of more than five to one.
Compared with semi-retirees and early retirees, pre-retirees have the lowest life satisfaction. One reason is the prevalence of financial stress. Around one in two pre-retirees worries about money at least monthly; one in three worries about money daily.
Pre-retirees feel the least financially capable, have the lowest emotional resilience and are the least likely to live consistently within their values system. That’s not a coincidence – when we live according to our values, we are happier and more resilient.
Figure 3: Financial advisers are the preferred source of professional advice
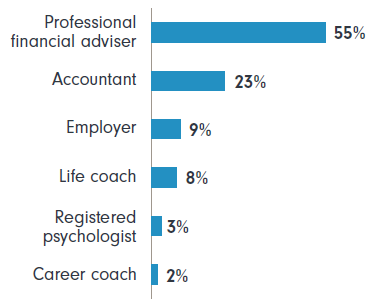
The importance of a sense of control
Major life changes like retirement are challenging. Pre-retirees approach retirement cautiously, wary of the number of uncertainties around this unknown period of life.
A key driver of a positive emotional experience at retirement is a sense of control, or agency, in the decision.
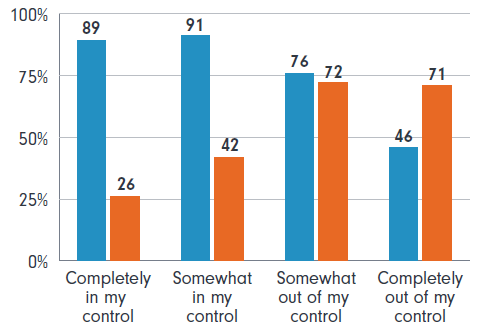
Those who felt completely in control of when they stopped working full time had an overwhelmingly positive emotional experience – nine in 10 experienced positive emotions, and only one in 10 experienced negative emotions.
But those who didn’t perceive they had a choice in when they stopped full-time work had a terrible time. Seven in 10 of those who felt completely out of control experienced negative emotions when they stopped full-time work, and less than one in two experienced positive emotions.
Figure 4: Sense of control drives emotional experience
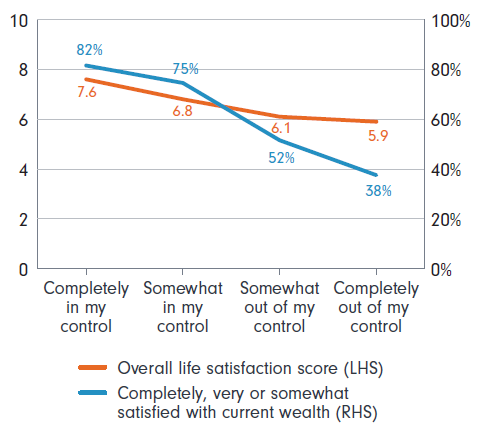
A sense of control over the retirement event is not just a driver of emotional experience, it is also a key driver of life satisfaction. Semi-retirees who felt completely in control of when they finished working full time have higher life satisfaction than those who felt less in control.
Those who felt completely out of control when they stopped working full-time have the lowest life satisfaction scores.
On a scale of zero to 10, where zero is no life satisfaction and 10 is perfect life satisfaction, those who perceived they were completely in control have a life satisfaction score of 7.6.
However, those who felt completely out of control have a life satisfaction score of just 5.9.
Satisfaction with wealth is also strongly correlated with feeling in control of retirement.
Four in five of those who felt completely in control of finishing full-time work are satisfied with their current wealth, while less than two in five of those who felt completely out of control are satisfied with their wealth.
Figure 5: Sense of control drives life and wealth satisfaction
Taking control of retirement
We can’t control everything when it comes to our retirement, but there are some things we can control. With a little planning, we can control the likelihood of being made redundant, and we can control the consequences if we suffer from ill health or we’re required to care for someone suffering from ill health.
Most of us put lots of energy into building our careers, but not necessarily the inevitable wind-down phase of our careers. And while most of us say we want to transition into retirement, very few take active steps to make it happen.
Extracted from Fidelity’s report New Life, Old Life.
Richard Dinham is Head of Client Solutions and Retirement at Fidelity International, a sponsor of Firstlinks. This document is issued by FIL Responsible Entity (Australia) Limited ABN 33 148 059 009, AFSL 409340 (‘Fidelity Australia’), a member of the FIL Limited group of companies commonly known as Fidelity International. This document is intended as general information only. You should consider the relevant Product Disclosure Statement available on our website www.fidelity.com.au.
For more articles and papers from Fidelity, please click here.
© 2021 FIL Responsible Entity (Australia) Limited. Fidelity, Fidelity International and the Fidelity International logo and F symbol are trademarks of FIL Limited. FD18634.